

Netadmin. Tunneling. DNS. Newbie guide to setting up a PF firewall. Level: Beginner Eric Bullen.

(ericb-howto@thedeepsky.com) Sr. Systems Engineer, Yahoo! Inc. January 11, 2008 Since PF replaced IPF on OpenBSD starting with OpenBSD 3.0, it has become a world-class firewalling solution. There are a few things that you need to have ready prior to following this how-to. First and formost, you should have your firewall plugged into a network (with at least one other computer on it as well) so that it can receive and send traffic. Few things are more important to have secure than a firewall. To activate PF, and have it start automatically on boot-up, edit your /etc/rc.conf.local file so that you add the line pf=YES to it. Listing 1. Next, create a "pass all" pf.conf so that on boot-up, OpenBSD will read it in.
Listing 2. If you look at Listing 2, you will see some place holders beginning with a "##". Once you have rebooted, it's time to check to see if everything you made changes to came up successfully. Listing 3. Listing 4. Listing 5. Becomes... and Nice eh? Testez votre adresse IP, la rapidité de la connexion et résoudre les problèmes de lenteur.
Dans cet article, nous allons voir comment l'utiliser un tunnel SSH, afin de surfer anonymement sur Internet.
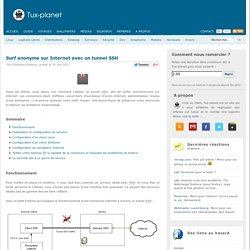
Les connexions étant chiffrées, aucun tiers (fournisseur d'accès Internet, administrateur réseau d'une entreprise...) ne pourra analyser votre trafic réseau. Une bonne façon de préserver votre anonymat et déjouer les tentatives d'espionnage. Sommaire Fonctionnement Pour mettre en place ce système, il nous faut bien entendu un serveur dédié avec SSH. Voici un petit schéma qui explique le fonctionnement d'une connexion Internet à travers un tunnel SSH : La méthode reste assez simple, si l'on ne rentre pas dans les détails : On branche le navigateur Internet de son PC en mode proxy sur l'adresse 127.0.0.1:8080Le trafic est alors acheminé à l'aide d'un tunnel SSH chiffré, vers le serveurCelui-ci s'occupe ensuite d'aller chercher les informations sur Internet à votre placeLes données reviennent sur la machine cliente par le même chemin.
Cisco. Security. DNS cache poisoning: still works and still makes lots of damage. I was teaching this week at University.

It was a pretty normal class until I heard the following from one of my students: What happened to google? A couple of seconds after, many people started to make the same complaint and one minute after nobody had access to google. I typed the google URL from my computer and got the following screen: First thing I though was that google suffered an attack. When I looked for the owner of that IP address, ARIN says it is not precisely google. At this time I found out we were victim of a DNS cache poisoning attack.Since the network admin was not at his office because class was in the night, there was nothing I could do but wait for the DNS cache to expire. How this attack works and How we can protect ourselves The DNS process works as follows to resolve ip address from a fully qualified domain name (FQDN): Client sends a query to the internal DNS looking for an ip address for a machine name.
The attack works as follows: