

Watch The Earth Open And Close During Japan’s 2011 Earthquake. Over 18,000 people were killed by a magnitude 9.0 earthquake and subsequent tsunami that struck Northeastern Japan on March 11, 2011.
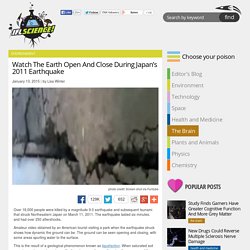
The earthquake lasted six minutes, and had over 250 aftershocks. Amateur video obtained by an American tourist visiting a park when the earthquake struck shows how dynamic the ground can be. Why Can't We Predict Earthquakes. Earthquakes: The Prehistoric Record. Www.glencoe.com/sites/common_assets/science/virtual_labs/E27/E27.html. Seismic Education Site: UPSeis. UPSeis (pronounced "up size") is a program created to teach young people (and not-so-young people) more about the planet we live on and how it works.

The UPSeis program is divided into two parts: this web site and a school program. In the UPSeis web site, we'll be talking mostly about the science of seismology and earthquakes: where they happen, why they happen, and what kinds of problems they cause. We'll tell you things you may already know and some stuff you may have never thought about. GEOL212 - Planetary Geology. Seismology Deformation of solids: Stress: A mechanical force applied to a solid Strain: The resulting change in the solid's shape Objects can be strained in three different ways: Elastic deformation: Generally, when a solid is strained, it will return to its original shape when the stress is removed.

This is because its chemical bonds, although stretched, have not broken. E.G. stretch a piece of nylon and its shape changes as chemical bonds are stretched, storing energy, but when you stop pulling, the energy is released in the form of the work needed to restore the solid to its original shape. Folded quartz veins and foliation. Deformation in the planets: In a planet's uppermost layers, rock (or ice) primarily deforms elastically or brittlely. April 2014. Earthquakes are the breaking and cracking of the rocks inside the continental plates.
The breaks happen after stress has built up in the surrounding area. There are usually very few or no quakes when the plates move slowly. When there is a fast movement of the plate, there is a snap (like breaking a cracker). BASIC EARTHQUAKE FACTS #1 (study jams)Earthquakes occur when vast plates, or rocks, within the Earth suddenly break or shift under stress, sending shock waves rippling. How Seismic Waves Tell Us About Earth’s Core. Seismic waves. Seismic Waves. Www.cde.ca.gov/ta/tg/sr/documents/cstrtqscience10.pdf. Www.tryengineering.org/lessons/seismograph.pdf. Academics.concord.edu/sckuehn/VirtualEarthquake.pdf. Seismic Monitor.
Www.geology.sdsu.edu/visualgeology/naturaldisasters/Chapters/Chapter6Earthquake.pdf. Electronic Desktop Project - Virtual Earthquake. Why Do Earthquakes Happen? Earthquakes are usually caused when rock underground suddenly breaks along a fault.

This sudden release of energy causes the seismic waves that make the ground shake. When two blocks of rock or two plates are rubbing against each other, they stick a little. They don't just slide smoothly; the rocks catch on each other. The rocks are still pushing against each other, but not moving. After a while, the rocks break because of all the pressure that's built up. Earthquake-like seismic waves can also be caused by explosions underground.
Www.glencoe.com/sites/common_assets/science/virtual_labs/ES09/ES09.html. How a Seismograph Works. Earthquakes: The Seismograph. Earth's tectonic plates are in constant motion and, because the plates are not all moving in the same direction, the boundaries where they meet are often violent places.
Boundaries where two plates move away from each other, usually found on the ocean floor, give rise to spectacular undersea volcanoes. In places where plates collide, huge slabs of crust buckle to create mountains, or one slides above and the other below to trigger violent volcanic eruptions on Earth's surface. Along other boundaries, plates slide haltingly past each other, causing earthquakes as they bind and then suddenly break loose.
Moving tectonic plates produce unfathomable force. Earthquakes - Interactive Science Illustration. Www.instructorscorner.org/media/resources/schools/Masters/EDU_Earthquakes/6-8 Dynamic Earth.pdf. Www.tryengineering.org/lessons/seismograph.pdf. Coloring Pages. Seismograph.gif (612×792) Seismic Waves. Seismic Waves Prof.

Lawrence braile@purdue.edu (March, 2006) Seismic Waves: Because of the elastic properties of Earth materials (rocks) and the presence of the Earth's surface, four main types of seismic waves propagate within the Earth. Slinky Demonstrations of P and S Waves: The P and S waves have distinctive particle motions (Figures 1-4) and travel at different speeds. Demonstrating the S or Shear wave is performed in a similar fashion except that the person who creates the shear disturbance does so by moving his or her hand quickly up and then down. P and S waves can also be generated in the slinky by an additional method that reinforces the concept of elasticity and the elastic rebound theory which explains the generation of earthquakes by plate tectonic movements (Bolt, 1993, p. 74-77; 2004, p. 113-116). Figure 5. Surface Waves: The Love wave (Figure 4) is easy to demonstrate with a slinky or a double length slinky.
What are the layers of the earth? Three hundred years ago the famous scientist Isaac Newton calculated, from his studies of planets and the force of gravity, that the average density of the Earth is twice that of surface rocks and therefore that the Earth's interior must be composed of much denser material.

We now know that the earth is made up of 4 layers: How do we know about the different layers of the earth? Information today comes from studies of the paths and characteristics of seismic waves from earthquake waves traveling through the Earth, as well as from laboratory experiments on surface minerals and rocks at high pressure and temperature and studies of the Earth's motions in the Solar System, its gravity and magnetic fields, and the flow of heat from inside the Earth. About Seismic Waves What are the different types of Seismic Waves? Seismic waves are waves of energy that travel through the earth, for example as a result of an earthquake, explosion, or some other process that imparts low-frequency acoustic energy. Education - Multimedia Discovery Missions.
Earthquakes and Plates Mankind has long dreamed of a way to predict earthquakes and escape their terrible power.

Scientists and amateurs alike have tried to link quakes to phenomena as diverse as animal behavior, tides, weather, the movements of the planets, the rise and fall of water in wells, even to psychic visions. Unfortunately, none of these factors can be linked consistently enough with earthquakes to provide a useful forecasting tool.
For now, the most reliable clues to future quakes are the patterns of past earth movements. These allow geologists to suggest where earthquakes are most likely to strike. Www.iris.edu/hq/files/programs/education_and_outreach/aotm/8/Seismograph_Background.pdf. What Is Seismology and What Are Seismic Waves? Seismology is the study of earthquakes and seismic waves that move through and around the earth.

A seismologist is a scientist who studies earthquakes and seismic waves. Seismic waves are the waves of energy caused by the sudden breaking of rock within the earth or an explosion. They are the energy that travels through the earth and is recorded on seismographs. Seismic Tomography. Earthquakes. Earthquakes Introduction An earthquake is a shaking motion of a portion of the earth's crust. this motion results from the passage of elastic waves traveling through the earth away from a place of rupture or faulting. The location of the rupture or faulting, which may be within or below the earth's crust, is called the focus . The point on the earth's surface directly above the focus is called the epicenter . Earthquake foci can occur down to a depth of 435 miles, although 85% of them occur near the surface (less than 40 mile depth). Traveltime_background. How%20To%20Use%20Quake%20Chart. Earthquakes Waves and Epicenter Location. US Earthquake Information by State/Territory.