

Insulation Materials. Insulation materials run the gamut from bulky fiber materials such as fiberglass, rock and slag wool, cellulose, and natural fibers to rigid foam boards to sleek foils.
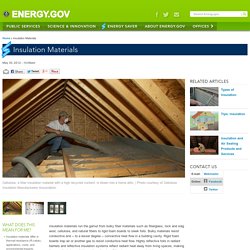
Bulky materials resist conductive and -- to a lesser degree -- convective heat flow in a building cavity. Rigid foam boards trap air or another gas to resist conductive heat flow. Highly reflective foils in radiant barriers and reflective insulation systems reflect radiant heat away from living spaces, making them particularly useful in cooling climates. Other less common materials such as cementitious and phenolic foams and vermiculite and perlite are also available. Fiberglass Fiberglass (or fiber glass) -- which consists of extremely fine glass fibers -- is one of the most ubiquitous insulation materials. Manufacturers now produce medium- and high-density fiberglass batt insulation products that have slightly higher R-values than the standard batts. Mineral Wool Insulation Materials Cellulose Insulation Material Cotton.
009. 041. 80. A study on residential heating energy requirement and optimum insulation thickness. O.
Kaynakli, Mechanical Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering and Architecture, University of Uludag, TR-16059 Bursa, Turkey Received 6 April 2007, Accepted 5 July 2007, Available online 22 August 2007 Choose an option to locate/access this article: Check if you have access through your login credentials or your institution Check access doi:10.1016/j.renene.2007.07.001 Get rights and content Abstract Heat loss from buildings has a considerable share in waste of energy especially in Turkey since no or little insulation is used in existing and new buildings. Keywords Heating energy requirements; Degree hour; Optimum insulation thickness Copyright © 2007 Elsevier Ltd. Toxicologic and acute lethal hazard evaluation of thermal decomposition products of synthetic and natural polymers. Department of Industrial Environmental Health Sciences, Graduate School of Public Health, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 15261 USA Received 11 May 1979, Accepted 9 August 1979, Available online 27 September 2004 Choose an option to locate/access this article: Check if you have access through your login credentials or your institution Check access Get rights and content Thermal decomposition products from a series of cellular synthetic polymers and several other polymers, synthetic or natural, were investigated.

Historical Cohort Mortality Study of a Continuous Filament F... : Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine. An historical cohort mortality study of a continuous filament fiberglass manufacturing plant was undertaken to determine whether an elevated lung cancer risk would be observed on a cohort basis.

A nested case-control study of white male lung cancer deaths was incorporated into the study design. An interview survey to obtain information on sociodemographic factors, including smoking, and an historical environmental reconstruction to identify elements in the plant environment to which workers might be exposed were included in the study design. Respirable glass (Beta™) fibers were produced only from 1963 to 1968. The lung cancer odds ratio (OR) among those workers exposed to respirable glass fibers is below unity, as are ORs for exposure to asbestos, refractory ceramic fibers, respirable silica (except for the lowest exposure level), total chrome and arsenic. Quantitative Risk Assessment for a Glass Fiber Insulation Product. Regular Article Owens Corning, One Owens Corning Parkway, Toledo, Ohio, 43659 Received 29 January 1997, Available online 15 April 2002 Choose an option to locate/access this article: Check if you have access through your login credentials or your institution Check access doi:10.1006/rtph.1997.1087.

Hierarchical Cluster Analysis Applied to Workers Exposures in Fiberglass Insulation Manufacturing. + Author Affiliations Jyun-de Wu.

Author to whom correspondence should be addressed: Tel.: +1 530 754-8164; E-mail: jdwu@epm.ucdavis.edu The objectives of this study were to explore the application of cluster analysis to the characterization of multiple exposures in industrial hygiene practice and to compare exposure groupings based on the result from cluster analysis with that based on non-measurement-based approaches commonly used in epidemiology.
Cluster analysis was performed for 37 workers simultaneously exposed to three agents (endotoxin, phenolic compounds and formaldehyde) in fiberglass insulation manufacturing. Different clustering algorithms, including complete-linkage (or farthest-neighbor), single-linkage (or nearest-neighbor), group-average and model-based clustering approaches, were used to construct the tree structures from which clusters can be formed. Glass fibre, cluster analysis, exposure groups, occupational groups, epidemiology.
An Error Occurred Setting Your User Cookie. An Error Occurred Setting Your User Cookie. Fungal production of volatiles during growth on fiberglass. Fungal colonization of fiberglass insulation in the air distribution system of a multi-story office building: VOC production and possible relationship to a sick building syndrome. Colonization of fiberglass insulation used in heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems. Effect of relative humidity on fungal colonization of fiberglass insulation.