

Aerospace Research Central (AIAA) NextGen Air Transportation System. ITT Exelis - Electronic Systems. ATM Brochure.pdf (application/pdf Object) NextGen JPDO Joint Planning Environment (JPE) National Airspace System Enterprise Architecture. Air traffic control. Air traffic management is an aviation term encompassing all systems that assist aircraft to depart from an aerodrome, transit airspace, and land at a destination aerodrome, including air traffic control (ATC), aeronautical meteorology, air navigation systems (aids to navigation), Air Space Management (ASM), Air Traffic Services (ATS), and Air Traffic Flow Management (ATFM), or Air Traffic Flow and Capacity Management (ATFCM).
The increasing emphasis of modern ATM is on interoperable and harmonised systems that allow an aircraft to operate with the minimum of performance change from one airspace to another. ATC systems have traditionally been developed by individual States that concentrated on their own requirements, creating different levels of service and capability around the world. Single European Sky ATM Research. Single European Sky ATM Research (SESAR) is the name given to the collaborative project that is intended to completely overhaul the European airspace and its Air Traffic Management (ATM).
The actual programme is managed by the SESAR Joint Undertaking - as a Public–private partnership (PPP). Project[edit] The SESAR project is composed of three phases:[1] a Definition phase (2004–2008), to deliver an ATM master plan defining the content, the development and deployment plans of the next generation of ATM systems. This definition phase is led by Eurocontrol, and co-funded by the European Commission under the Trans-European Transport Networks programme and executed by a large consortium of all air transport stakeholders.a Development phase (2008–2013), to produce the required new generation of technological systems and components as defined in the definition phase.
SESAR’s target concept relies on a number of new key features:[citation needed] History[edit] Dates[edit] References[edit] Tactical air navigation system. VORTAC TGO (TANGO) Germany.
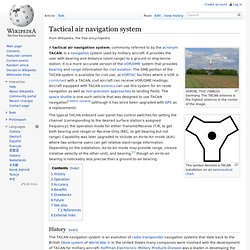
The TACAN antenna is the highest antenna in the center of the image. The typical TACAN onboard user panel has control switches for setting the channel (corresponding to the desired surface station's assigned frequency), the operation mode for either Transmit/Receive (T/R, to get both bearing and range) or Receive Only (REC, to get bearing but not range). Capability was later upgraded to include an Air-to-Air mode (A/A) where two airborne users can get relative slant-range information. Depending on the installation, Air-to-Air mode may provide range, closure (relative velocity of the other unit), and bearing,[1] though an air-to-air bearing is noticeably less precise than a ground-to-air bearing.
History[edit] Operation[edit] A US Air Force TACAN Antenna. TACAN in general can be described as the military version of the VOR/DME system. The distance measurement component of TACAN operates with the same specifications as civil DMEs. Accuracy[edit] Benefits[edit] TACAN Whitepaper. How ADS-B works. ADS-B is a system in which electronic equipment onboard an aircraft automatically broadcasts the precise location of the aircraft via a digital data link.
The data can be used by other aircraft and air traffic control to show the aircraft’s position and altitude on display screens without the need for radar. The system involves an aircraft with ADS-B determining its position using GPS. A suitable transmitter then broadcasts that position at rapid intervals, along with identity, altitude, velocity and other data. Dedicated ADS-B grounds stations receive the broadcasts and relay the information to air traffic control for precise tracking of the aircraft. Automatic – Requires no pilot input or external interrogation. Dependant – Depends on accurate position and velocity data from the aircraft’s navigation system (eg.
Surveillance – Provides aircraft position, altitude, velocity, and other surveillance data to facilities that require the information. Broadcasts may include: ADS-B Technologies: What is ADS-B?