

CAELinux. List of free electronics circuit simulators. Problems donating?
| Other ways to give | Frequently asked questions | By donating, you are agreeing to our donor privacy policy. The Wikimedia Foundation is a nonprofit, tax-exempt organization.By donating, you are agreeing to our donor privacy policy and to sharing your information with the Wikimedia Foundation and its service providers in the U.S. and elsewhere. The Wikimedia Foundation is a nonprofit, tax-exempt organization.By donating, you are agreeing to our donor privacy policy and to sharing your information with the Wikimedia Foundation and its service providers in the U.S. and elsewhere.
*Recurring payments will be debited by the Wikimedia Foundation until you notify us to stop. We'll send you an email receipt for each payment, which will include a link to easy cancellation instructions. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Qucs project: Quite Universal Circuit Simulator. PSpice. PSpice is a SPICE analog circuit and digital logic simulation program for Microsoft Windows.
The name is an acronym for Personal SPICE - SPICE itself being an acronym for Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit Emphasis. History[edit] PSpice was initially developed by MicroSim and is used in electronic design automation. The company was bought by OrCAD, which was subsequently purchased by Cadence Design Systems. PSpice was the first version of UC Berkeley SPICE available on a PC, having been released in January 1984 to run on the original IBM PC.
Version 3.06 was released in 1988, also came on two 5.25 floppy discs, and had a "Student Version" available which would allow a maximum of up to ten transistors to be inserted. Features[edit] During its development, PSpice has evolved into an analog mixed signal simulator. Introduction[edit] SPICE was first developed in the University of California, Berkeley, USA in early 1970s. gEDA. Gschem and gerbv showing a simple connector design under creation using components from the gEDA Suite.
Screenshot showing the layout editor PCB in action. The term gEDA refers to two things: A set of software applications (CAD tools) used for electronic design released under the GPL. As such, gEDA is an ECAD (electronic CAD) or EDA (electronic design automation) application suite. gEDA is mostly oriented towards printed circuit board design (as opposed to integrated circuit design). The gEDA applications are often referred to collectively as "the gEDA Suite".The collaborative of free software/open-source developers who work to develop and maintain the gEDA toolkit. The word "gEDA" is a conjunction of "GPL" and "EDA". History[edit] Originally, the project planned to also write a PCB layout program. Other open-source EDA programs were created at about the same time. Detailed Description[edit] Platforms[edit] Gnucap:start [] Quite Universal Circuit Simulator. Quite Universal Circuit Simulator (Qucs) is an open source electronics circuit simulator software released under GPL.
It gives you the ability to set up a circuit with a graphical user interface and simulate the large-signal, small-signal and noise behaviour of the circuit. Pure digital simulations are also supported using VHDL and/or Verilog. Qucs supports a growing list of analog and digital components as well as SPICE sub-circuits. It is intended to be much simpler to use and handle than other circuit simulators like gEDA or PSPICE. Analysis types[edit] Analysis types include S-parameter (including noise), AC (including noise), DC, Transient Analysis, Harmonic Balance (not yet finished), Digital simulation (VHDL and Verilog-HDL) and Parameter sweeps. Features at a glance[edit] QUCS has a graphical interface for schematic capture.
The documentation offers many useful tutorials (WorkBook), reports (ReportBook) and a technical description of the simulator. Free Registration. GNU Project. The GNU logo, by Etienne Suvasa The GNU Project i/ɡnuː/[1] is a free software, mass collaboration project, announced on 27 September 1983, by Richard Stallman at MIT.
Its aim is to give computer users freedom and control in their use of their computers and computing devices, by collaboratively developing and providing software that is based on the following freedom rights: users are free to run the software, share it (copy, distribute), study it and modify it. GNU software guarantees these freedom-rights legally (via its license), and is therefore free software; the use of the word "free" always being taken to refer to freedom.
In order to ensure that the entire software of a computer grants its users all freedom rights (use, share, study, modify), even the most fundamental and important part, the operating system (including all its numerous utility programs), needed to be written. Circuit Simulator Applet. This is an electronic circuit simulator.
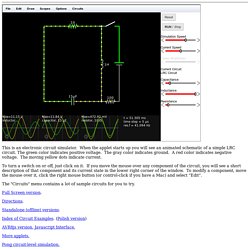
When the applet starts up you will see an animated schematic of a simple LRC circuit. The green color indicates positive voltage. The gray color indicates ground. A red color indicates negative voltage. The moving yellow dots indicate current. To turn a switch on or off, just click on it. The "Circuits" menu contains a lot of sample circuits for you to try.
Ngspice - Browse /ng-spice-rework at SourceForge.net.