

Human Numbers Through Time. By Susan K.
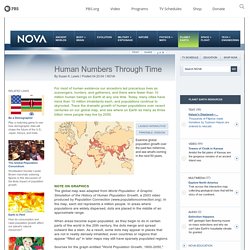
Lewis Posted 04.20.04 NOVA For most of human existence our ancestors led precarious lives as scavengers, hunters, and gatherers, and there were fewer than 10 million human beings on Earth at any one time. Today, many cities have more than 10 million inhabitants each, and populations continue to skyrocket. Trace the dramatic growth of human populations over recent centuries on our global map, and see where on Earth as many as three billion more people may live by 2050. Note on Graphics The global map was adapted from World Population: A Graphic Simulation of the History of Human Population Growth, a 2003 video produced by Population Connection (www.populationconnection.org).
When areas become super-populated, as they begin to do in certain parts of the world in the 20th century, the dots merge and spread outward like a stain. Illustrations. From the Top of the World... Science Assessment ~ Topics ~ Cells. Below is a list of key ideas related to Cells.

For each key idea, you will find a list of sub-ideas, a list of items, results from our field testing, and a list of student misconceptions. After clicking on a tab, click on it again to close the tab. All living things are composed of one or more cells. Students are expected to know that: All organisms, including animals, plants, fungi, and microorganisms, are made up of cells. Boundaries: Students are not expected to know the terms "prokaryote" or "eukaryote" or the differences between these types of cells. Frequency of selecting a misconception was calculated by dividing the total number of times a misconception was chosen by the number of times it could have been chosen, averaged over the number of students answering the questions within this particular idea.
Www.biology.washington.edu/hhmi/materials/O09_Health.pdf. Google Body - Google Labs. Print Teachers Guides. Life Science. What is an energy pyramid Energy pyramid An energy pyramid is a graphical model of energy flow in a community.
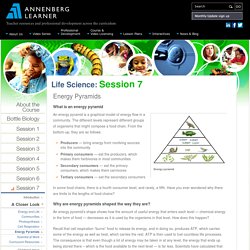
The different levels represent different groups of organisms that might compose a food chain. From the bottom-up, they are as follows: Producers — bring energy from nonliving sources into the community Primary consumers — eat the producers, which makes them herbivores in most communities Secondary consumers — eat the primary consumers, which makes them carnivores Tertiary consumers — eat the secondary consumers In some food chains, there is a fourth consumer level, and rarely, a fifth. Why are energy pyramids shaped the way they are? An energy pyramid’s shape shows how the amount of useful energy that enters each level — chemical energy in the form of food — decreases as it is used by the organisms in that level.
Recall that cell respiration “burns” food to release its energy, and in doing so, produces ATP, which carries some of the energy as well as heat, which carries the rest. KS2 Bitesize: Science - Living things. Dnr.state.il.us/education/ilbiodiversitybasics/Section1.pdf. Video Segments: The Secret World of Sharks and Rays. Science Online Resources. OLogy: Going, Going... Gone? Energy Transfer. Www.science-class.net/Graphic_Organizers/GO_energy_transfer.pdf. LSI: Life Science Investigation. Meiosis: An Interactive Animation. Diploid Cell (2N): From a preceding mitotic division, the Oogonium (Spermatogonium) enters meiosis with DIPLOID (2N) chromosomes but TETRAPLOID (4N) DNA.
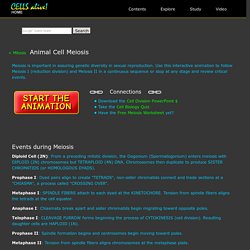
Chromosomes then duplicate to produce SISTER CHROMATIDS (or HOMOLOGOUS DYADS). Prophase I: Dyad pairs align to create "TETRADS", non-sister chromatids connect and trade sections at a "CHIASMA", a process called "CROSSING OVER". Metaphase I: SPINDLE FIBERS attach to each dyad at the KINETOCHORE. Tension from spindle fibers aligns the tetrads at the cell equator. Anaphase I: Chiasmata break apart and sister chromatids begin migrating toward opposite poles. Telophase I: CLEAVAGE FURROW forms beginning the process of CYTOKINESIS (cell division). Prophase II: Spindle formation begins and centrosomes begin moving toward poles. Metaphase II: Tension from spindle fibers aligns chromosomes at the metaphase plate. Anaphase II: CHROMATIDS separate and begin moving to the poles. Biome/Habitat Animal Printouts. Science Classroom. Lessons Microscope Mania Pond Water Survey Hydra Investigation Animal Classification Challenge Incredible Edible Cells - Cell Project Construction Zone - Cell Project Mitosis Flip Books Genetics with a Smile + SpongeBob Genetics DNA Keychains & Replication Protein Power Game Egg-cellent Ideas for Osmosis & Diffusion Human Body Activities (Body Systems, Skeletal System, Muscular System) Also see Silly Science - a dichotomous key activity in General Science section!
Internet Lessons • The Organ Trail - Challenge your students to create a "Wanted" poster about an organ. This download provides project guidelines, student information, and project worksheets. Links for students can be found on the Health & Human Body links page of the Kid Zone. • Microscopes Online (pdf) (Internet Lesson) - Use this worksheet to help your students explore the history of the microscope as well as other sites listed on the Cells & Microscopes page of the Kid Zone . Also available. . . . | Back to top |