

RAID Levels Explained. If you've ever looked into purchasing a NAS device or server, particularly for a small business, you've no doubt come across the term "RAID.

" RAID stands for Redundant Array of Inexpensive (or sometimes "Independent") Disks. In general, a RAID-enabled system uses two or more hard disks to improve the performance or provide some level of fault tolerance for a machine—typically a NAS or server. Fault tolerance simply means providing a safety net for failed hardware by ensuring that the machine with the failed component, usually a hard drive, can still operate. Fault tolerance lessens interruptions in productivity, and it also decreases the chance of data loss. The way in which you configure that fault tolerance depends on the RAID level you set up. RAID. RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 10 Explained with Diagrams. By Ramesh Natarajan on August 10, 2010 RAID stands for Redundant Array of Inexpensive (Independent) Disks.
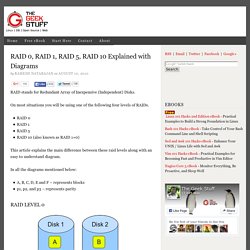
On most situations you will be using one of the following four levels of RAIDs. RAID 0RAID 1RAID 5RAID 10 (also known as RAID 1+0) This article explains the main difference between these raid levels along with an easy to understand diagram. In all the diagrams mentioned below: A, B, C, D, E and F – represents blocksp1, p2, and p3 – represents parity Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 0. Minimum 2 disks.Excellent performance ( as blocks are striped ).No redundancy ( no mirror, no parity ).Don’t use this for any critical system.
Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 1. Minimum 2 disks.Good performance ( no striping. no parity ).Excellent redundancy ( as blocks are mirrored ). Advantage, disadvantage, use. RAID is a technology that is used to increase the performance and/or reliability of data storage.
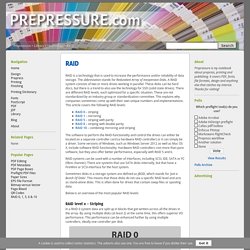
The abbreviation stands for Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks. A RAID system consists of two or more drives working in parallel. These disks can be hard discs, but there is a trend to also use the technology for SSD (solid state drives). There are different RAID levels, each optimized for a specific situation. These are not standardized by an industry group or standardization committee. RAID 0 – stripingRAID 1 – mirroringRAID 5 – striping with parityRAID 6 – striping with double parityRAID 10 – combining mirroring and striping.
Storgae RAID array, Storage Servers and Subsystems , Unified IP-SAN, iSCSI & Fibre SAN or NAS Raid. Mission-Critical, High Availability Enterprise Rugged Storage array Systems Â… The ultimate Back-up NAS IP storage RAID solution!

Up to 200TB in single chassis or enclosure scales to 2-PTB Related page: Cluster Server Unlimited Data Backup & Storage. Simplified IP NAS Storage Solutions...up to 200TB STORAGE CAPACITY Cepoint R-STOR™ , RS-212, RS316 and Rx524, RX-8600 STORAGE RAID array systems are built for enterprise applications, while the RMS- series are designed and manufactured for Reliability, performance and durability in the most hostile Military or Industrial environments.
Serial ATA stand alone NAS IP systems, SAS/SATA to SCSI or SATA to FC-AL 4GB/s Fibre Channel Host Bus Disk Arrays. MISSION-CRITICAL High Performance ISCSI SAN /Fiber-Channel SAN or simple NAS STORAGE SCALABLE ENTERPRISE SOLUTIONS are easy to implement, install operate & maintain. What is a hardware-based RAID? RAID Data Recovery. A RAID is considered hardware-based when it is implemented in hardware, either on the motherboard directly or a separate RAID card.
Windows views the entire RAID as a single disk. The individual component disks are controlled by the RAID controller and not directly accessible to Windows. RAID (redundant array of independent disks) levels 0, 1, 3 and 5 are the levels typically implemented in hardware-based solutions. Hardware-based RAID uses an intelligent drive controller and a redundant array of disk drives to protect against data loss in the event of media failure and to improve the performance of read/write operations. Server-based RAID vs. controller-based RAID. RAID Architecture: Pivot3 Launches Cost-Effective Clustered IP Storgae Solution Based On Industry's First Distributed RAID Architecture. Pivot3 Inc., the inventor of virtual distributed RAID, recently announced its entry into the scalable network storage market with an IP-based storage cluster that delivers up to five times the performance at half of the cost of competitive solutions.

The Pivot3 RAIGE (RAID Across Independent Gigabit Ethernet) Storage Cluster is the first system based on the ground-breaking Pivot3 block-level virtualization architecture that reduces storage infrastructure costs by up to 50 percent while significantly increasing scalability and data availability. "We want to be able to scale to hundreds of thousands of subscriber sites and millions of cameras," stated Rick Bentley, founder and CEO of Connexed Technologies, a hosted video surveillance provider and a Pivot3 customer. "Pivot3 has brought to fruition the type of storage solution we have only envisioned. RAID-Based Storage. RAID is an acronym standing for Redundant Array of Independent Disks[1].

As the name implies, RAID is a way for multiple disk drives to act as a single disk drive. RAID techniques were first developed by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley in the mid-1980s. At the time, there was a large gap in price between the high-performance disk drives used on the large computers installations of the day, and the smaller, slower disk drives used by the still-young personal computer industry. RAID was viewed as a method of having many less expensive disk drives fill in for higher-priced hardware. More importantly, RAID arrays can be constructed in different ways, and will have different characteristics depending on the final configuration.