

The Smell-Tasting Experiment. The Human Eye and Single Photons. [Physics FAQ] - [Copyright] Original by Philip Gibbs 1996.

The human eye is very sensitive but can we see a single photon? The answer is that the sensors in the retina can respond to a single photon. However, neural filters only allow a signal to pass to the brain to trigger a conscious response when at least about five to nine arrive within less than 100 ms. If we could consciously see single photons we would experience too much visual "noise" in very low light, so this filter is a necessary adaptation, not a weakness. Some people have said that single photons can be seen and quote the fact that faint flashes from radioactive materials (for example) can be seen. Scuba Diving Training & Certification. March 2005 By John Francis How good is the visibility today?
It's an absorbing question for a primarily visual animal who's peering at an alien world through a mask. And the usual answer, "There's 60-foot vis" or 100-foot or whatever, is often misleading. Human sensation and perception. Several simple investigations give an insight into the working of the human brain – exploring perception, learning or how we respond to our surroundings.

Practice makes perfect? Carry out three simple tests of sensorimotor skills. Present results graphically and interpret in terms of how sensorimotor skills have developed during the test. Assessing skin sensitivity – touch discrimination Touch the skin on different parts of the body with two points a measured distance apart. Cogtest. Simple Reaction Time Test The Reaction Time test is a classic test used to assess psychomotor speed.

The appearance of the stimulus is completely visual (unlike Set Shifting Test where an auditory tone is also heard) and occurs after a random delay from the presentation of a crosshair (centred both horizontally and vertically on the screen) that is used to centre the participants' eyes prior to the onset of the stimulus. There are two different phases to this test, namely the practice phase and the main trials phase. The practice phase enables the participant to become familiar with the test and to reach a stable baseline before advancing to the main trials. 24 stimuli are presented, and the participant needs to achieve a criterion of at least 20 correct in order to advance. Feedback is provided throughout the course of this phase. Reverse Spoke Illusion. What to observe.

Online Depth Perception Test. This simple online test will help you determine whether you have fully functional depth perception (AKA stereoscopic vision, binocular vision, 3-D vision).
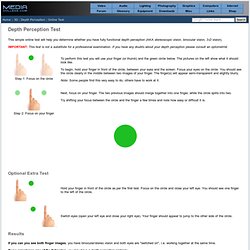
IMPORTANT: This test is not a substitute for a professional examination. If you have any doubts about your depth perception please consult an optometrist. Optional Extra Test Results If you can you see both finger images, you have binocular/stereo vision and both eyes are "switched on", i.e. working together at the same time. Tonedeaf Test: Test your musical skills in 6 minutes! While working at the music and neuroimaging lab at Beth Israel/Harvard Medical School in Boston, I developed a quick online way to screen for the tonedeafness.
It actually turned out to be a pretty good test to check for overall pitch perception ability. The test is purposefully made very hard, so excellent musicians rarely score above 80% correct. Neurons, Synapses, Action Potentials, and Neurotransmission - The Mind Project. Function of neurons Because our main interest lies in exploring how information processing occurs in the brain, we are going to ignore glia.

But before we see how neurons process information (and what that means), you need to know a few things about the structure of neurons. Structure of neurons While there are as many as 10,000 specific types of neurons in the human brain, generally speaking, there are three kinds of neurons: motor neurons (for conveying motor information), sensory neurons (for conveying sensory information), and interneurons (which convey information between different types of neurons).
The following image identifies how neurons come in various shapes and sizes. Neuronal signaling. SensorySystems Chapter. Cortical representation of the vestibular system as evidenced by brain electrical activity mapping of vestibular late evoked potentials. <a href=" representation of the vestibular system as evidenced by brain electrical activity mapping of vestibular late evoked potentials.

</a> Abstract We examined the space and temporal distributions of the rotatory ro·ta·to·ryadj.1. Of, relating to, causing, or characterized by rotation. 2. Mentioned in: Multiple Sclerosis [VestEP]) in humans. Frontal lobeThe largest, most forward-facing part of each side or hemisphere of the brain. Angular gyrus one arching over the superior temporal sulcus, continuous with the middle temporal gyrus. postcentralis, which corresponds to the primary somatosensory somatosensory /so·ma·to·sen·sory/ (so?
So·mat·o·sen·so·ryadj. fields, Brodmann's areas Brodmann's areas. Vestibular system. The vestibular system detects motion of the head in space and in turn generates reflexes that are crucial for our daily activities, such as stabilizing the visual axis (gaze) and maintaining head and body posture.
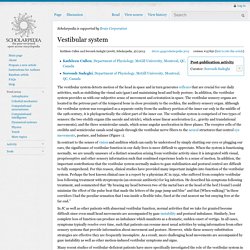
In addition, the vestibular system provides us with our subjective sense of movement and orientation in space. Perception Lecture Notes: Auditory Pathways and Sound Localization. What you should know from this lecture Auditory pathway: cochlea, cochlear nucleus, superior olive, inferior colliculus, medial geniculate nucleus, auditory cortex Crossing fibers Tonotopic organization Auditory scene analysis Spatial localization Interaural intensity difference (IID) Interaural time difference (ITD) Medial and lateral superior olive Coincidence detectors Cone of confusion Head-related transfer function (HRTF) Auditory Pathways.