

Sleep-deprived people make risky decisions based on too much optimism. DURHAM, N.C., and SINGAPORE -- The powers that be in Las Vegas figured out something long before neuroscientists at two Duke University medical schools confirmed their ideas this week: Trying to make decisions while sleep-deprived can lead to a case of optimism.

The scientists showed, using a functional MRI, that a night of sleep deprivation leads to increased brain activity in brain regions that assess positive outcomes, while at the same time this deprivation leads to decreased activation in the brain areas that process negative outcomes. Sleep-deprived individuals in the study tended to make choices that emphasized monetary gain, and were less likely to make choices that reduced loss. While this wasn't true for all of the subjects, the findings are worth heeding. This is the first study to show that sleep deprivation can change the way the brain assesses economic value, independent of its effects on vigilant attention. The study was published by the Journal of Neuroscience on March 8.
Creativity linked to mental health. New research shows a possible explanation for the link between mental health and creativity.

By studying receptors in the brain, researchers at the Swedish medical university Karolinska Institutet have managed to show that the dopamine system in healthy, highly creative people is similar in some respects to that seen in people with schizophrenia. High creative skills have been shown to be somewhat more common in people who have mental illness in the family. Creativity is also linked to a slightly higher risk of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
Certain psychological traits, such as the ability to make unusual pr bizarre associations are also shared by schizophrenics and healthy, highly creative people. And now the correlation between creativity and mental health has scientific backing. The Naked Scientists Online, Science Podcast and Science Radio Show. The Top 10 Psychology Studies of 2010. The end of 2010 fast approaches, and I'm thrilled to have been asked by the editors of Psychology Today to write about the Top 10 psychology studies of the year. I've focused on studies that I personally feel stand out, not only as examples of great science, but even more importantly, as examples of how the science of psychology can improve our lives. Each study has a clear "take home" message, offering the reader an insight or a simple strategy they can use to reach their goals , strengthen their relationships, make better decisions, or become happier.
If you extract the wisdom from these ten studies and apply them in your own life, 2011 just might be a very good year. Neuron-galaxy.jpg (JPEG Image, 1008x633 pixels) - Scaled (96%) 10 Simple Postures That Boost Performance. Psychological research suggests simple actions can project power, persuade others, increase empathy, boost cognitive performance and more…
10 More Brilliant Social Psychology Studies. 10 Hidden Benefits of Smiling. 47 Mind-Blowing Psychology-Proven Facts You Should Know About Yourself. I’ve decided to start a series called 100 Things You Should Know about People.

8 Things Everybody Ought to Know About Concentrating. “Music helps me concentrate,” Mike said to me glancing briefly over his shoulder.

Mike was in his room writing a paper for his U.S. History class. New Bandages Latest in Healthcare Technology - High Tech Bandages and Band-Aids. ChitoGauze (Photograph courtesy of HemCon Medical Technologies, Inc.)

Five Body Parts You May Be Able to Regrow Soon(ish) December 18, 2009 3:30 AM Patching Damaged Hearts Early attempts to grow heart-repair patches with embryonic stem cells kept running into a glitch: because oxygen and nutrients only penetrated the outer edges of the patch, cells in the center died.
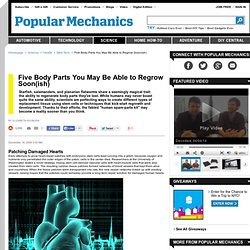
Researchers at the University of Washington tested a novel strategy, mixing stem cell-derived vascular cells with heart-muscle cells that were also created from stem cells. The resulting cardiac-tissue patches formed networks of blood vessels that kept them alive and nourished. HighWire Free Online Full-text Articles. Scirus - for scientific information. Neurological Control - Neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitter Molecules Neurotransmitters can be broadly split into two groups – the ‘classical’, small molecule neurotransmitters and the relatively larger neuropeptide neurotransmitters.
Within the category of small molecule neurotransmitters, the biogenic amines (dopamine, noradrenaline, serotonin and histamine) are often referred to as a discrete group because of their similarity in terms of their chemical properties. Click on the links in the table above to read more about some of the important neurotransmitters. Serotonin Although the CNS contains less than 2% of the total serotonin in the body, serotonin plays a very important role in a range of brain functions. Love Deactivates Brain Areas For Fear, Planning, Critical Social Assessment.
Love Deactivates Brain Areas For Fear, Planning, Critical Social Assessment.

New neurons help us to remember fear. Fear burns memories into our brain, and new research by University of California, Berkeley, neuroscientists explains how.

Scientists have long known that fear and other highly emotional experiences lead to incredibly strong memories. In a study appearing online today (Tuesday, June 14) in advance of publication in the journal Molecular Psychiatry, UC Berkeley’s Daniela Kaufer and colleagues report a new way for emotions to affect memory: The brain’s emotional center, the amygdala, induces the hippocampus, a relay hub for memory, to generate new neurons. The figure shows newly born nerve cells (green) colocalizing with a neuronal marker which indicates immature nerve cells (red).