

Hemopericardium - Wikipedia. Hemopericardium refers to blood in the pericardial sac of the heart.

It is clinically similar to a pericardial effusion, and, depending on the volume and rapidity with which it develops, may cause cardiac tamponade.[1] The condition can be caused by full-thickness necrosis (death) of the myocardium (heart muscle) after myocardial infarction, chest trauma,[2] and by over-prescription of anticoagulants.[3][4] Other causes include ruptured aneurysm of sinus of Valsalva and other aneurysms of the aortic arch.[5] Hemopericardium can be diagnosed with a chest X-ray or a chest ultrasound, and is most commonly treated with pericardiocentesis.[6] While hemopericardium itself is not deadly, it can lead to cardiac tamponade, a condition that is fatal if left untreated.[6] Mechanism[edit] There have also been cases reported in which hemopericardium was noted as an initial manifestation of essential thrombocythemia.[7] Symptoms[edit] Diagnosis[edit] Cause and prevention[edit] Treatment and prognosis[edit]
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma - Wikipedia. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is a group of blood cancers that includes all types of lymphoma except Hodgkin's lymphomas.[1] Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and feeling tired.

Other symptoms may include bone pain, chest pain, or itchiness. Some forms are slow growing while others are fast growing.[1] Lymphomas are types of cancer that develops from lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell.[2] Risk factors include poor immune function, autoimmune diseases, Helicobacter pylori infection, hepatitis C, obesity, and Epstein-Barr virus infection.[1][3] The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies lymphomas into five major groups, including one for Hodgkin's lymphoma.[4] Within the four groups for NHL there are over 60 specific types of lymphoma.[5][6] Diagnosis is by examination of a bone marrow or lymph node biopsy. Anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis is a severe and potentially life-threatening reaction to a trigger such as an allergy.

It's also known as anaphylactic shock. This page covers: Symptoms What to do Triggers Prevention. Lazarus syndrome - Wikipedia. Lazarus syndrome, also known as autoresuscitation after failed cardiopulmonary resuscitation,[1] is the spontaneous return of circulation after failed attempts at resuscitation.[2] Its occurrence has been noted in medical literature at least 38 times since 1982.[3][4] It takes its name from Lazarus who, in the New Testament of The Bible, was raised from the dead by Jesus.[5] Occurrences of the syndrome are extremely rare and the causes are not well understood.

One hypothesis for the phenomenon is that a chief factor (though not the only one) is the buildup of pressure in the chest as a result of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). The relaxation of pressure after resuscitation efforts have ended is thought to allow the heart to expand, triggering the heart's electrical impulses and restarting the heartbeat.[2] Other possible factors are hyperkalemia or high doses of epinephrine.[5] Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency. A1AT Deficiency Information. A1AT is a protein made by cells in the liver.

It passes out from the liver into the bloodstream and can travel to the lungs. Its main function is to protect the lungs from damage caused by other types of proteins called enzymes. Enzymes are essential for the normal working and development of the body. In the lungs, certain enzymes called proteases help to fight infection, by removing germs (bacteria) and may also be released to try to protect the lungs from tobacco smoke. Sciatica. Introduction Sciatica is the name given to any sort of pain that is caused by irritation or compression of the sciatic nerve.

The sciatic nerve is the longest nerve in your body. It runs from the back of your pelvis, through your buttocks, and all the way down both legs, ending at your feet. Signs and symptoms. Uremia-Kidney Cares Community. Glandular fever. Introduction Glandular fever is a type of viral infection that mostly affects young adults.

It is also known as infectious mononucleosis, or "mono". Rheumatoid arthritis. Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a long-term condition that causes pain, swelling and stiffness in the joints.

The hands, feet and wrists are commonly affected, but it can also cause problems in other parts of the body. There may be periods where your symptoms become worse, known as a flare-up or flare. Lupus. Lupus is a complex and poorly understood condition that affects many parts of the body and causes symptoms ranging from mild to life-threatening.
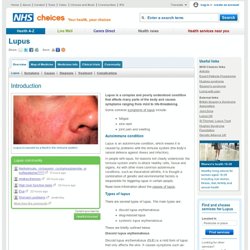
Some common symptoms of lupus include: fatigue skin rash joint pain and swelling Autoimmune condition Lupus is an autoimmune condition, which means it is caused by problems with the immune system (the body’s natural defence against illness and infection). In people with lupus, for reasons not clearly understood, the immune system starts to attack healthy cells, tissue and organs. Ludwig's angina.
Ludwig's angina, otherwise known as angina ludovici, is a serious, potentially life-threatening cellulitis,[1] or connective tissue infection, of the floor of the mouth, usually occurring in adults with concomitant dental infections and if left untreated, may obstruct the airways, necessitating tracheotomy.

It is named after the German physician Wilhelm Friedrich von Ludwig who first described this condition in 1836.[2][3] Other names include "angina Maligna" and "Morbus Strangularis". Ludwig's angina should not be confused with angina pectoris, which is also otherwise commonly known as "angina". The word "angina" comes from the Greek word ankhon, meaning "strangling", so in this case, Ludwig's angina refers to the feeling of strangling, not the feeling of chest pain, though there may be chest pain in Ludwig's angina if the infection spreads into the retrosternal space. About Zika Virus Disease.
Hepatitis. Hepatitis is the term used to describe inflammation of the liver. It's usually the result of a viral infection or liver damage caused by drinking alcohol. There are several different types of hepatitis, most of which are outlined below. Some types will pass without any serious problems, while others can be long-lasting (chronic) and cause scarring of the liver (cirrhosis), loss of liver function and, in some cases, liver cancer.
This page covers: Symptoms of hepatitis. Legionnaires' disease. Legionnaires’ disease is a serious lung infection caused by Legionella bacteria. Initial symptoms usually include flu-like symptoms, such as: mild headaches muscle pain high temperature (fever), usually 38C (100.4F) or above chills tiredness changes to your mental state, such as confusion Once bacteria begin to infect your lungs, you may also experience symptoms of pneumonia, such as: a persistent cough – which is usually dry at first, but as the infection develops you may start coughing up phlegm or, rarely, blood shortness of breath chest pains See your GP as soon as possible if you develop the symptoms above. It usually takes six to seven days between getting the infection and the start of symptoms (known as the incubation period), although it can be any time from two to 19 days.
As Legionnaires' disease has similar symptoms to other illnesses, your recent travel history will be relevant in making a diagnosis. How does Legionnaires’ disease spread? Increased risk. Meningococcal Meningitis - Meningitis Research Foundation. Meningococcal infection is the most common cause of bacterial meningitis in the UK and Ireland1. Meningococcal bacteria (Neisseria meningitidis) can cause meningitis or septicaemia, or a combination of these diseases. There are several strains or 'groups' of meningococcal bacteria such as A,B,C,W, X and Y. In the past 50 years, most meningococcal disease in the UK and Ireland2 has been due to group B (MenB) and group C (MenC), although the MenC vaccine introduced in 1999 has now successfully reduced cases to just a handful each year.
Alpha-1 Foundation. The Liver in Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Know the signs and symptoms of Alpha-1 liver disease. Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) can cause liver problems in infants, children or adults – as well as the better-known adult lung disease. In people with Alpha-1 (Alphas), large amounts of abnormal alpha-1 antitrypsin protein (AAT) are made in the liver; nearly 85 percent of this protein gets stuck in the liver. If the liver cannot break down the abnormal protein, the liver gradually gets damaged and scarred. Currently, there is no way to prevent the abnormal AAT from getting stuck in the liver. Vitiligo. Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Epidermolysis bullosa is a group of genetic conditions that cause the skin to be very fragile and to blister easily.
Blisters and skin erosions form in response to minor injury or friction, such as rubbing or scratching. Developmental co-ordination disorder in children. MRSA infection. Deep vein thrombosis. Gum Disease (Gingivitis): Causes, Risk Factors ... - Healthline. Osteoporosis. Introduction. Toxoplasmosis. Electromagnetic hypersensitivity. Scoliosis. Scoliosis is the abnormal twisting and curvature of the spine. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Myasthenia gravis. Churg-Strauss syndrome Symptoms. Amyloidosis. Congenital heart disease. Alien hand syndrome. Sickle cell anaemia. Norovirus. Hypoglycemia - Symptoms, Causes and Treatment. Wegener's Granulomatosis; Klinger's Syndrome Information.
What Is Hemophilia? What Is Vasculitis? Jaundice. Gilbert's syndrome. Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Coeliac disease. Irritable bowel syndrome. Pneumonia. Hernia. Parkinson's disease. Pulmonary Oedema. What is Alzheimer's disease? What is dementia? Ebola virus. Asthma. Autoimmune Diseases: MedlinePlus. Multiple Sclerosis. Pneumothorax.