

Etic-grupo10 - El Cognitivismo. Carbon.ucdenver.edu/~bwilson/Constructivism.pdf. Constructivism - Learning and Teaching. Constructivism is a learning theory found in psychology which explains how people might acquire knowledge and learn.

It therefore has direct application to education. The theory suggests that humans construct knowledge and meaning from their experiences. Constructivism is not a specific pedagogy. Piaget's theory of Constructivist learning has had wide ranging impact on learning theories and teaching methods in education and is an underlying theme of many education reform movements. Research support for constructivist teaching techniques has been mixed, with some research supporting these techniques and other research contradicting those results.
Resources What is constructivism? Concept to Classroom > Constructivism as a Paradigm for Teaching and LearningProvides a workshop on the concept of constructivism beginning with an explanation of the term and ending with a demonstration of how the concept can be applied in the classroom. Concept to Classroom. Examples & case studies. Tecnicas Didacticas. John Dewey John Dewey (1859-1952) escribió acerca de filosofía, psicología, educación, ciencia política, y artes.
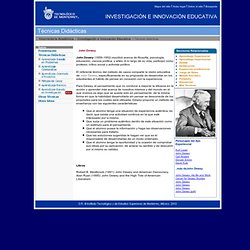
A lo largo de su vida, participó como profesor, crítico social y activista político. El referente teórico del método de casos comparte la visión educativa de John Dewey, específicamente en su propuesta de desarrollar en los estudiantes el hábito de pensar en conexión con la experiencia. Para Dewey, el pensamiento que no conduce a mejorar la eficacia en la acción y aprender más acerca de nosotros mismos y del mundo en el que vivimos es algo que se queda sólo en pensamiento, de la misma forma en que la habilidad desarrollada sin pensar se desconecta de los propósitos para los cuales será utilizada. Dewey propone un método de enseñanza con las siguientes características: Que el alumno tenga una situación de experiencia auténtica, es decir, que exista una actividad continua en la que esté interesado por sí mismo.
Bruner - Learning Theory in Education. By Saul McLeod published 2008,updated The outcome of cognitive development is thinking.
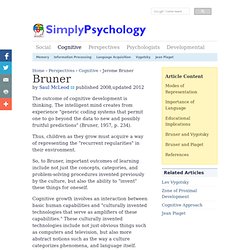
The intelligent mind creates from experience "generic coding systems that permit one to go beyond the data to new and possibly fruitful predictions" (Bruner, 1957, p. 234). Thus, children as they grow must acquire a way of representing the "recurrent regularities" in their environment. So, to Bruner, important outcomes of learning include not just the concepts, categories, and problem-solving procedures invented previously by the culture, but also the ability to "invent" these things for oneself. Cognitive growth involves an interaction between basic human capabilities and "culturally invented technologies that serve as amplifiers of these capabilities. " The aim of education should be to create autonomous learners (i.e., learning to learn).
Vygotsky. Cognitive Theory. By By Saul McLeod 2009, updated 2015 Piaget's (1936) theory of cognitive development explains how a child constructs a mental model of the world.
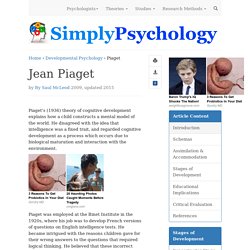
He disagreed with the idea that intelligence was a fixed trait, and regarded cognitive development as a process which occurs due to biological maturation and interaction with the environment. Piaget was employed at the Binet Institute in the 1920s, where his job was to develop French versions of questions on English intelligence tests. He became intrigued with the reasons children gave for their wrong answers to the questions that required logical thinking. He believed that these incorrect answers revealed important differences between the thinking of adults and children. Piaget (1936) described his work as genetic epistemology (i.e. the origins of thinking). What Piaget wanted to do was not to measure how well children could count, spell or solve problems as a way of grading their I.Q.
Piaget's Theory Differs From Others In Several Ways: Schemas. Constructivism as a Paradigm for Teaching and Learning. What is constructivism?
How does this theory differ from traditional ideas about teaching and learning? What does constructivism have to do with my classroom? Expert interview What is the history of constructivism, and how has it changed over time? What are some critical perspectives? What are the benefits of constructivism? What is the history of constructivism, and how has it changed over time? The concept of constructivism has roots in classical antiquity, going back to Socrates's dialogues with his followers, in which he asked directed questions that led his students to realize for themselves the weaknesses in their thinking. In this century, Jean Piaget 1 and John Dewey 2 developed theories of childhood development and education, what we now call Progressive Education, that led to the evolution of constructivism.
Piaget believed that humans learn through the construction of one logical structure after another. Dewey called for education to be grounded in real experience.