

Renewable and Non-Renewable Sources. By: Kelly-Rose Bradford - Updated: 8 Apr 2016| *Discuss As the UK strives to reach its target of deriving 10% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2010 renewable and reusable energy is a hot topic from the classroom to parliament.

However, it's all very well trying to get our kids' to be more environmentally aware and to think about protecting the Earth's resources – but how do we explain it in laymen's terms that youngsters can really get to grips with? Well for starters, equip youngsters with a sound knowledge of what is renewable and what isn't! Non-renewable sources of energy – in other words, when it's gone, it's gone! Renewable sources are what we should all be aiming for – think, for example water, tides, wind and solar energy!
Types of Non-Renewable Fuels So what are fossil fuels? Types of Fossil Fuel Coal Coal comes from fossilised plants and is mined from underground. Oil Oil comes from fossilised animals. Natural Gas Methane occurs naturally under the sea and land. Nuclear. Reactions: Thermodynamics. What are heat and cold?

It's a pretty simple idea. When you think of heat, you probably think of fire. When you think of cold, you might think of an ice cube. StudyJams. StudyJams. You Have the Power - National Geographic Society. Energy. Facts About Energy for Kids - Easy Science. When you think of energy, what do you think of – the Sun, gasoline or maybe electricity?
All of these are forms of energy, but there are other kinds of energy too. Energy is all around you. It is the force that allows things to move and happen. Even when you’re asleep or just reading a book, your body uses energy to make your heart beat, your blood flow and your muscles move. The Energy Balance. Earth gets all its energy from the Sun and loses energy into space If more energy is lost into space than is received from the Sun, the planet gets cooler.

If it loses less energy than it receives, the planet will warm up. Have you noticed that it is often cooler when there are clouds in the sky? Some types of clouds act like giant sun umbrellas, shading the Earth and reflecting the sunlight that hits them. Other types of clouds act like a jacket, holding the heat in and preventing it from leaving the atmosphere. Today, most clouds act more like a sun umbrella and help keep our climate cool. While it might be quite warm in the countryside on a summer day, it can get unbearably hot in a nearby city! Solar Energy. Solar Energy for Kids Solar energy is the light and heat that Earth receives from the Sun.
On the side of Earth facing the Sun, a square kilometer at the sea level receives about 700 megawatts of solar power every minute. Only a minuscule fraction of the available solar energy is used to generate electricity. Pictures & School Presentations : Science Videos & Lessons:(Reviewed by K-12 teachers) Search Videos Suggest Science Videos Click below to find & suggest other science videos. ENERGY STAR KIDS. Energy and kids. Top 6 solar energy inventions. Thermal Energy Facts. Methods of Heat Transfer. If you have been following along since the beginning of this lesson, then you have been developing a progressively sophisticated understanding of temperature and heat.

You should be developing a model of matter as consisting of particles which vibrate (wiggle about a fixed position), translate (move from one location to another) and even rotate (revolve about an imaginary axis). These motions give the particles kinetic energy. Temperature is a measure of the average amount of kinetic energy possessed by the particles in a sample of matter. The more the particles vibrate, translate and rotate, the greater the temperature of the object. Thermodynamics & Heat: Energy Transfer. If there is a temperature difference in a system, heat will naturally move from high to low temperatures.
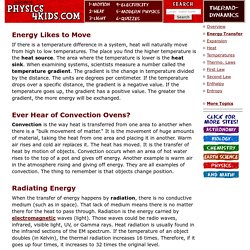
The place you find the higher temperature is the heat source. The area where the temperature is lower is the heat sink. When examining systems, scientists measure a number called the temperature gradient. The gradient is the change in temperature divided by the distance. The units are degrees per centimeter. Scientists have also discovered that objects that are good at giving off thermal radiation are also good at absorbing the same energy. Conduction is a situation where the heat source and heat sink are connected by matter.
If you touch an ice cream cone, the ice cream heats up because you are a warmer body. Or search the sites for a specific topic. Kinds of Energy. NOTE: If you want to learn about Energy in terms of Renewable and Non-renewable Energy, please select an option below: What is energy?

Look around you. Is anything moving? Can you hear, see or feel anything? Sure... this is because something is making something happen, and most probably, there is some power at work. Look at the sketch below to see an example of things working, moving, or happening... with energy. Energy moves cars along the roads and makes aeroplanes fly. KINDS OF ENERGY With the above explanation in mind, let us learn more. Energy can be (is) stored or transferred from place to place, or object to object in different ways. Kids Zone: What is Energy: Different Forms of Energy. Energy exists in many different forms.
Examples of these are: light energy, heat energy, mechanical energy, gravitational energy, electrical energy, sound energy, chemical energy, nuclear or atomic energy and so on. These forms of energy can be transferred and transformed between one another. This is of immense benefit to us. For a source of energy to end up as electricity it may undergo many transformations before it can power the light bulb in your home.
The Energy Story - Introduction. Energy is one of the most fundamental parts of our universe.

We use energy to do work. Energy lights our cities. Energy powers our vehicles, trains, planes and rockets. Energy warms our homes, cooks our food, plays our music, gives us pictures on television. Energy powers machinery in factories and tractors on a farm. Energy Kids: Energy Information Administration. Department of Energy. Antilles - Different Forms of Energy. Department of Energy.