

World Rice Production 2015/2016. History of rice cultivation -Includes links to countries who produce rice. Oryza sativa was domesticated from the wild grass Oryza rufipogon roughly 10,000–14,000 years ago.
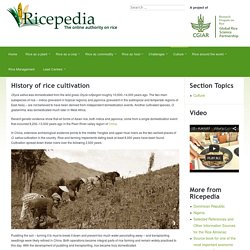
The two main subspecies of rice – indica (prevalent in tropical regions) and japonica (prevalent in the subtropical and temperate regions of East Asia) – are not believed to have been derived from independent domestication events. Another cultivated species, O. glaberrima, was domesticated much later in West Africa. Recent genetic evidence show that all forms of Asian rice, both indica and japonica, come from a single domestication event that occurred 8,200–13,500 years ago in the Pearl River valley region of China.
In China, extensive archeological evidence points to the middle Yangtze and upper Huai rivers as the two earliest places of O. sativa cultivation in the country. Rice and farming implements dating back at least 8,000 years have been found. Movement to western India and south to Sri Lanka was also accomplished very early. Rice productivity - Ricepedia. Productivity in global rice environments Rice is grown in more than a hundred countries, with a total harvested area of approximately 158 million hectares, producing more than 700 million tons annually (470 million tons of milled rice).

Nearly 640 million tons of rice are grown in Asia, representing 90% of global production. Sub-Saharan Africa produces about 19 million tons and Latin America some 25 million tons. In Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, almost all rice is grown on small farms of 0.5−3 ha. Yields range from less than 1 t/ha under very poor rainfed conditions to more than 10 t/ha in intensive temperate irrigated systems. The highest rice yields have traditionally been obtained from plantings in high-latitude areas that have long day length and where intensive farming techniques are practiced, or in low-latitude desert areas that have very high solar energy. Rice growing in Australia. IRRI - Protecting the environment. Encyclopedia Britannica-Rice.
Where is rice grown? - Ricepedia. Rice grows in a wide range of environments and is productive in many situations where other crops would fail.
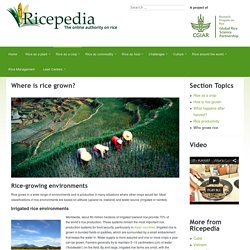
Most classifications of rice environments are based on altitude (upland vs. lowland) and water source (irrigated or rainfed). Rice_and_water.pdf. Rice_growing_production_process.pdf. IRRI - Rice and the environment. Climate change Climate change poses an additional problem on the world’s agricultural and natural resource systems that must already cope with growing food demand due to population growth in many countries.
IRRI not only adapts rice to the effects of climate change but explores ways to reduce greenhouse gases from rice production. Soil and nutrient management Soils support life, and without soils, many of the world’s living organisms will find it difficult to survive and thrive. Besides forests and grasslands, this includes economically important plants like rice, which feeds more than half of the world’s population. Coping with water scarcity Like all living things, rice needs water for its growth and development. Drought, submergence, and salinity management Farmers who earn a living from areas that are unfavorable owing to problems of flooding, drought, or salinity oftentimes do not get enough rice for the whole year or are steeped in poverty.
Crop health Diversified cropping systems. Savewater.com.au - The Australian rice industry and water. Net Water Use by Irrigated Crop Type Australia often experiences drought conditions, which limits water resource availability and can severely limit rice production.
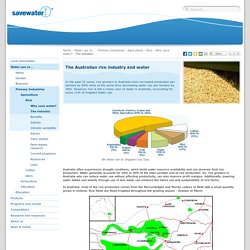
Water generally accounts for 20% to 30% of the total variable cost of rice production. Shrinking resources - Ricepedia. Declining natural resources For every one billion people added to the world’s population, 100 million more tons of rice (paddy) need to be produced annually.

This must be achieved with less land, less water, and less labor, in more efficient, environmentally friendly production systems that are more resilient to climate change and with fewer greenhouse gas emissions . Declining yields and less land, water, and labor Yield growth has fallen, partially as a result of the decline in investment in productivity research since the early 1990s, from 2.2% during 1970–1990 to less than 0.8% in the 1990s and 2000s. Rice area in the major production countries has been decreasing because of the conversion of land for other purposes.
Pressure on land use As a consequence of economic growth, current rice cultivation areas are likely to be lost to urban expansion, land conversion to biofuels, and diversification into other agricultural products. Water scarcity. Ricegrowers' Association of Australia.