

Phonological Awareness. Phonological awareness. Phonological awareness (PDF, 54 KB) Before they can start to work with print, learners need to be able to hear the sounds in spoken words.
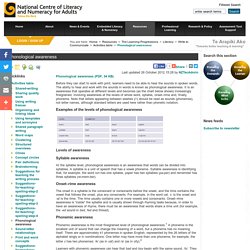
The ability to hear and work with the sounds in words is known as phonological awareness. It is an awareness that operates at different levels and becomes (as the chart below shows) increasingly finegrained, involving awareness at the levels of whole word, syllable, onset–rime and, finally, phoneme. Note that letters appearing between slashes (//) should be read as sounds (phonemes), not letter names, although standard letters are used here rather than phonetic notation. What is Phonological Awareness? - Clever Classroom Blog. This post includes the following reading points.
Hey-ho! I just love all things literacy and specifically working with words. I want to delve deeper into phonological development, because.. well.. I just love it! I’m a bit of a nerd that way! You know that phonological and phonemic awareness skills are important and also necessary to understand as a Pre-K-2 teacher. It is vital that you know and understand what phonological and phonemic awareness is, as it is the foundation for reading success. According to Calfee, Lindamood & Lindamood, 1973: Children’s ability to attend to, and manipulate phonemes strongly correlate with their reading success through to the end of their schooling.
It can be tricky to wrap your head around. Lap it all up in one neat blog post that can also be downloaded fo’ free you all! Phonological Awareness » The Learning Staircase. There is considerable research from all over the world into the importance of different aspects of phonological awareness.

Phonological awareness is often a major weakness in learners with dyslexia or similar processing difficulties. Background information Phonological awareness is often referred to as phonemic awareness, but there is a crucial difference between these terms. The term ‘phonemic awareness’ comes from the word ‘phoneme’, which is a single sound in language. This includes the following individual skills: Identification of initial, final and medial sounds in wordSegmentation (breaking words into individual sounds)Blending (blending individual sounds to make words)Phoneme transposition (ability to ‘swap’ sounds) The term ‘phonological awareness’ comes from the word ‘phonology’, which is the sounds and sound patterns of language.
All of the above aspects of phonemic awareness PLUS Onset + rimeRhymeSyllabificationWord RetrievalAuditory discrimination. Phonological Awareness » The Learning Staircase. There is considerable research from all over the world into the importance of different aspects of phonological awareness.
Phonological Awareness. Phonological and Phonemic Awareness – What is it?

I can hardly even say it – let alone know what it means LOL!!!! If your brain works a little like mine (in ‘mysterious’ ways !!!!) , I hope the following explanation helps… Thanks to Sue for clarification of the following terms….. * Phonological Awareness – is a broad concept that not only includes phonemic awareness (see below) but also encompasses awareness of things like words, rhyme, syllables and onset and rime. * Phonemic Awareness – is the ability to hear, say and manipulate sounds in words and is a sub-skill of phonological awareness. * Phonics – involves making the connection between the single sounds (phonemes) and their related letter patterns (graphemes) when reading and writing Stages More Terms Charts. ENGLISH PHONOLOGICAL AWARENESS & BILINGUAL EDUCATION. Lots of EFL students in public schools in Indonesia have problems in English pronunciation.

It has become a major learning problem for English as Foreign Language (EFL) Learners in Indonesia. I cannot really blame them because there is not enough exposure to the sound systems of the language. The learners are not aware of the speech sounds of English (English phonology). Thus, they have difficulty in the four language skills i.e., (a) listening, (b) speaking, (c) reading, and (d) writing.
(a) Listening In order to produce a language, we need to hear the speech and understand it before producing it. Surely, a good listener would have enough information to produce a well-spoken language. (b) Speaking EFL learners must understand English pronunciation in order to be able to transfer a concept into a spoken language where sounds delivered are recognizable by the listener. (c) Reading Reading involves understanding the speech sounds of written symbols.