

Cerebral Palsy in the Classroom. Lesson Plans and Teacher Timesavers - Huge Collection - Instant Lessons View Collection Mega Worksheets.
A Beauty Queen with Cerebral Palsy - Heroes Among Us, Good Deeds. Abbey Curran, 20 Kewanee, Ill.
Growing up on a hog farm in northwestern Illinois, Abbey Curran used to love watching the local beauty queens parade across the stage at the Henry County Fair. "They were so beautiful," she recalls. "I wanted to be like them. " But Abbey was different: Born with cerebral palsy, she wore leg braces until age 10 and limped, dragging her left foot behind her. One day in high school, she saw a flyer announcing the contest.
That was all Abbey needed to hear. AccessApps. History[edit] 14 September 2008 - AccessApps download site launched on JISC RSC Scotland North & East website28 November 2008 - JISC RSC Scotland North & East awarded Scottish Open Source Education Excellence Award[1]11 May 2009 - AccessApps incorporated into EduApps14 May 2009 - AccessApps wins IMS Global Best Accessibility Solution award[2]
JISC RSC Scotland N&E: EduApps, AccessApps, LearnApps, TeachApps. Computer accessibility. In human-computer interaction, computer accessibility (also known as Accessible computing) refers to the accessibility of a computer system to all people, regardless of disability or severity of impairment.
Augmentative and alternative communication. An AAC user indicates a series of numbers on an eye gaze communication board in order to convey a word.
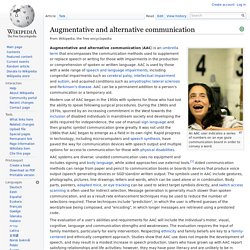
Augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) is an umbrella term that encompasses the communication methods used to supplement or replace speech or writing for those with impairments in the production or comprehension of spoken or written language. AAC is used by those with a wide range of speech and language impairments, including congenital impairments such as cerebral palsy, intellectual impairment and autism, and acquired conditions such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Parkinson's disease. AAC can be a permanent addition to a person's communication or a temporary aid. The evaluation of a user's abilities and requirements for AAC will include the individual's motor, visual, cognitive, language and communication strengths and weaknesses. The evaluation requires the input of family members, particularly for early intervention.
Stephen Hawking. English theoretical physicist, cosmologist, and author Stephen William Hawking CH CBE FRS FRSA (8 January 1942 – 14 March 2018) was an English theoretical physicist, cosmologist, and author who was director of research at the Centre for Theoretical Cosmology at the University of Cambridge at the time of his death.[18][19][8] He was the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at the University of Cambridge between 1979 and 2009.
Hawking was born in Oxford, into a family of doctors. Trackball. Compared with a mouse, a trackball has no limits on effective travel; at times, a mouse can reach an edge of its working area while the operator still wishes to move the screen pointer farther.
With a trackball, the operator just continues rolling, whereas a mouse would have to be lifted and re-positioned. Some trackballs, such as Logitech's optical-pickoff types, have notably low friction, as well as being dense (glass), so they can be spun to make them coast. The trackball's buttons may be situated to that of a mouse or to a unique style that suits the user. Large trackballs are common on CAD workstations for easy precision. Before the advent of the touchpad, small trackballs were common on portable computers, where there may be no desk space on which to run a mouse. History[edit] DATAR's trackball used four disks to pick up motion, two each for the X and Y directions. Environmental control device.
An environmental control system is a form of electronic assistive technology which enables people with significant disabilities to independently access equipment in their environment e.g. home or hospital.
An environmental control controller is the device that controls the equipment – like a remote control. Chorded keyboard. A chorded keyboard minus the board, typically designed to be used while held in the hand, is called a keyer.
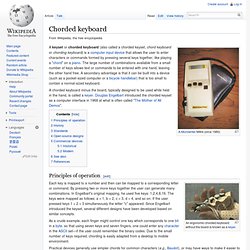
Douglas Engelbart introduced the chorded keyset as a computer interface in 1968 at what is often called "The Mother of All Demos". Principles of operation[edit] An ergonomic chorded keyboard without the board is known as a keyer. Each key is mapped to a number and then can be mapped to a corresponding letter or command. By pressing two or more keys together the user can generate many combinations. Practical devices generally use simpler chords for common characters (e.g., Baudot), or may have ways to make it easier to remember the chords (e.g., Microwriter[1]), but the same principles apply. Douglas Engelbart filed two new patents for mobile chorded keyset devices[citation needed] and TipTap.mobi released a chording app for the iPhone with Douglas Engelbart in 2010.[2] Music therapist - How can music therapy help a child with cerebral palsy?
Cerebral Palsy: Hope Through Research. Team Hoyt. Team Hoyt in the 2008 Boston Marathon, near the halfway point in Wellesley Team Hoyt is father and son Dick Hoyt (born June 1, 1940[1]) and Rick Hoyt (born January 10, 1962), from Holland, Massachusetts, who have competed together in various athletic endeavors, including marathons and triathlons.
Cerebral palsy. Cerebral palsy (CP) is a general term for a group of permanent, non-progressive movement disorders that cause physical disability,[1] mainly in the areas of body movement.[2] There may also be problems with sensation, depth perception, and communication ability. Difficulty with cognition and epilepsy is found in about one-third of cases.
There are a number of subtypes including a type characterized by spasticity, a type characterized by poor co-ordination, and types which feature both symptoms or neither. Cerebral palsy is caused by damage to the motor control centers of the developing brain and can occur during pregnancy, during childbirth, or after birth up to about age three.[3][4] About 2% of all cerebral palsy cases are believed to be due to a genetic cause.[5] Cerebral palsy is not an infectious disease and is not contagious. Most cases are diagnosed at a young age rather than during adolescence or adulthood. Signs and symptoms[edit]