

Geothermal Oil Wells. From PESWiki Geothermal power in hot water coming up from abandoned oil wells using "hot dry rock" heat mining via artificial geo-thermal reservoirs.[1] High costs associated with drilling have made many geothermal projects uneconomical.
However, much of that work may already be done. There are over one million abandoned oil and gas wells around the world. Many contain hot water that can be used to generate electricity or hydraulic power. Companies Deluge, Inc. - The Natural Energy Engine™ is a revolutionary new engine powered solely by hot water, well below the boiling point.
Geothermal Energy Improves U.S. Oil spill. Oil spills penetrate into the structure of the plumage of birds and the fur of mammals, reducing its insulating ability, and making them more vulnerable to temperature fluctuations and much less buoyant in the water.
Cleanup and recovery from an oil spill is difficult and depends upon many factors, including the type of oil spilled, the temperature of the water (affecting evaporation and biodegradation), and the types of shorelines and beaches involved.[1] Spills may take weeks, months or even years to clean up.[2] Oil spills can have disastruous consequences for society; both economically, environmentally, and socially. As a result of these consequences oil spill accidents can initiate intense media attention and political uproar.
YouTube. (1) Oil spill & Gas emissions. Concession Map - Egypt Oil & Gas. Gemsa, Egypt - Area - Oilfield. Abandoned Wells in Egypt. "البترول" تؤكد توقف التسرب البترولى بـ"الجمشة" نهائياً أكدت اللجنة المشكلة من الأجهزة المعنية بمكافحة التلوث بالشركة العامة ووزارة البترول، بالتعاون مع شئون جهاز البيئة ومحميات البحر الأحمر، التوقف النهائى للتسرب البترولى، بعد عدة أسابيع من تدفق البترول بالجمشة وإحداث تلوث بيئى على مساحة ستة آلاف متر داخل مياه البحر.
صرح المهندس وحيد سلامة، رئيس قطاع محميات البحر الأحمر، بأن التسرب البترولى توقف نهائياً بمنطقة خليج الجمشة، ولم يظهر أى تدفق جديد، وأن المؤشر يدل على أن الوضع استقر فى منطقة الآبار، وأن باقى التلوث فى مياه البحر قد تم محاصرتها بشفط السيارات والحواجز المطاطية وقش الأرز. 27,000 abandoned oil and gas wells in the Gulf of Mexico. Photo Source: AP Photo/California State Lands Commission.Nearshore wellhead excavated.In this undated photo released by the California State Lands Commission, a nearshore wellhead is excavated off California.
In state waters, California has resealed scores of its abandoned wells since the 1980s, but in federal waters, the official policy is out-of-sight, out-of-mind. Neither industry nor government checks for leaks at the more than 27,000 oil and gas wells abandoned in the Gulf of Mexico since the late 1940s. Abandoned wells are known sometimes to fail both on land and offshore. It happens so often that a technical term has been coined for the repair job: ‘re-abandonment.’ By Jeff Donn and Mitch Weiss, Associated Press. The calls for action follow an Associated Press investigation that found federal regulators do not typically inspect plugging of these offshore wells or monitor for leaks afterward. In its investigation, the AP found a series of warnings. Sen. Original Article. Geothermal electricity. Geothermal electricity is electricity generated from geothermal energy.
Technologies in use include dry steam power plants, flash steam power plants and binary cycle power plants. Geothermal power in the United Kingdom. The potential for exploiting geothermal energy in the United Kingdom on a commercial basis was initially examined by the Department of Energy in the wake of the 1973 oil crisis.
Several regions of the country were identified, but interest in developing them was lost as petroleum prices fell. Although the UK is not actively volcanic,[1] a large heat resource is potentially available via shallow geothermal ground source heat pumps, shallow aquifers and deep saline aquifers in the mesozoic basins of the UK.[2] Geothermal energy is plentiful beneath the UK, although it is not readily accessible currently except in specific locations.[3] Southampton District Energy Scheme History[edit] The potential for exploiting geothermal energy in the United Kingdom on a commercial basis was initially examined by the Department of Energy in the wake of the 1973 oil crisis.
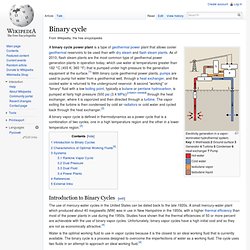
Binary cycle. Electricity generation in a vapor-dominated hydrothermal system.Key:1 Wellheads 2 Ground surface 3 Generator 4 Turbine 5 Condenser 6 Heat exchanger 7 Pump Hot water.
Geothermal energy. From hot springs, geothermal energy has been used for bathing since Paleolithic times and for space heating since ancient Roman times, but it is now better known for electricity generation.
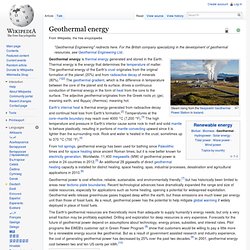
Worldwide, 11,400 megawatts (MW) of geothermal power is online in 24 countries in 2012.[5] An additional 28 gigawatts of direct geothermal heating capacity is installed for district heating, space heating, spas, industrial processes, desalination and agricultural applications in 2010.[6] Geothermal power is cost effective, reliable, sustainable, and environmentally friendly,[7] but has historically been limited to areas near tectonic plate boundaries. Recent technological advances have dramatically expanded the range and size of viable resources, especially for applications such as home heating, opening a potential for widespread exploitation. Geothermal wells release greenhouse gases trapped deep within the earth, but these emissions are much lower per energy unit than those of fossil fuels.
History. Enhanced geothermal system. Enhanced geothermal system 1 Reservoir 2 Pump house 3 Heat exchanger 4 Turbine hall 5 Production well 6 Injection well 7 Hot water to district heating 8 Porous sediments 9 Observation well 10 Crystalline bedrock Water travels through fractures in the rock, capturing the rock's heat until forced out of a second borehole as very hot water.
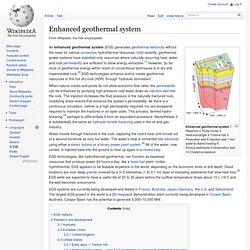
The water's heat is converted into electricity using either a steam turbine or a binary power plant system.[4] All of the water, now cooled, is injected back into the ground to heat up again in a closed loop. EGS technologies, like hydrothermal geothermal, can function as baseload resources that produce power 24 hours a day, like a fossil fuel plant. Unlike hydrothermal, EGS appears to be feasible anywhere in the world, depending on the economic limits of drill depth. EGS systems are currently being developed and tested in France, Australia, Japan, Germany, the U.S. and Switzerland.