

Gout. Clinical diagnosis may be confirmed by seeing the characteristic crystals in joint fluid.
Treatment with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), steroids, or colchicine improves symptoms. Once the acute attack subsides, levels of uric acid are usually lowered via lifestyle changes, and in those with frequent attacks, allopurinol or probenecid provides long-term prevention. Gout has become more common in recent decades, affecting about 1–2% of the Western population at some point in their lives. The increase is believed to be due to increasing risk factors in the population, such as metabolic syndrome, longer life expectancy, and changes in diet. Gout was historically known as "the disease of kings" or "rich man's disease.
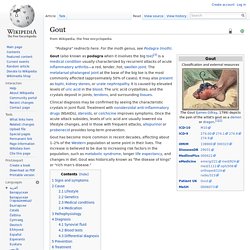
" Signs and symptoms Gout presenting in the metatarsal-phalangeal joint of the big toe: Note the slight redness of the skin overlying the joint. Cause Lifestyle Genetics Medical conditions Gout frequently occurs in combination with other medical problems. Medication. Radiographic Evaluation of Arthritis: Inflammatory Conditions1. Rheumatoid Arthritis Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies Returning to the proposed algorithm, if one observes joint space narrowing, signs of inflammation, multiple joint involvement, and distal involvement in the hands and feet with added features of bone proliferation, a seronegative spondyloarthropathy is suggested.

This category includes psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. Differentiation among these disorders largely relies on the distribution of radiographic abnormalities and clinical information. In addition, other findings that help differentiate the seronegative spondyloarthropathies from rheumatoid arthritis are that cartilaginous joints and entheses are involved to a greater extent, the latter representing the osseous attachment sites of ligaments and tendons. Axial involvement may also occur, leading to bilateral symmetric or asymmetric sacroiliitis. Radiographic Evaluation of Arthritis: Degenerative Joint Disease and Variations1.
Typical Osteoarthritis The sequence of osteoarthritis described above can be somewhat variable.

Regardless, when osteoarthritis is identified, it is important to consider which joint is involved, the severity of the radiographic changes, the distribution of osteoarthritis, and the age of the patient to make the distinction between typical and atypical osteoarthritis. Atypical Osteoarthritis If radiographic findings of osteoarthritis are identified but the involved joint is not one commonly affected by osteoarthritis, the severity of the findings are excessive or unusual, or the age of the patient is unusual, then other less common causes for cartilage damage and osteoarthritis should be considered. Possible causes for this atypical appearance of osteoarthritis include trauma, crystal deposition disease, neuropathic joint, and hemophilia. Polyarticular Joint Pain: Symptoms of Joint Disorders: Merck Manual Professional. Monarticular Joint Pain: Symptoms of Joint Disorders: Merck Manual Professional. Joint Pain, Monoarticular : A Merck Manual of Patient Symptoms podcast Monarticular pain may originate from the joint itself or surrounding structures.
There may be pain (arthralgia) or also inflammation (arthritis) with redness, warmth, and swelling. Pain may occur only with use, suggesting a mechanical problem (eg, osteoarthritis, tendinitis), or also at rest, suggesting inflammation (eg, crystal disease, septic arthritis). There may or may not be fluid within the joint (effusion). Prompt assessment is essential to exclude infection. Pathophysiology Monarticular pain may originate. 통풍치료 #### 통풍은 기원전 약 5세기의 히포크라테스 시절부터 기술된 오래된 관절염으로서 풍부한 음식과 알코올 소비가 많은 왕이나 귀족들에게 발생하는 병으로 잘 알려져 있으며 발생률은 인구 1000명중 약 5명 정도이다.

건강보험심사평가원에 따르면 통풍으로 진료받은 인원은 2007년 16만3000명에서 2011년에는 24만 명으로 5년간 47.5% 증가했으며 통풍 환자 2명 중 1명은 40~50대 중년층이었고 50대가 25.6%로 가장 많았으며 40대(22.6%), 60대(17.9%) 순이었다고 하였다. 또한 특히 남성 환자가 여성보다 10배나 많았다고 하였다(2012.11.21). 여성에서는 폐경기 이전까지는 여성호르몬의 영향으로 요산을 제거하는 능력이 유지되지만 폐경기 이후에는 통풍 발생이 증가된다고 한다. 통풍 환자의 약 10~20%가 가족력이 있다고 한다. 최근 20, 30대 젊은 층에서도 통풍에 시달리는 사람들이 증가하는데 이는 동물성 단백질의 섭취가 많아지는등 식생활이 서양화 된데다 비만의 증가, 스트레스로 과음하는 경우가 많기 때문이다. [ 요산을 증가 시켜 통풍을 유발시킬수 있는 요인 ] 혈중 요산수치가 높은 사람에서 항상 통풍이 발생하는것은 아니다(무증상 고요산혈증).실제로 고요산증환자의 상당수가 통풍이 생기지 않는다고 한다. 통풍이 생기는데는 요산치가 높은것은 필수적인것이 아니지만 아마도 요산치의 급속한 변화가 통풍의 발작과 관계된다고 한다. 아래와 같은 여러 상황이 통증발작을 일으킬수가 있다. [ 통풍과 음주 ] 과음이 통풍환자에게 좋지 않다는 사실은 잘 알려져 있다.