

Dehydration Synthesis Gizmo. WSCC Biology. Membrane Structure and Function. CHAPTER 3 PART 2. Copy of Biology Mind Map(cell membrane) by zaza zaza on Prezi. Ch. 5: The working cell. Biology 12 Late Afternoon - ricksclassportalsite. Cellular Pursuit Unit C Membrane Structure and Function Do Study Guide pages: 23-26 Unit D Ezymatics Read: Inquiry Into Life-10th Edition:Read pages 101 to 112 and pages 397 to 398.
Factors affecting Enzyme Action Temperature and pH: Do Study Guide pages: 30-33 Do Study Guide pages: 10-13 Unit E DNA and Functions Read: Inquiry Into Life-10th Edition: Read pages 501 to 522, 433, 568 to 569, 525 to 535. Cotransporters. Chapters Lodish 4th edition: Chapter 21 pages 921 - 924 Moyes and Schulte: Chapter 3 Before we discuss cotransporters we will take some time to explain the basis for the membrane potential in animal cells.
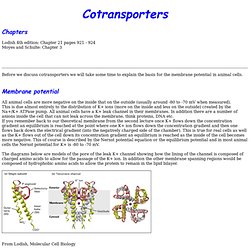
Membrane potential All animal cells are more negative on the inside that on the outside (usually around -80 to -70 mV when measured). This is due almost entirely to the distribution of K+ ions (more on the inside and less on the outside) created by the Na+/K+ ATPase pump. Epithelia. Chapters Lodish 4th edition: Chapter 21 pages 921 - 924 Moyes and Schulte: Chapter 3 and 11 Epithelia: stomach, intestine and kidney etc.

We are going to use a few examples of different epithelial to illustrate how ATPase pumps and transporters work together. Membrane Channels - Membrane Channels, Membrane Potential, Cell Membrane. Gleesonbiology / C3. Student Outcome: C3.1 Describe the structure and function of the cell membrane in terms of the fluid mosaic model.
Fluidity of the Plasma Membrane At body temperature, the phospholipid bilayer has consistency of olive oil.In each single part of the bi-layer, the phospholipid tails "wiggle", and entire phospholipid molecules can move sideways at a rate of about 2 µm — the length of a prokaryotic cell — per second.Phospholipid molecules rarely flip-flop from one layer to the other.Fluidity of the phospholipid bilayer allows cell membranes to be flexible.Some proteins are held in place by cytoskeletal filaments; most drift in fluid bilayer.
Animalcellbiology. Extracellular matrix (ECM) is the material found around cells and biochemically partly made by the cell.

It is composed of complex mixtures of proteins, proteoglycans, and, in the case of bone tissue, contains mineral deposits as well. Protein; almost all of the proteins found in the ECM are glycoproteins which include any of a group of complex compounds containing sugar units or polysaccharides combined with amino acid units or polypeptides. Some examples are collagen, laminin and fibronectin. Elastin is not a glycoprotein but is simply a protein and provides flexibility to skin arteries and bones.Proteoglycan; are partially similar to glycoproteins but are made up mostly of carbohydrate consisting of various polysaccharide side chains linked to a protein, and resemble polysaccharides rather than proteins in their properties. They usually have groups of carbohydrate chains attached to a protein backbone. Cell Membrane Transport. • What membranes do • Separate material: ICF / ECF • Allow exchange of material: ICF / ECF • Why transport is important • Obtaining O2 and nutrients • Getting rid of waste products • Selectively permeable • Permeable = to pass through.

Thebasisoflife.wikispaces. I.
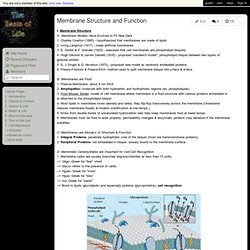
Membrane StructureA. Membrane Models Have Evolved to Fit New Data 1. Charles Overton (1895) - hypothesized that membranes are made of lipids 2. Irving Langmuir (1917) - made artificial membranes 3. 细胞生物学(双语) Chapter 5 The Movement of Substances Across Cell Membranes.

Active Transport. Review Guide: Osmosis and Diffusion. Original Document: Chapter Review; Diffusion and Osmosis What do you Know?

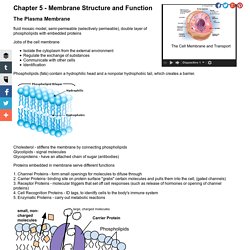
1. Label the three images below as isotonic/ hypertonic/ hypotonic (with regard to the solution the cell is placed in) Hypertonic ...........................Isotonic...........................hypotonic. GlycoWord - Glycoforum. Cell Membrane Structure and Function. The Plasma Membrane fluid mosaic model, semi-permeable (selectively permeable), double layer of phospholipids with embedded proteins.
Chapter 07 - Membrane Structure and Function. Membrane Structure and Function. Membranes are vital because they separate the cell from the outside world. They also separate compartments inside the cell to protect important processes and events. Cellular membranes have diverse functions in the different regions and organelles of a cell. However, at the electron microscopic level, they share a common structure following routine preparative steps. The above figure shows the typical "Unit" membrane which resembles a railroad track with two dense lines separated by a clear space. Membranes. The plasma membrane surrounds the cell and functions as an interface between the living interior of the cell and the nonliving exterior.All cells have one.It regulates the movement of molecules into and out of the cell. The fluid-mosaic model states that membranes are fluids with a mosaic of proteins embedded within the membrane. Phospholipids Most of the lipids in a membrane are phospholipids.Phospholipids contain glycerol, two fatty acids, and a phosphate group.
The phosphate group is polar (hydrophilic), enabling it to interact with water. The fatty acid tails are nonpolar (hydrophobic) and do not interact with water. MEMBRANES. This text is divided into seven major sections: Fat and Why it Matters. The carbon-hydrogen part of a fat is typically drawn like this: But this is somewhat messy. What if we just don’t draw the Hydrogen atoms, and just leave the bonds? We’d then have to remember the convention, that a – indicates a bond to an H, but it would be simpler. We get this: But this is a 2-dimensional representation that’s convenient to type. The Carbon atoms sort of zig-zag; they are not in an absolutely straight line. Using this simplified diagram, it becomes much easier to describe the differences between saturated and unsaturated fats. Biology Animations.
Introduction to Lipids. A Cellular World. Cell Membrane Function. Both eukaryotic cells, including plant cells and animal cells, and prokaryotic cells, e.g. bacteria, are enclosed by a cell membrane. Learn Science at Scitable. Figure 1: The phosphorylation of a protein can make it active or inactive. Phosphorylation can either activate a protein (orange) or inactivate it (green). Kinase is an enzyme that phosphorylates proteins. What is “Protein#Synthesis” ? - LifeSun. Proteins are large biological molecules consisting of one or more chains of amino acids. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, replicating DNA, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in folding of the protein into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.