

Definition of a Leader. A leader is "a person who influences a group of people towards the achievement of a goal".
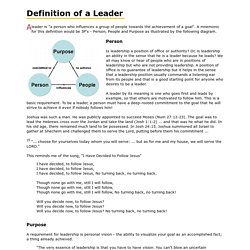
A mnemonic for this definition would be 3P's - Person, People and Purpose as illustrated by the following diagram. Person Is leadership a position of office or authority? Or, is leadership an ability in the sense that he is a leader because he leads? We all may know or hear of people who are in positions of leadership but who are not providing leadership. A leader by its meaning is one who goes first and leads by example, so that others are motivated to follow him. Joshua was such a man. 15 "... choose for yourselves today whom you will serve: ... but as for me and my house, we will serve the LORD.
" This reminds me of the song, "I Have Decided to Follow Jesus" Purpose A requirement for leadership is personal vision - the ability to visualize your goal as an accomplished fact; a thing already achieved. "The very essence of leadership is that you have to have vision. People In God's call to Moses ... The Importance of Culture in Organizations. Every organization has its own culture.

Since many employees spend 40 or more hours at their workplace, their organization’s culture obviously affects both their work lives as well as their personal lives. Organizational culture refers to the beliefs, ideologies, principles and values that the individuals of an organization share. This culture is a determining factor in the success of the organization. Unity A shared organizational culture helps to unite employees of different demographics. Loyalty Organizational culture helps to keep employees motivated and loyal to the management of the organization.
Related Reading: Importance of a Healthy Corporate Culture Competition. What is organizational culture? definition and meaning. Difference Between Situational Leadership & Path Leadership Theories. Business leaders range from owners of small businesses to project managers, division heads, chief financial officers and chief executive officers at corporations.
Leaders must be proficient in business administration skills, such as finance and human resource management, and be able to bring out the best in their employees. Leadership theories try to model the behavior of leaders under different circumstances. The situational and path-goal leadership theories suggest that workplace and employee characteristics affect leadership styles. Basics Both theories hold that employee motivation depends on leadership and that managers should adapt to their employees and workplaces. Facts: Situational Leadership Theory Situational leadership models are based on the work of University of Washington professor Fred Fiedler and leadership consultants Paul Hersey and Kenneth H.
Related Reading: Trait vs. Facts: Path-Goal Leadership Theory Use About the Author Have Feedback? Trait, Behavioural and Situational theories. The SMExcellence website is operated as an education project by the University of Western Sydney (UWS) as a free service.
This website is not intended to be an advisory service. The material contained on this website has been compiled from information and material provided or created by UWS students, UWS staff and also through contributions by supporters, government organisations and sponsors of SMExcellence. SMExcellence is not intended to take the place of professional advice and UWS advises that any person accessing the SMExcellence website will need to take appropriate professional advice for their particular circumstances. While UWS attempts to ensure accuracy and reliability of the information contained on the SMExcellence website , SMExcellence makes no guarantee, warranty or promise, express or implied, concerning the content or accuracy of documents or information appearing on this website.
Trait vs. Situational Approach for Leadership. Part of your responsibility as a small business owner is leadership.
Two options for leadership include the trait or situational approach. Each type of approach has a different focus. When choosing between the two, think about which approach would prove the most practical and helpful for you and your employees. Trait Leadership Trait leadership focuses on the leader and the traits he exhibits. Trait-Leadership Advantages The trait leadership approach embodies the idea that leaders are exceptional individuals who possess a combination of valuable traits.
Describe the Major Similarities & Differences Between the Trait & Behavior Leadership Theories. Leadership theories debate over what makes a good leader.
Over the years, many schools of thought have developed that give different explanations about where leaders come from, how they can be identified, and what causes an “executive” rather than a “servile” personality. Trait theory and behaviorism are two similar approaches to these questions. They both see leadership as an objective set of qualities or actions that must be mastered. They differ on who can develop these behaviors.