

Oliver Hearn
Solar electricity PV (photovoltaic) panels explained - benefits, costs, savings, earnings, suitability.
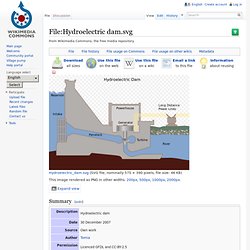
Hydro - Renewable Technologies - REA. Hydro power is produced when the kinetic energy of flowing water, is converted into electricity by a turbine connected to an electricity generator.

Though the UK generates only about 1.3% (5000GKh) of its electricity from hydro electric schemes, hydroelectricity has proven to be an efficient and reliable technology, as most modern plants have energy conversion efficiencies above 90%. Research estimates the remaining hydro potential in the UK ranges from 850-1550MW, which could contribute significantly to the UK’s renewable energy targets. Currently hydroelectricity is covered under the Government’s Feed-in Tariff (FITs) scheme as well as the Renewables Obligation (RO). Installations up to 50kW are eligible for the FITs, installations between 50kW and 5MW can choose between FITs or ROCs and installations over 5MW are only eligible for ROCs. For more information on the FITs and the RO see the DECC website. Hydropower can be exploited at various different scales. File:Hydroelectric dam.svg.
Cancel Edit Delete Preview revert Text of the note (may include Wiki markup) Could not save your note (edit conflict or other problem).
Please copy the text in the edit box below and insert it manually by editing this page. Upon submitting the note will be published multi-licensed under the terms of the CC-BY-SA-3.0 license and of the GFDL, versions 1.2, 1.3, or any later version. See our terms of use for more details. Add a note Draw a rectangle onto the image above (press the left mouse button, then drag and release). Save To modify annotations, your browser needs to have the XMLHttpRequest object. Hydroelectricity explained. Hydroelectricity. Scottish Hydro - Green Energy, Electricity and Gas Supplier for Scotland. Wind - Renewable Technologies - REA. Windmills, wind turbines and wind pumps can be used to produce renewable electricity.

Wind power equipment ranges from small water pumps and chargers (used to charge batteries at remote locations) to large multi-megawatt wind turbines arranged in wind farms that supply power to the electricity grid. This equipment has been developed to provide a range of power outputs, from under 100W up to 3MW onshore, and up to 7MW offshore. The overall reliability of wind turbines is high – over 97% availability is standard for modern turbines – and modern machines are designed to have a useful life of about 25 years. Turbines can have fixed or variable speed rotors, can be pitch or stall regulated, or in the case of small turbines can have furling rotor blades.
When used for electricity generation, turbines can generate either direct or alternating current. Large Scale Onshore/Offshore. Solar Power Deals, Tools & Information. Small Wind Turbines Scotland UK. REA - Renewable Energy Association. Renewable energy: Solar, wind, wave, tidal and hydropower. Renewable energy. Micro-CHP - micro combined heat & power - boilers, systems & costs. Wind turbines for homes explained - benefits, costs, savings, earnings, suitability. Solar Power Uk 2012 - Events - REA.
Hydroelectricity explained. Hydroelectricity. Hydroelectricity is the term referring to electricity generated by hydropower; the production of electrical power through the use of the gravitational force of falling or flowing water.
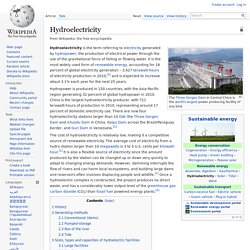
It is the most widely used form of renewable energy, accounting for 16 percent of global electricity generation – 3,427 terawatt-hours of electricity production in 2010,[1] and is expected to increase about 3.1% each year for the next 25 years. Hydropower is produced in 150 countries, with the Asia-Pacific region generating 32 percent of global hydropower in 2010.
China is the largest hydroelectricity producer, with 721 terawatt-hours of production in 2010, representing around 17 percent of domestic electricity use. There are now four hydroelectricity stations larger than 10 GW: the Three Gorges Dam and Xiluodu Dam in China, Itaipu Dam across the Brazil/Paraguay border, and Guri Dam in Venezuela.[1] Wind turbine. A wind turbine is a device that converts kinetic energy from the wind into electrical power.
A wind turbine used for charging batteries may be referred to as a wind charger. The result of over a millennium of windmill development and modern engineering, today's wind turbines are manufactured in a wide range of vertical and horizontal axis types. The smallest turbines are used for applications such as battery charging for auxiliary power for boats or caravans or to power traffic warning signs. Slightly larger turbines can be used for making small contributions to a domestic power supply while selling unused power back to the utility supplier via the electrical grid.
Solar panel. An installation of 24 solar modules in rural Mongolia A solar photovoltaic module is composed of individual PV cells.
This crystalline-silicon module has an aluminium frame and glass on the front. A half-built homemade solar module, made from individual cells soldered together Theory and construction[edit] Polycrystalline PV cells connected in a solar module. Electrical connections are made in series to achieve a desired output voltage and/or in parallel to provide a desired current capability. Bypass diodes may be incorporated or used externally, in case of partial module shading, to maximize the output of module sections still illuminated.