

Radicalisme. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
En France et en Wallonie, le radicalisme est l'expression de la Franc-maçonnerie dominante en politique. Types de radicalisme[modifier | modifier le code] La gauche radicale entend résoudre les problèmes sociaux par un changement de société radical et définitif.Ceux appelés communément Radicaux de Gauche prônent des idées laïques et sociales-démocrates.Le Parti radical valoisien prône des idées laïques et progressistes.Le radicalisme entend résoudre l'ensemble des problèmes de notre société indépendamment des solutions socialistes ou néolibérales.
Il prône néanmoins un pouvoir législatif et exécutif fort.Le fondamentalisme religieux. Purist. Fundamentalism. Fundamentalism is the demand for a strict adherence to orthodox theological doctrines usually understood as a reaction against Modernist theology.[1] The term "fundamentalism" was originally coined by its supporters to describe five specific classic theological beliefs of Christianity, and that developed into a movement within the Protestant community of the United States in the early part of the 20th century, and that had its roots in the Fundamentalist–Modernist Controversy of that time.[2] While the word was originally used to refer to this specific movement within Protestantism, it has come to be applied to a broad tendency among certain groups mainly, although not exclusively, in religion in general.
The term usually has a religious connotation indicating unwavering attachment to a set of irreducible beliefs.[4] "Fundamentalism" is sometimes used as a pejorative term, particularly when combined with other epithets (as in the phrase "right-wing fundamentalists").[5][6] Hubris. Hubris (/ˈhjuːbrɪs/, also hybris, from ancient Greek ὕβρις), means extreme pride or self-confidence.
Hubris often indicates a loss of contact with reality and an overestimation of one's own competence, accomplishments or capabilities, especially when the person exhibiting it is in a position of power. The adjectival form of the noun hubris is "hubristic". Ancient Greek origin[edit] In ancient Greek, hubris referred to actions that shamed and humiliated the victim for the pleasure or gratification of the abuser.[1] The term had a strong sexual connotation, and the shame reflected on the perpetrator as well.[2] In Greek literature, hubris usually refers to infractions by mortals against other mortals.
Aristotle defined hubris as shaming the victim, not because of anything that happened to a person or might happen to a person, but merely for that person's own gratification.[4] Hubris is not the requital of past injuries—that is revenge. Hybris. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
Mythologie[modifier | modifier le code] Dans la mythologie grecque, Hybris est une divinité allégorique personnifiant l’hybris. Eschyle lui attribue pour mère Dyssebia (l'Impiété)[2] tandis qu'Hygin la range parmi les enfants de la Nuit et de l'Érèbe[3]. Certains manuscrits de la Bibliothèque du pseudo-Apollodore font état de son commerce amoureux avec Zeus, qu'elle aurait rendu père du dieu Pan, mais le nom d'Hybris provient peut-être d'une mauvaise lecture de celui de la nymphe arcadienne Thymbris. Le plus souvent, c'est Coros, le dieu personnifiant la Satiété, que lui attribue pour fils Pindare[4]. Lust. Lust is an emotion or feeling of intense desire in the body.
The lust can take any form such as the lust for knowledge, the lust for sex or the lust for power. It can take such mundane forms as the lust for food as distinct from the need for food. Lust is a powerful psychological force producing intense wanting for an object, or circumstance fulfilling the emotion.[1] In religion[edit] Religions, especially Christianity, separate the definition of passion and lust by further categorizing lust as type of passion for something that does not belong to oneself, therefore being morally wrong. Buddhism[edit] Lust holds a critical position in the philosophical underpinnings of Buddhist reality. Suffering (dukkha) is inherent in all life.Suffering is caused by lust.There is a natural way to eliminate all suffering from one's life.The Noble Eightfold Path is that way.
Luxure. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
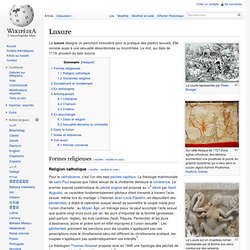
Sur cette fresque de 1727 d'une église orthodoxe, des démons tourmentent une prostituée (ê pornê, en graphie byzantine) qui a vécu dans la luxure (Agios Ioannis Prodromos, Kastoria, Grèce). La Luxure sur un chapiteau roman représentée par la femme aux seins mordus par des serpents La luxure désigne un penchant immodéré pour la pratique des plaisirs sexuels. Elle renvoie aussi à une sexualité désordonnée ou incontrôlée. Le mot, qui date de 1119, provient du latin luxuria. Gluttony. Gluttony, derived from the Latin gluttire meaning to gulp down or swallow, means over-indulgence and over-consumption of food, drink, or wealth items to the point of extravagance or waste.
In some Christian denominations, it is considered one of the seven deadly sins—a misplaced desire of food or its withholding from the needy. In Judaism[edit] According to the list of 613 commandments that Jews must keep according to the Rambam, gluttony or excessive eating or drinking is prohibited. It is listed as #169. Gourmandise.