

English words from Chinese. English words from Chinese This list parallels my similar pages on words from Arabic and Amerindian languages.

The main sources are the OED, the AHD, a number of Chinese dictionaries, ZhongWen.com, and Wikipedia (for nailing down the exact characters). I’ve included a number of proper names, partly because it's fun to know that (e.g.) Mao means 'wool', partly because Chinese place names tend to have clear, simple etymologies with useful words in them. M. = Mandarin, C. = Cantonese (given, I’m afraid, in whatever transliteration was near at hand). Japanese has borrowed Chinese words at various periods. Thanks to Hirofumi Nagamura, Philip Newton, bicoherent, Ran, Rachel Kronick, and Marnen Laibow-Koser for corrections. Chinese. You need a unicode-enabled browser with Chinese fonts installed to see the Chinese in this write-up.
All Mandarin Chinese is phoneticised as pinyin. 顏色 You would imagine that colors would be one of the most easily translatable of concepts across all languages, but that is certainly a fallacy when it comes to Chinese, because many Chinese names for colors may in fact correspond to a number of different English colors, depending on the context. In particular, the naming of Chinese colors would seem to be done by a people who are congenitally blue-yellow color blind, or who have had chronic exposure to ultraviolet light (Lindsey DT, Brown AM. 2002 see full reference at the end). Light blues are often synonymous with green; dark blues are often synonymous with grey or black.
Red The usual word for the color red is 紅 hóng. The vermilion pigment derived from cinnabar is called 朱 zhū. 緋 Fēi denotes a shade of red that the English would call scarlet. 黈 Tǒu is an obsolete word for 'yellow'. Chinese-English Dictionary. To search for pinyin ü, use "u:" (u followed by a colon) or "v".

If you are willing to host this dictionary, I have made the necessary files available in a zip file. To set up a mirror, you will need CGI access on your server. If this site is not working, please visit one of the following mirror sites: Mirror Sites: This Chinese/English dictionary provides a searchable interface for the CEDICT dictionary originally put together by Paul Denisowksi. Searches can be conducted by Chinese (using either the GB, Big5, or Unicode encodings), pinyin, or English. Some points to remember when using this dictionary: You can download the dictionary data at the CEDICT website. For a off-line way to search the dictionary, please check out the CEL utility from Richard Warmington. List of ethnic groups in China. Tibetan people. The Tibetan people (Tibetan: བོད་པ་, Wylie: Bodpa; Chinese: 藏族; pinyin: Zàng Zú) are an ethnic group that is native to Tibet.
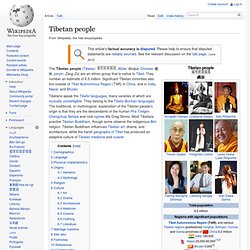
They number an estimate of 6.5 million. Significant Tibetan minorities also live outside of Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR) in China, and in India, Nepal, and Bhutan. Tibetans speak the Tibetic languages, many varieties of which are mutually unintelligible. They belong to the Tibeto-Burman languages. Li people. The Li (黎; pinyin: Lí) or Hlai are a minority ethnic group, the vast majority of whom live off the southern coast of mainland China on Hainan Island,[2] where they are the largest minority ethnic group.
Divided into the five branches of the Qi, Ha, Run, Sai and Meifu,[3] the Li have their own distinctive culture and customs. Background[edit] They refer to themselves as the Hlai people, but they are sometimes colloquially known as "Sai" or "Say", and during the Sui Dynasty they were known by the name Liliao. The Li form one of the 56 ethnic groups officially recognized by the People's Republic of China. Origin and history[edit]
Province (China) A province (shěng or 省), formally provincial level division, is the highest-level Chinese administrative division.
There are 34 such divisions, classified as 22 provinces, 4 municipalities, 5 autonomous regions, 2 Special Administrative Regions, and the claimed Taiwan Province.[1] The PRC claims sovereignty over the territory administered by the Republic of China (ROC), claiming most of it as its Taiwan Province. The ROC also administers some offshore islands which form Fujian Province, ROC. These were part of an originally unified Fujian province, which since the stalemate of the Chinese Civil War in 1949 has been divided between the PRC and ROC.
Every province has a Communist Party of China provincial committee, headed by a secretary beside the two special administrative regions. Types of province[edit] Municipality[edit] Municipality (Chinese: 直辖市; pinyin: zhíxiáshì): A higher level of city which is directly under the Chinese government, with status equal to that of the provinces. Zhuang people. The Zhuang people (Chinese: 壮族; pinyin: Zhuàngzú; Zhuang: Bouxcuengh) are an ethnic group who mostly live in the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region in southern China.
Some also live in the Yunnan, Guangdong, Guizhou and Hunan provinces.