

Choice Theory.
Probability theory. Entropy. Where T is the absolute temperature of the system, dividing an incremental reversible transfer of heat into that system (dQ).
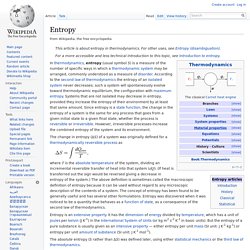
(If heat is transferred out the sign would be reversed giving a decrease in entropy of the system.) The above definition is sometimes called the macroscopic definition of entropy because it can be used without regard to any microscopic description of the contents of a system. The concept of entropy has been found to be generally useful and has several other formulations. Entropy was discovered when it was noticed to be a quantity that behaves as a function of state, as a consequence of the second law of thermodynamics. The absolute entropy (S rather than ΔS) was defined later, using either statistical mechanics or the third law of thermodynamics. Reconciling Thermodynamic and State Definitions of Entropy. Operational risk management. The term Operational Risk Management (ORM) is defined as a continual cyclic process which includes risk assessment, risk decision making, and implementation of risk controls, which results in acceptance, mitigation, or avoidance of risk.
ORM is the oversight of operational risk, including the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes and systems; human factors; or external events. Four Principles of ORM[edit] The U.S. Department of Defense summarizes the principles of ORM as follows:[1] Accept risk when benefits outweigh the cost.Accept no unnecessary risk.Anticipate and manage risk by planning.Make risk decisions at the right level. Three Levels of ORM[edit] In Depth In depth risk management is used before a project is implemented, when there is plenty of time to plan and prepare. Deliberate. ORM University. Chapter 1 Overview Reference Publications: Air Force Policy Directive 90-9, Operational Risk Management Air Force Instruction 90-901, Operational Risk Management Air Force Pamphlet 90-902, Operational Risk Management (ORM) Guidelines and Tools The Air Force's Operational Risk Management (ORM) Concept is based on the following tenets:

Risk Management - References. The most important part of your risk management effort is process and the way you use it.

If you do not have a process yet, we recommend that you start using tools that will help you develop a process. The "Process Assets" compartment of this toolkit contains tools that can help you define, tailor, implement, and monitor a risk management process on your program or within your organization. These tools include guidance, steps, and descriptions of elements of the process. The "Support Assets" compartment of the toolkit contains detailed information that you can use at specific steps of the process. Safety Education - Civil Air Patrol. Home « Safety « Safety Education Safety Education ALL SAFETY TESTING FOR RESOURCES ON THIS PAGE IS COMPLETED IN eSERVICES UNDER ONLINE SAFETY EDUCATION Copyright © 2014 Civil Air Patrol National Headquarters.
All Rights Reserved. Feedback Site Map CAP National Headquarters 105 South Hansell Street Bldg. 714 Maxwell AFB, AL 36112-6332 Interested in Membership? Contact Your Local Unit Already a Member? Click Here to Visit the CAP Members Site Follow CAP. Probability. These concepts have been given an axiomatic mathematical formalization in probability theory (see probability axioms), which is used widely in such areas of study as mathematics, statistics, finance, gambling, science (in particular physics), artificial intelligence/machine learning, computer science, and philosophy to, for example, draw inferences about the expected frequency of events.
Probability theory is also used to describe the underlying mechanics and regularities of complex systems.[4] Interpretations[edit] When dealing with experiments that are random and well-defined in a purely theoretical setting (like tossing a fair coin), probabilities can be numerically described by the statistical number of outcomes considered favorable divided by the total number of all outcomes (tossing a fair coin twice will yield head-head with probability 1/4, because the four outcomes head-head, head-tails, tails-head and tails-tails are equally likely to occur).
Etymology[edit] History[edit] where. Example: Probability through counting outcomes. Conditional Probability and Combinations. Example: Dependent probability. HDSL Media. Here are links to stories about research done by Jennifer Lerner Professor Lerner was interviewed about her work on NPR's "Science Friday.

": In a short presentation to the Center for Public Leadership at Harvard Kennedy School, Professor Lerner described the research she is undertaking on how leaders approach decision making: In this short video, Professor Lerner talks about her courses at the Harvard's Kennedy School of Government, and the Kennedy School's Management, Leadership, and Decision Science field of study: Professor Lerner was interviewed by the producers of NOVA in advance of the broadcast of "Mind Over Money," an episode of the PBS weekly science magazine that featured her research into emotion and economic decision making: Professor Lerner spoke at a panel discussion on the occasion of the premiere of "Mind Over Money" at the Museum of Finance in New York: David Laibson Josh Greene Dave Rand.
_106997461.mp3 (audio/mpeg Object) Decision Sciences Institute.