

Relativistic Doppler effect - Wiki. Diagram 1.
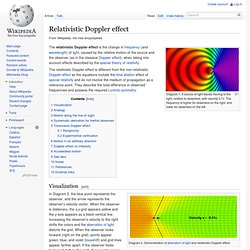
A source of light waves moving to the right, relative to observers, with velocity 0.7c. The frequency is higher for observers on the right, and lower for observers on the left. The relativistic Doppler effect is the change in frequency (and wavelength) of light, caused by the relative motion of the source and the observer (as in the classical Doppler effect), when taking into account effects described by the special theory of relativity. The relativistic Doppler effect is different from the non-relativistic Doppler effect as the equations include the time dilation effect of special relativity and do not involve the medium of propagation as a reference point. They describe the total difference in observed frequencies and possess the required Lorentz symmetry. Visualization[edit] In Diagram 2, the blue point represents the observer, and the arrow represents the observer's velocity vector.
Diagram 3. Analogy[edit] Motion along the line of sight[edit] away from him (where where and . To. 21.08030904. Beam phase modulation for improved synthetic aperture detection and estimation. Abstract: Phase modulated beam patterns are substituted for the constant-phase versions that have been used in prior synthetic aperture systems.

Relative movement between a radar/sonar/ultrasound platform and a point target causes a sequence of echoes from the point target to be phase and amplitude modulated by the beam pattern, as well as by the usual quadratic phase variation caused by range changes. Azimuth, range rate, and azimuth rate estimation, as well as detection in clutter, are substantially improved by appropriate beam pattern phase modulation, which is applied to the transmitter and/or receiver beam patterns. Phase modulated beam patterns are synthesized with array element weighting functions that are designed for high ambiguity function peak-to-sidelobe level, reduction of unwanted ambiguity ridge lines, and adequate spatial sampling. Claims: 1. 2. 3. Description: [0002]Not Applicable [0003]Not Applicable. Doppler effect - Wiki. Change of wavelength caused by motion of the source An animation illustrating how the Doppler effect causes a car engine or siren to sound higher in pitch when it is approaching than when it is receding.
The pink circles are sound waves. When the car is moving to the left, each successive wave is emitted from a position further to the left than the previous wave. So for an observer in front (left) of the car, each wave takes slightly less time to reach him than the previous wave. The waves "bunch together", so the time between arrival of successive wavefronts is reduced, giving them a higher frequency. Doppler effect of water flow around a swan For waves that propagate in a medium, such as sound waves, the velocity of the observer and of the source are relative to the medium in which the waves are transmitted.
Development[edit] General[edit] and emitted frequency is given by:[5] where. Inverse synthetic aperture radar - Wiki. Inverse synthetic aperture radar (ISAR) is a radar technique to generate a two-dimensional high resolution image of a target.
It is analogous to conventional SAR only where the required relative motion is from the imaged object with the radar stationary. ISAR technology utilizes the movement of the target rather than the emitter to create the synthetic aperture. ISAR radars have a significant role aboard maritime patrol aircraft to provide them with radar image of sufficient quality to allow it to be used for target recognition purposes. In situations where other radars display only a single unidentifiable bright moving pixel, the ISAR image is often adequate to discriminate between various missiles, military aircraft, and civilian aircraft. Radar Cross Section (RCS) Imaging[edit] If the target is rotated through 'large' angles, the Doppler frequency history of a scatter becomes non linear, following a sine-wave trajectory.
Synthetic aperture radar - Wiki. Synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) is a form of radar whose defining characteristic is its use of relative motion, between an antenna and its target region, to provide distinctive long-term coherent-signal variations, that are exploited to obtain finer spatial resolution than is possible with conventional beam-scanning means.
It originated as an advanced form of side-looking airborne radar (SLAR). SAR is usually implemented by mounting, on a moving platform such as an aircraft or spacecraft, a single beam-forming antenna from which a target scene is repeatedly illuminated with pulses of radio waves at wavelengths anywhere from a meter down to millimeters. The many echo waveforms received successively at the different antenna positions are coherently detected and stored and then post-processed together to resolve elements in an image of the target region. SAR images have wide applications in remote sensing and mapping of the surfaces of both the Earth and other planets. Image appearance[edit]