

Energy storage. The Llyn Stwlan dam of the FfestiniogPumped Storage Scheme in Wales.
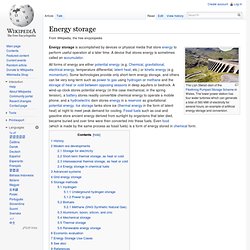
The lower power station has four water turbines which can generate a total of 360 MW of electricity for several hours, an example of artificial energy storage and conversion. History[edit] Energy storage as a natural process is as old as the universe itself - the energy present at the initial formation of the universe has been stored in stars such as the Sun, and is now being used by humans directly (e.g. through solar heating), or indirectly (e.g. by growing crops or conversion into electricity in solar cells). Inside an electrical socket. Transducer. A transducer is a device that converts a signal in one form of energy to another form of energy.[1] Energy types include (but are not limited to) electrical, mechanical, electromagnetic (including light), chemical, acoustic and thermal energy.
While the term transducer commonly implies the use of a sensor/detector, any device which converts energy can be considered a transducer. Transducers are widely used in measuring instruments. An actuator accepts energy and produces movement (action). The energy supplied to an actuator might be electrical or mechanical (pneumatic, hydraulic, etc.). Radio waves. Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum longer than infrared light.
Radio waves have frequencies from 300 GHz to as low as 3 kHz, and corresponding wavelengths ranging from 1 millimeter (0.039 in) to 100 kilometers (62 mi). Like all other electromagnetic waves, they travel at the speed of light. Naturally occurring radio waves are made by lightning, or by astronomical objects.