

Pesticide Roundup Provokes Cell Division Dysfunction at the Level of CDK1/Cyclin B Activation - Chemical Research in Toxicology. Station Biologique de Roscoff, Université Pierre et Marie Curie (UFR 937), Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS, UMR 7127), BP 74, 29682 Roscoff Cedex, France Chem.

Res. Toxicol., 2002, 15 (3), pp 326–331 DOI: 10.1021/tx015543g Publication Date (Web): February 22, 2002 Copyright © 2002 American Chemical Society Section: Abstract To assess human health risk from environmental chemicals, we have studied the effect on cell cycle regulation of the widely used glyphosate-containing pesticide Roundup. Citing Articles View all 38 citing articles Citation data is made available by participants in CrossRef's Cited-by Linking service. This article has been cited by 6 ACS Journal articles (5 most recent appear below). Effects of Glyphosate and its Formulation, Roundup, on Reproduction in Zebrafish (Danio rerio)Tamsyn M. Glyphosate. Glyphosate (N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine) is a broad-spectrum systemic herbicide used to kill weeds, especially annual broadleaf weeds and grasses known to compete with commercial crops grown around the globe.
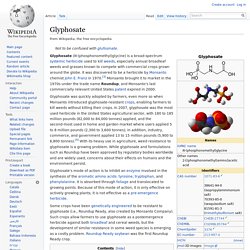
It was discovered to be a herbicide by Monsanto chemist John E. Franz in 1970.[3] Monsanto brought it to market in the 1970s under the trade name Roundup, and Monsanto's last commercially relevant United States patent expired in 2000. Glyphosate was quickly adopted by farmers, even more so when Monsanto introduced glyphosate-resistant crops, enabling farmers to kill weeds without killing their crops. Glyphosate's mode of action is to inhibit an enzyme involved in the synthesis of the aromatic amino acids: tyrosine, tryptophan, and phenylalanine. It is absorbed through foliage and translocated to growing points.
Some crops have been genetically engineered to be resistant to glyphosate (i.e., Roundup Ready, also created by Monsanto Company). Discovery[edit] Chemistry[edit] Use[edit] Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) Polychlorinated Biphenyl (PCB) PCBs belong to a broad family of man-made organic chemicals known as chlorinated hydrocarbons.
PCBs were domestically manufactured from 1929 until their manufacture was banned in 1979. They have a range of toxicity and vary in consistency from thin, light-colored liquids to yellow or black waxy solids. Due to their non-flammability, chemical stability, high boiling point, and electrical insulating properties, PCBs were used in hundreds of industrial and commercial applications including electrical, heat transfer, and hydraulic equipment; as plasticizers in paints, plastics, and rubber products; in pigments, dyes, and carbonless copy paper; and many other industrial applications.
Commercial Use of PCBs Although no longer commercially produced in the United States, PCBs may be present in products and materials produced before the 1979 PCB ban. Release and Exposure of PCBs PCBs can accumulate in the leaves and above-ground parts of plants and food crops. Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) Polychlorinated biphenyl. Chemical structure of PCBs.
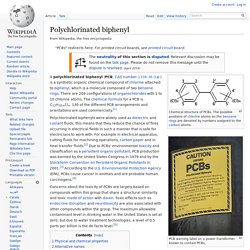
The possible positions of chlorine atoms on the benzene rings are denoted by numbers assigned to the carbon atoms. PCB warning label on a power transformer known to contain PCBs. A polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB; CAS number 1336-36-3 ) is a synthetic organic chemical compound of chlorine attached to biphenyl, which is a molecule composed of two benzene rings. There are 209 configurations of organochlorides with 1 to 10 chlorine atoms. The chemical formula for a PCB is C12H10-xClx. 130 of the different PCB arrangements and orientations are used commercially.[1] Polychlorinated biphenyls were widely used as dielectric and coolant fluids, this means that they reduce the chance of fires occurring in electrical fields in such a manner that is safe for electricians to work with.
Concerns about the toxicity of PCBs are largely based on compounds within this group that share a structural similarity and toxic mode of action with dioxin. Alternative names[edit] Italy[edit]