

Industrial Closures in Delhi. Aditya Nigam November 2000 replayed on a larger scale, what November 1996 had initiated.

(See report in Revolutionary Democracy, April 1997). If the first spate of industrial closures in 1996 had targeted 168 ‘hazardous’ industries in the capital for relocation, this time round the figure was completely vague and could have varied from anywhere between 30, 000 to 90, 000 units. If the closures of 1996 followed the Supreme Court orders of 8 July that year, this time too the immediate impetus came from this highest institution of the country that is meant to ensure justice at large.
Neither then nor now did the Court consider the workers as interested parties whose opinions needed to be taken into account. Delhi to decommission four power plants. Delhi to decommission four power plants. IP Power Plant to Vikas Bhavan redev. Minutes%20of%20meeting%20for%20IP%20Estate%20website. Re- Development of Vikas Bhawan, I.P. Power Station and DTC Head Quarters and Bus Depot at IP Estate. IP power plant in disuse will be an art gallery. CM inaugurates new govt office in Civil Lines. NGOs unite against thermal plants. Yamuna Action Plan.
Okhla sewage plant kicks off. Wiki: YAP. WHITE PAPER ON DELHI POLLUTION. CHAPTER 1 : Introduction CHAPTER 2 : Air Pollution CHAPTER 3 : Vehicular Pollution CHAPTER 4 : Water Pollution CHAPTER 5 : Solid Waste Management CHAPTER 6 : Industrial Pollution.

SIDBI green_financing. Eco City Project. The urban areas of the country are facing problems of deterioration of environmental and socio-economic conditions.
The major concerns are unplanned and haphazard development, poor sanitary and living conditions, urbanization and associated problems including slums, poor/inadequate infrastructure and pollution problems. While there are several causes for urban degradation such as population migration, environmental considerations not adequately being incorporated into plans (Master Plans), uncoordinated and haphazard development, weak implementation of plans and laws and inadequate institutional competences, one of the major concerns is resource crunch. The Government (municipality, local bodies etc.) is not generally having adequate funds to deal with the needed infrastructure facilities, significantly since they do not have mechanisms for recovery of investments and to make the services or infrastructure provided sustainable.
Eco-cities for India. In this article, an ecological planner shares his perspective on the relevance of the concept of eco-cities in India, the eco-cities being planned and the challenges that need to be addressed.
Cities are both engines for growth and sources of concentrated environmental problems. With urbanization and economic growth, opportunities are more in the cities than in rural areas, thus encouraging immigration from rural areas to urban areas. Urbanization is increasing in many of the developing nations today and about 50 percent of the world’s population lives in urban areas and about 90 percent of global urban growth now takes place in developing countries.
Between the years 2000 and 2030, developing countries are projected to triple their entire built-up urban areas. This unprecedented urban expansion also means that cities, nations and the international development community face many challenges and opportunities. Eco-cities Eco city aims at: Eco-city initiatives in China and India. Kitakyushu to Manesar. Manesar may soon be home to India’s first eco-city, a place where people live in an environment-friendly way.
A team from Toshiba that studied this initiative submitted its pre-feasibility report to Rajeev Arora, managing director, Haryana State Industrial and Infrastructure Develop-ment Corporation (HSIIDC). The eco-city project was first proposed when the Prime Minister visited Japan as a part of the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor idea. A memorandum of understanding (MoU) was signed between the two countries, and subsequently, Maharashtra, Gujarat and Haryana were identified as the sites for the project. An MoU was also signed between HSIIDC, DMICDC and a consortium of Japanese firms led by Toshiba. These include NEC, Tokyo Gas and Energy Advanced Companies Ltd. Arora said the feasibility report will now be analysed in detail by HSIIDC. He said the feasibility study covered aspects such as water, water recycling, power, logistics, solid waste management and transport. Surat to be India's first 'Eco City'
Bhopal disaster. The Bhopal disaster, also referred to as the Bhopal gas tragedy, was a gas leak incident in India, considered the world's worst industrial disaster.[1] It occurred on the night of 2–3 December 1984 at the Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL) pesticide plant in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh.
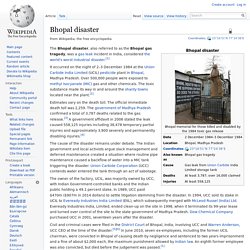
Over 500,000 people were exposed to methyl isocyanate (MIC) gas and other chemicals. The toxic substance made its way in and around the shanty towns located near the plant.[2] Estimates vary on the death toll. The official immediate death toll was 2,259. SGS India - Brownfield Analysis - Environment. Brownfields – unused and abandoned sites – are scars on the landscape and often the legacy of our industrial past.
They are the result of heavy industrial activity that did not pay as much attention to environmental concerns as we do today. If managed efficiently and professionally, these brownfield sites have great potential in land recycling programmes. Sites can be redeveloped and redeployed for the good of whole communities. Our brownfield management services help you to examine your disused site. Rail Land Development Authority. Indian Railways turning green. The Railway Budget is out and we thought it might be a good idea to discuss it from a green point of view.

While we have seen a lot of opinion on the budget and perhaps more on the political ramifications and in what will be a first- the party in power opposing its own budget. So to provide an entirely different view point, let us see how green the railway budget is. Some of the Green Initiatives of the railway budget are- Setting up of 72 MW capacity windmill plants in Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and West Bengal.Setting up of 200 remote railway stations as ‘green energy stations’ powered entirely by solar energy. The railways have immense potential for use of solar energy. Railways plans to turn a green leaf through renewable energy. Updated: Thu, Mar 15 2012. 12 42 AM IST New Delhi: In an attempt to become environment-friendly, the Indian Railways plans to set up renewable energy generation capacities—such as wind power, solar energy and bio-diesel plants—for its own use, railway minister Dinesh Trivedi said in his budget speech on Wednesday.
Clean-up: A file photo of a worker cleaning railway tracks. Rail corrosion due to human waste costs the railways more than Rs350 crore every year, the railway minister said. The renewable energy plans of the railways include setting up 72 megawatts (MW) wind power plants in Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and West Bengal. This will also help the carrier avail fiscal incentives, including tax breaks for 10 years and depreciation benefits, besides a chance to earn carbon credits.
“The rail corrosion costs railways more than Rs350 crore every year.