

Rape Statistics. Rape statistics. Comparison of selected countries' rape rates, 2002.
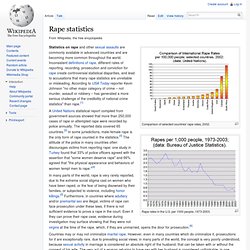
Rape rates in the U.S. per 1000 people, 1973-2003. Statistics on rape and other sexual assaults are commonly available in advanced countries and are becoming more common throughout the world. Inconsistent definitions of rape, different rates of reporting, recording, prosecution and conviction for rape create controversial statistical disparities, and lead to accusations that many rape statistics are unreliable or misleading. According to USA Today reporter Kevin Johnson "no other major category of crime – not murder, assault or robbery – has generated a more serious challenge of the credibility of national crime statistics" than rape.[1] A United Nations statistical report compiled from government sources showed that more than 250,000 cases of rape or attempted rape were recorded by police annually.
Countries may or may not criminalize marital rape. Under-reporting[edit] The World Health Organization's ranking of the world's health systems. Source: WHO World Health Report - See also Spreadsheet Details (731kb)
Education Index. The United Nations publishes a Human Development Index every year, which consists of the Life Expectancy Index, Education index, and Income index.[1] The Education Index is calculated from the Mean years of schooling index and the Expected years of schooling index.[1] Education is a major component of well-being and is used in the measure of economic development and quality of life, which is a key factor determining whether a country is a developed, developing, or underdeveloped nation.
Ranking[edit] Change in value from the last report is given as follows: = increase. = steady. = decrease. The latest index was released in the Human Development Report in October 2009.[2] This statistical update covers the period up to 2007: 1 is the highest possible theoretical score, indicating perfect education attainment. All countries considered to be developed countries possess a minimum score of 0.8 or above, although the great majority have a score of 0.9 or above. See also[edit] School leaving age. The 10 Most Educated Countries in the World. In the past 50 years, college graduation rates in developed countries have increased nearly 200%, according to Education at a Glance 2011, a recently published report by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).

The report shows that while education has improved across the board, it has not improved evenly, with some countries enjoying much greater rates of educational attainment than others. Based on the report, 24/7 Wall St. identified the 10 developed countries with the most educated populations. List of countries by literacy rate. World map indicating literacy by country in 2011 (2011 UN Human Development Report and Individual statistics departments) Grey = no data This is a list of countries by literacy rate.
The figures represent a mixture of data collected by the CIA World Factbook,[1] and national self-reported data. Where data was unavailable older figures were used. For highly developed/high income countries where literacy statistics were not collected, a rate of 99% was assumed. Life expectancy. Life expectancy is the expected (in the statistical sense) number of years of life remaining at a given age.[1] It is denoted by ,[a] which means the average number of subsequent years of life for someone now aged , according to a particular mortality experience.
Because life expectancy is an average, a particular person may well die many years before or many years after their "expected" survival. The term "maximum life span" has a quite different meaning. 6a00e0098226918833012876a6070f970c-800wi (JPEG Image, 786x1250 pixels) - Scaled (51%) Happy Planet Index. Map showing countries shaded by their position in the Happy Planet Index (2006).
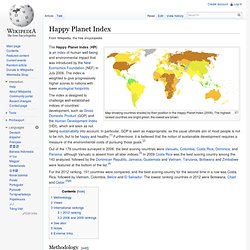
The highest-ranked countries are bright green; the lowest are brown. The index is designed to challenge well-established indices of countries’ development, such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and the Human Development Index (HDI), which are seen as not taking sustainability into account. In particular, GDP is seen as inappropriate, as the usual ultimate aim of most people is not to be rich, but to be happy and healthy.[1] Furthermore, it is believed that the notion of sustainable development requires a measure of the environmental costs of pursuing those goals.[2] Out of the 178 countries surveyed in 2006, the best scoring countries were Vanuatu, Colombia, Costa Rica, Dominica, and Panama, although Vanuatu is absent from all later indices.[3] In 2009 Costa Rica was the best scoring country among the 143 analyzed, followed by the Dominican Republic, Jamaica, Guatemala and Vietnam.
Quality-of-life Index. Method[edit] The survey uses nine quality of life factors to determine a nation's score.[1] They are listed below including the indicators used to represent these factors: Health: Life expectancy at birth (in years).
Source: US Census BureauFamily life: Divorce rate (per 1,000 population), converted into index of 1 (lowest divorce rates) to 5 (highest). Sources: UN; EuromonitorCommunity life: Variable taking value 1 if country has either high rate of church attendance or trade-union membership; zero otherwise. Source: World Values SurveyMaterial well being: GDP per person, at PPP in $. Life Quality Index. The Life Quality Index (LQI) is a compound social indicator of human welfare that reflects the expected length of life in good health and enhancement of the quality of life through access to income.
The Life Quality Index combines two primary social indicators: the expectancy of healthy life at birth, E, and the real gross domestic product per person, G, corrected for purchasing power parity as appropriate. Both are widely available and accurate statistics. Basic concept[edit]