

Why Running Helps Clear Your Mind. It is something of a cliché among runners, how the activity never fails to clear your head.
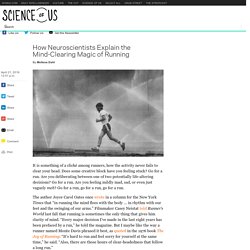
Does some creative block have you feeling stuck? Go for a run. Are you deliberating between one of two potentially life-altering decisions? Go for a run. Incidence of Running-Related Injuries Per 1000 h of running in Different Types of Runners: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Background No systematic review has identified the incidence of running-related injuries per 1000 h of running in different types of runners.

Objective. Influence of brain catecholamines on the development of fatigue in exercising rats in the heat - Hasegawa - 2008 - The Journal of Physiology. Abstract The purpose of the present study was to identify the effects of an acute injection of a dual dopamine (DA)/noradrenaline (NA) reuptake inhibitor (bupropion) on exercise performance, thermoregulation and neurotransmitters in the preoptic area and anterior hypothalamus (PO/AH) of the rat during exercise in the heat.

Body core temperature (Tcore), brain temperature (Tbrain) and tail skin temperature (Ttail) were measured. A microdialysis probe was inserted in the PO/AH, and samples for measurement of extracellular DA, NA and serotonin (5-HT) levels were collected. Rats received either bupropion (17 mg kg−1; hot-BUP) or saline (1 ml kg−1; hot) 20 min before the start of exercise and ran at a speed of 26 m min−1 until exhaustion in a warm environment (30°C). Rats also ran until exhaustion in a cool environment (18°C; cool). Aspectos médicos a tener en cuenta en el corredor de montaña (II), por Daniel Brotons. Aspectos médicos a tener en cuenta en el corredor de montaña (I), por Daniel Brotons. Exercise & The Brain. Thermoregulation, fatigue and brain neurotransmission during prolonged exercise in normal and high ambient temperatures. Fatigue should be acknowledged as a complex phenomenon influenced by both peripheral and central factors.

Because strenuous exercise is associated with cerebral metabolic and neurohumoral alterations that may relate to central fatigue, it is important to explore the influence of neurotransmitters (specifically serotonine, dopamine and noradrenaline) on the outcome of performance and in particular on fatigue. Prolonged exercise may induce homeostatic disturbances within the central nervous system that subsequently attenuates motor activation. Therefore, strenuous exercise is a challenge not only to the cardiorespiratory and locomotive systems but also to the brain.
Central nervous system fatigue. Neurochemical Mechanisms[edit] While many neurochemical changes have been observed during central nervous system fatigue, no current experimental method can provide a direct causal link between the neurochemical changes and fatigue.

However, existing methods have provided enough evidence to suggest that serotonin and dopamine are significant drivers of central nervous system fatigue.[1] Serotonin[edit] Journal of Sport and Health Science. Dr. Daniel Brotons, médico especialista en ultratrails. 0912f50c2eea5e8cdb000000.pdf.