

English Grammar Lesson: Past Simple. The Past Perfect Tense. Past Continuous. Past Continuous tense – Past Progressive GRAMMAR. Curso gratuito en línea para aprender inglés GRATIS – PAST CONTINUOUS / PAST CONTINUOUS – USOS y ESTRUCTURA – LECCION 32 GRAMATICA (PreIntermedio) Hello Song: La grange (zztop) In this post we are going to talk about the past continuous.
We will look at the syntax and the use of this tense. We are also going to compare it to the past simple and see the differences. Grammar Lessons - Past Continuous Tense (Past Progressive) The past continuous: The past continuous, also called past progressive, is used to refer to an action that was continuous (i.e. an action that was going on) at a particular time in the past.
This page will present the form and the use of the past continuous (progressive.) (More on the present continuous / progressive) Before you continue the lesson, read the following passage and try to see how the verbs in bold are formed and used. The form of the past continuous: The past continuous is formed as follows: The affirmative form: Examples: Yesterday evening I was watching a film, when someone knocked on the door. The interrogative form: Examples: What were you doing yesterday evening? The negative form: Examples: I wasn't reading a book yesterday evening; I was watching a film. Past Continuous Exercise 1. Grammar Lessons - The Simple Past of Regular and Irregular Verbs. The simple past tense This page will present the simple past tense: its form and its use.
Before you continue the lesson read the following passage and try to see how the verbs are formed and used. Regular verbs: The verbs "lived, started, died" are regular past forms. List of verbs. Grammar Exercises - Simple Past Tense. Present Simple vs Present Continuous - Learn English Tenses (Lesson 1) The Present Perfect Tense. Present Perfect - Lección de Inglés: Presente perfecto- AulaF cil - Curso de Ingl s. En cumplimiento del Real Decreto-ley 13/2012, AulaFacil.com solicita su permiso para obtener datos anónimos de su navegación en esta web, además de emplear plugins sociales que requieran de cookies.De esta forma todo nuestro contenido será expandido por toda la red, pudiendo crear nuevos y ofrecerlos siempre de una forma completamente gratiuta a todo tipo de público.

¿Acepta nuestra política de privacidad? SíNoPolítica de privacidad Utilizamos cookies propias y de terceros para mejorar la experiencia de navegación, ofrecer contenidos, publicidad de interés y estadísticas de navegación. Al hacer scroll de más de 1000px, entendemos que ud. desea nuestros servicios y acepta nuestra Política de Privacidad y de CookiesAcepto | NO Acepto. Present Perfect Quiz #1. <p class="noscript"><strong class="error">Warning: </strong>This site will not work properly with JavaScript disabled.
<a href="/jshelp.htm">Learn More »</a></p> Contact Us Student Contact Form Teacher Contact Form [Close] Help & FAQs Student Help Teacher Help [Close] Membership Options Student Membership Teacher Membership [Close] My Account My Student Account My Teacher Account [Close] Log On - Log Off Student Log On Teacher Log On Log Off [Close] Lesson Topics. English Grammar Lessons. Regular actions or events He plays tennis most weekends.

Facts The sun rises in the east. Facts known about the future We leave at 8.30 next Monday thoughts and feelings about the time of speaking I don't feel very well. The Present Continuous is used for: the time of speaking ('now') Shh, I'm trying to hear what they are saying . Things which are true at the moment but not always We're looking for a new flat. Look at these examples : I don't usually have cereals for breakfast but I'm having some this morning because there is nothing else. Note how, in all these examples, we use the present continuous to talk about events which are temporary/limited in time and the present simple to talk about events which are habits/permanent. exercise 1 exercise 2. Basic English - Present Simple vs. Present Continuous Quiz - 30 Essential Lessons for Beginning English Learners. Curso Ingles Online / Present Perfect Continuous. Present Perfect Continuous - Lección de Inglés: Presente perfecto continuo-
El presente perfecto continuo, muchas veces tiene la equivalencia de la traducción "llevar + gerundio" en español, pero el uso de esta forma es más frecuente en inglés.
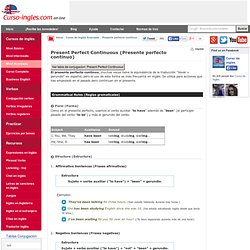
Se utiliza para acciones que has empezado en el pasado pero continuan en el presente. Grammatical Rules (Reglas gramaticales) Form (Forma) Como en el presente perfecto, usamos el verbo auxiliar "to have" además de "been" (el participio pasado del verbo "to be") y más el gerundio del verbo. Structure (Estructura) Affirmative Sentences (Frases afirmativas)Estructura Sujeto + verbo auxiliar ("to have") + "been" + gerundio.Ejemplos:They've been talking for three hours.Play They've been talking for three hours. Present Perfect Progressive (Present Perfect Continuous) Present Perfect Continuous Exercises on Present Perfect Progressive The present perfect progressive expresses an action that recently stopped or is still going on.
It puts emphasis on the duration or course of the action. Present Perfect Continuous. The present perfect continuous (also called present perfect progressive) is a verb tense which is used to show that an action started in the past and has continued up to the present moment.
The present perfect continuous usually emphasizes duration, or the amount of time that an action has been taking place. Read on for detailed descriptions, examples, and present perfect continuous exercises. Present Perfect Continuous Forms The present perfect continuous is formed using has/have + been + present participle. Questions are indicated by inverting the subject and has/have. Statement: You have been waiting here for two hours.Question: Have you been waiting here for two hours?