

18 commands to monitor network bandwidth on Linux server. Network monitoring on Linux This post mentions some linux command line tools that can be used to monitor the network usage.
These tools monitor the traffic flowing through network interfaces and measure the speed at which data is currently being transferred. Incoming and outgoing traffic is shown separately. Some of the commands, show the bandwidth used by individual processes. This makes it easy to detect a process that is overusing network bandwidth. The tools have different mechanisms of generating the traffic report. Here is a list of the commands, sorted by their features. 1. 1. Nload is a commandline tool that allows users to monitor the incoming and outgoing traffic separately. So if you just need to take a quick look at the total bandwidth usage without details of individual processes, then nload will be handy. $ nload Installing Nload - Fedora and Ubuntu have got it in the default repos. . # fedora or centos $ yum install nload -y # ubuntu/debian $ sudo apt-get install nload 2. iftop. Créer et Installer un certificat SSL sous NGinx. Install and Config Fail2Ban in Debian 7 Wheezy.
Fail2Ban (authentication failure monitor) is an intrusion prevention software, written in Python.
Fail2Ban analyzes various services log files (ssh, apache, postfix etc) and if it detects possible attacks (mainly Brute-force attacks), it creates rules on the firewall ( and many others) or tcp wrappers () to ban (temporarily or permanently) the wannabe hacker. Simultaneously, fail2Ban informs system administrator with email for its activity in real time. Some activities which considered as attacks are: multiple attempts for ssh connection using accounts that do not exist in the system multiple attempts for ssh connection switching passwords Apache requests for web pages often requested by bots and scanners.
You do not need fail2ban (not even iptables) if your hosting provider offers a dedicated hardware firewall. Hardware firewalls as Cisco ASA 550 series and even smaller devices as FortiGate-60C can offer protection, which fail2ban offers (and moreover). Setup Configuration In summary: SystemMonitorScripts – RRDtool Trac. Notes ¶ The scripts and methods described here are by no means universal.
They are rather meant as a starting point for adaption to your own needs, without the hassle of learning all about RRDtool before you can even start. They have been tested mainly on Debian Etch machines. Prerequisites ¶ On Debian, you need to install some extra packages if you want the full monitoring capabilities.
Lm-sensors - for CPU and system temparature readings. In conclusion: the command apt-get install grep sed net-tools rrdtool lm-sensors smartmontools sysstat should prepare a properly installed system flawlessly. Installation and Setup ¶ Installation is really easy, just unpack the attached file as user "root" in the "/" directory. tar xzvf rrdmontools.tar.gz Setup is also done quite quickly, just open up /var/local/rrd/rrdcreate.sh with your favourite editor and change the lines.
PirateBox + COPS (Calibre OPDS (and HTML) PHP Server) So...
I managed to get COPS (see title) installed on my PirateBox 0.6.3 on an MR3020. (In case you don't know what Calibre is or what it does, you can find more info here.) COPS is great application that allows me to have a fully searchable book archive with book descriptions, ratings, and other metadata. This is how I did it: 1. The Spamhaus Project. Welcome! Recording Changes to the Repository. You have a bona fide Git repository and a checkout or working copy of the files for that project.

You need to make some changes and commit snapshots of those changes into your repository each time the project reaches a state you want to record. Remember that each file in your working directory can be in one of two states: tracked or untracked. Tracked files are files that were in the last snapshot; they can be unmodified, modified, or staged. Untracked files are everything else — any files in your working directory that were not in your last snapshot and are not in your staging area. When you first clone a repository, all of your files will be tracked and unmodified because you just checked them out and haven’t edited anything. Login. Le blog de NicoLargoTerminator, le terminal ultime sous GNU/Linux. Une des grande différence entre un Linuxien et un Windowsien est le temps passé devant le terminal (console en mode graphique).
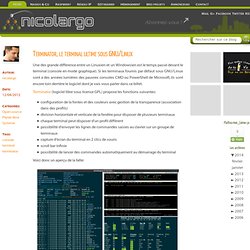
Si les terminaux fournis par défaut sous GNU/Linux sont à des années lumières des pauvres consoles CMD ou PowerShell de Microsoft, ils sont encore loin derrière le logiciel dont je vais vous parler dans ce billet. Terminator (logiciel libre sous licence GPL) propose les fonctions suivantes: configuration de la fontes et des couleurs avec gestion de la transparence (association dans des profils)division horizontale et verticale de la fenêtre pour disposer de plusieurs terminauxchaque terminal peut disposer d'un profil différentpossibilité d'envoyer les lignes de commandes saisies au clavier sur un groupe de terminauxcapture d'écran du terminal en 2 clics de sourisscroll bar infiniepossibilité de lancer des commandes automatiquement au démarrage du terminal Voici donc un aperçu de la bête: Autre fonction très utile, le regroupement. A Cloud as an Interface. Nmap - Free Security Scanner For Network Exploration & Security Audits.