

Flexor carpi ulnaris muscle. The flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) muscle is a muscle of the human forearm that acts to flex and adduct the hand.
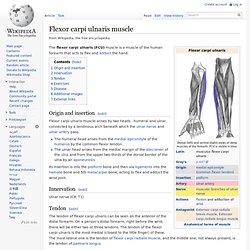
Origin and insertion[edit] Flexor carpi ulnaris muscle arises by two heads - humeral and ulnar, connected by a tendinous arch beneath which the ulnar nerve and ulnar artery pass. The humeral head arises from the medial epicondyle of the humerus by the common flexor tendon.The ulnar head arises from the medial margin of the olecranon of the ulna and from the upper two-thirds of the dorsal border of the ulna by an aponeurosis. Its insertion is into the pisiform bone and then via ligaments into the hamate bone and 5th metacarpal bone, acting to flex and adduct the wrist joint.
Innervation[edit] Ulnar nerve (C8, T1) Flexor Carpi Ulnaris. Palmaris longus muscle. The palmaris longus is seen as a small tendon between the flexor carpi radialis and the flexor carpi ulnaris, although it is not always present.
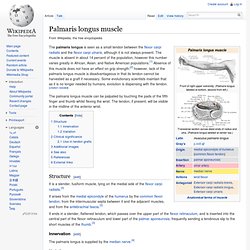
The muscle is absent in about 14 percent of the population, however this number varies greatly in African, Asian, and Native American populations.[1] Absence of this muscle does not have an effect on grip strength;[2] however, lack of the palmaris longus muscle is disadvantageous in that its tendon cannot be harvested as a graft if necessary. Some evolutionary scientists maintain that as it is no longer needed by humans, evolution is dispensing with the tendon. [citation needed] Palmaris Longus. Hypothenar eminence. The hypothenar muscles are a group of three muscles of the palm that control the motion of the little finger.
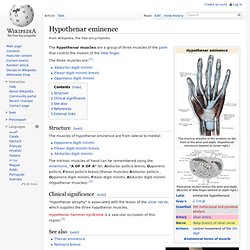
Carpal tunnel and thenar and hypothenar eminences The three muscles are:[1] Structure[edit] The muscles of hypothenar eminence are from lateral to medial: The intrinsic muscles of hand can be remembered using the mnemonic, "A OF A OF A" for, Abductor pollicis brevis, Opponens pollicis, Flexor pollicis brevis,(thenar muscles) Adductor pollicis , Opponens digiti minimi, Flexor digiti minimi, Abductor digiti minimi (Hypothenar muscles). [2] Clinical significance[edit]
Hypothenar eminence. Thenar eminence. The thenar eminence (from the Greek "θέναρ" - thenar, "palm of the hand"[1] and the Latin word "eminentia", meaning projection,[2]) refers to the group of muscles on the palm of the human hand at the base of the thumb.
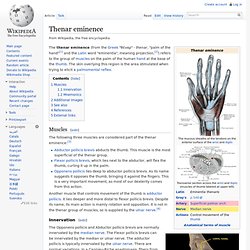
The skin overlying this region is the area stimulated when trying to elicit a palmomental reflex. Muscles[edit] The following three muscles are considered part of the thenar eminence:[3] Carpal tunnel and tenar and hypothenar eminences. Thenar Eminence. Extensor carpi ulnaris muscle. In human anatomy, the extensor carpi ulnaris is a skeletal muscle located on the ulnar side of the forearm.
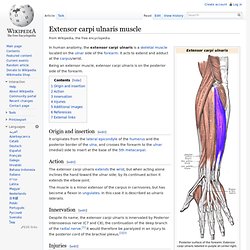
It acts to extend and adduct at the carpus/wrist. Being an extensor muscle, extensor carpi ulnaris is on the posterior side of the forearm. Origin and insertion[edit] Extesor Carpi Ulnaris. Extensor carpi radialis longus muscle. Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle. In human anatomy, extensor carpi radialis brevis is a muscle in the forearm that acts to extend and abduct the wrist.
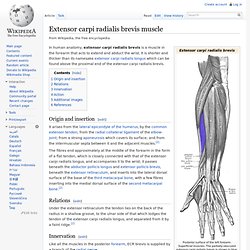
It is shorter and thicker than its namesake extensor carpi radialis longus which can be found above the proximal end of the extensor carpi radialis brevis. Origin and insertion[edit] Extensor Carpi Radialis. Flexor digitorum superficialis muscle. Flexor digitorum superficialis (flexor digitorum sublimis) is an extrinsic flexor muscle of the fingers at the proximal interphalangeal joints.
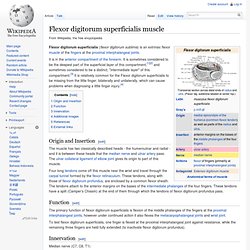
It is in the anterior compartment of the forearm. It is sometimes considered to be the deepest part of the superficial layer of this compartment,[1][2] and sometimes considered to be a distinct, "intermediate layer" of this compartment.[3] It is relatively common for the Flexor digitorum superficialis to be missing from the little finger, bilaterally and unilaterally, which can cause problems when diagnosing a little finger injury.[4] Flexor digitorum superficialis. Flexor digitorum profundus muscle. In human anatomy, the flexor digitorum profundus (FDP, Latin for "deep bender of the fingers") is a muscle in the forearm that flexes the fingers (also known as digits).
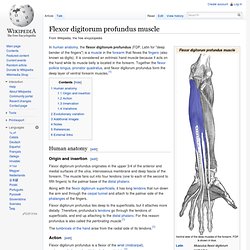
It is considered an extrinsic hand muscle because it acts on the hand while its muscle belly is located in the forearm. Flexor digitorum profundus. Flexor carpi radialis muscle. Flexor Carpi Radialis.