

Is Antarctica Gaining or Losing Ice? Nature May Have Just Settled The Debate - D-brief. West Antarctica is rapidly melting, while some parts of East Antarctica have seen increased snowfall.
(Credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio) For years, scientists have debated whether heavy inland snowfall on the vast East Antarctic Ice Sheet — Earth’s largest — balances out the rapid melting in West Antarctica. Given enough snowfall, the continent might not yet be contributing to sea level rise. Most research shows the melt rate is so high that the continent is indeed losing ice. But in 2015, a group of NASA scientists published a controversial study that found Antarctica was instead gaining ice. It contradicted prominent previous findings — including reports from the U.N.’s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. (Credit: Zwally et al., Journal of Glaciology, Volume 61, Number 230, December 2015, pp. 1019-1036(18)) For their part, a number of veteran climate scientists have challenged Zwally’s findings.
Why Is Antarctica's Sea Ice Growing While the Arctic Melts? Scientists Have an Answer. While Arctic ice is melting at a record pace, a team of NASA-led researchers say they can explain why Antarctic sea ice has been edging in the opposite direction.

That paradox has puzzled scientists for years and given climate-change deniers fodder to dispute global warming. The group found that the icy winds blowing off Antarctica, as well as a powerful ocean current that circles the frozen continent, are much larger factors in the formation and persistence of Antarctic sea ice than changes in temperature. The mighty Southern Ocean Circumpolar Current prevents warmer ocean water from reaching the Antarctic sea ice zone, helping to isolate the continent. The winds within that ice zone keep the water extremely cold, enabling the sea ice cover to grow in recent years even as global temperatures have risen markedly. Just Because Antarctica Might Be Gaining Ice Doesn't Mean Climate Change Isn't Happening. VICE News is closely tracking global environmental change.

Check out the Tipping Point blog here. Headlines about global warming frequently refer to melting ice, but a new study reports that Antarctica may actually have gained mass. The study, published in the Journal of Glaciology, analyzed satellite data from two time periods. Antártida está ganhando gelo, não perdendo, afirma estudo da Nasa - 05/11/2015 - Ambiente. Surpreendentemente, a Nasa mostrou que a Antártida está ganhando gelo, em vez de perdendo, como se poderia esperar de um planeta em processo de aquecimento.
Os pesquisadores da agência espacial americana mostraram que o fenômeno aconteceu durante todo o período analisado, de 1992 a 2008. Ao ano, o acúmulo de gelo na Antártida representa uma redução no nível dos oceanos de 0,23 mm –ou seja, de cerca de meio centímetro em 20 anos. A descoberta não significa, porém, que não exista aquecimento global.
A hipótese para explicar o fenômeno, aliás, relaciona-se justamente com a mudança climática em curso. A Antártida funciona desta forma: o gelo chega por meio da precipitação ("chuva"), e vai embora quando um bloco congelado se solta do continente, derretendo lentamente no mar, ou por meio de drenagem, ou seja, do escorrimento da água que vai aparecendo. Se houver mais gelo saindo do que entrando, há então um deficit. 2015 Antarctic maximum sea ice extent breaks streak of record highs. The sea ice cover of the Southern Ocean reached its yearly maximum extent on Oct. 6.
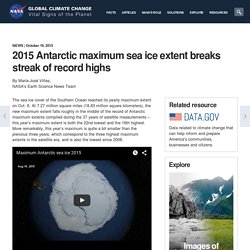
At 7.27 million square miles (18.83 million square kilometers), the new maximum extent falls roughly in the middle of the record of Antarctic maximum extents compiled during the 37 years of satellite measurements – this year’s maximum extent is both the 22nd lowest and the 16th highest. More remarkably, this year’s maximum is quite a bit smaller than the previous three years, which correspond to the three highest maximum extents in the satellite era, and is also the lowest since 2008.
Mais finas e quebradiças. Heavy Snowfall and Cold Wave in America Not Caused by Global Warming. The heavy snowfalls during the months of December 2013 and January 2014 were caused by the excessive snow and ice deposits formed in the Arctic region during August 2013.
Last year, fifty states in the U.S. experienced heavy snowfalls during the months of December 2013 and January 2014. Based on the information released on the internet, I found out that the snowfall was the aftermath of the unusual formation of extensive ice deposits in the Arctic region. However, it is explained on the basis of the “Global Warming” conception. We are told that the ice deposits on the surface of the sea in the North Polar Region melted and the resultant sea water on the surface evaporated with the heat and rose up. This affected the polar vortex, which usually circles the middle and upper troposphere and extends into stratosphere.
In the year 2007, BBC released a news item stating that a study conducted by Prof. Ganapathy Ponmudi is an independent scientist from Chennai, India. Melting Greenland's past to provide clues about its future. Explicit cookie consent. Ganho de gelo do mar na Antártica não compensa perda no Ártico. Antarctic sea ice hit 35-year record high Saturday - The Washington Post.
Antarctic sea ice extent on September 22 compared to 1981-2010 median depicted by orange curve (NSIDC) Antarctic sea ice has grown to a record large extent for a second straight year, baffling scientists seeking to understand why this ice is expanding rather than shrinking in a warming world.
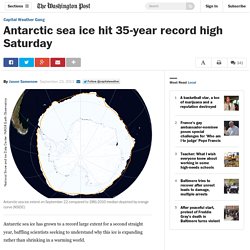
On Saturday, the ice extent reached 19.51 million square kilometers, according to data posted on the National Snow and Ice Data Center Web site. That number bested record high levels set earlier this month and in 2012 (of 19.48 million square kilometers). Records date back to October 1978. Despite Antarctic Gains, Global Sea Ice Is Shrinking. Claire Parkinson has been studying polar sea ice for about four decades.
She has been speaking to public audiences for nearly as long. And it was those public audiences who provoked one of the NASA climatologist’s latest research projects. Special Report - Science Nation. Videos reveal rich upside-down world under polar ice - life - 23 January 2015. Video: Underwater robot reveals algae under ice Appearances can be deceptive.
At first glance, the sea ice that covers polar regions in winter seems rather barren – but clinging to the bottom of it are remarkable upside-down algal "forests" that support a wide array of creatures. Not long ago Arctic researchers assumed phytoplankton blooms were restricted to open waters, and for good reason: the algae rely on light to survive and little of this makes it through a couple of metres of ice. A few years ago, however, researchers cruising in the Chukchi Sea between Alaska and Siberia found massive phytoplankton blooms beneath sea ice – with a biomass that was, in places, four times as much as the amount in open waters. It's now clear that the discovery was just the tip of the iceberg.
"With Nereid we saw not only a big bloom of plankton but also subsequent blooms of zooplankton feeding on the phytoplankton. Planeta água sob a terra. [imgcapa] Depois de duas décadas perfurando o solo numa das regiões mais frias e inóspitas do planeta, na Antártica, um grupo de cientistas russos conseguiu, no sábado 4, chegar às águas do Lago Vostok, um enorme bolsão subterrâneo de água doce preservado há 15 milhões de anos por uma camada de 4 quilômetros de gelo.
Área de cobertura de gelo na Antártica é a maior dos últimos 40 anos - Blog do Clima. Gelo diminui no Ártico e aumenta na Antártica. A Nasa, agência espacial americana, divulgou em seu site oficial imagens de satélites que mostram a diminuição do gelo marinho do Ártico, enquanto o do Antártico se expandiu. De acordo com a Nasa, de 1978 a 2010, a Antártica cresceu 17 mil quilômetros quadrados por ano. O aumento, porém, não é proporcional à diminuição do gelo no Ártico. A 3-D View of the Greenland Ice Sheet Opens Window on Ice History. Jan. 23, 2015 AUSTIN, Texas — Scientists using ice-penetrating radar data collected by NASA’s Operation IceBridge and earlier airborne campaigns have built the first comprehensive map of layers deep inside the Greenland Ice Sheet, opening a window on past climate conditions and the ice sheet’s potentially perilous future. This new map allows scientists to determine the age of large swaths of the second largest mass of ice on Earth, an area containing enough water to raise ocean levels by about 20 feet.
“This new, huge data volume records how the ice sheet evolved and how it’s flowing today,” said Joe MacGregor, the study’s lead author, a glaciologist at The University of Texas at Austin Institute for Geophysics (UTIG), a unit of the Jackson School of Geosciences. Greenland’s ice sheet has been losing mass during the past two decades, a phenomenon accelerated by warming temperatures. Subglacial Lakes Seen Refilling in Greenland. [image-50] Scientists using satellite images and data from NASA’s Operation IceBridge have found evidence of a drained and refilled subglacial lake beneath northeastern Greenland’s Flade Ice Cap.
This sub-ice body of water is only one of a handful that have been detected in Greenland and its presence sheds new light on how the Greenland Ice Sheet reacts to warming temperatures. Subglacial lakes are relatively common in Antarctica, and although recent studies have mathematically predicted possible locations for hundreds of such features in Greenland, few have actually been found. Bodies of water beneath the ice are normally detected either with ice-penetrating radar or by observing rapid changes in ice surface elevation such as bulges or basins. Uk.businessinsider. Vidéo > Quand les glaciers deviennent rouges... And now it's global COOLING! Return of Arctic ice cap as it grows by 29% in a year. 533,000 more square miles of ocean covered with ice than in 2012BBC reported in 2007 global warming would leave Arctic ice-free in summer by 2013Publication of UN climate change report suggesting global warming caused by humans pushed back to later this month By David Rose for The Mail on Sunday Published: 23:37 GMT, 7 September 2013 | Updated: 14:58 GMT, 11 October 2014 A chilly Arctic summer has left 533,000 more square miles of ocean covered with ice than at the same time last year – an increase of 29 per cent.
The rebound from 2012’s record low comes six years after the BBC reported that global warming would leave the Arctic ice-free in summer by 2013. Global Warming Computer Models Collapse; Arctic Ice Sheets Rapidly Expand as Planet Plunges into Global Cooling. A chilly Arctic summer has left nearly a million more square miles of ocean covered with ice than at the same time last year – an increase of 60 per cent. The rebound from 2012’s record low comes six years after the BBC reported that global warming would leave the Arctic ice-free in summer by 2013.
Instead, days before the annual autumn re-freeze is due to begin, an unbroken ice sheet more than half the size of Europe already stretches from the Canadian islands to Russia’s northern shores. The Northwest Passage from the Atlantic to the Pacific has remained blocked by pack-ice all year. Persistent Warming Driving Big Arctic Changes. SAN FRANCISCO — Not every year can be a record setter. But records are only one small piece of a larger puzzle that shows persistent change in the Arctic. And that change hasn’t slowed according to this year’s Arctic Report Card released at the American Geophysical Union’s Fall Meeting on Wednesday. Arctic Ocean temperatures in August 2014.Click image to enlarge. Credit: climate.gov Long-term trends in rising temperatures, spiraling sea ice loss, and ecosystem shifts paint a picture of a region in transition due to climate change that is transpiring at a much faster rate than the rest of the globe. What Would Happen To The Climate If We Stopped Emitting Greenhouse Gases Today?
Earth’s climate is changing rapidly. We know this from billions of observations, documented in thousands of journal papers and texts and summarized every few years by the United Nations' Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. The primary cause of that change is the release of carbon dioxide from burning coal, oil and natural gas. International climate talks in Lima this week are laying the foundation for next year’s UN climate summit in Paris. While negotiations about reducing emissions grind on, how much warming are we already locked into?
If we stop emitting greenhouse gases tomorrow, why would the temperature continue to rise? ScienceCasts: Climate Change and the Yin-Yang of Polar Sea Ice. Global Warming Expedition Foiled By Ice. Antarctic sea ice expands to record high level; Arctic sea ice shrinks to sixth lowest. Sea ice data updated daily with one-day lag. The year 2019 saw an early melt onset and high sea surface temperatures during summer in the Beaufort and Chukchi Seas. The September minimum extent ended up tied with 2007 and 2016 for second lowest in the satellite record. Autumn freeze up was slow. In December, the Chukchi Sea finally completely refroze, Hudson Bay iced over, and sea ice extended south into the Bering Sea. Antarctic sea ice is INCREASING: Big freeze breaks records - but scientists claim the rise is caused by global warming. Images suggest there is 7.7 million square miles of sea around continentThis is double size of the Antarctic and three times the size of AustraliaFast westerly winds, which go around Antarctica, are now moving southThis is linked to an increase in greenhouse gases and increase in sea iceSeparate study found region's glaciers are melting faster than ever before.
Antarctic sea ice continues to grow beyond record coverage. Updated. Área de cobertura de gelo na Antártica é a maior dos últimos 40 anos - Blog do Clima. Why is Antarctic sea ice at record levels despite global warming? Cientistas revelam 'aquecimento oculto' que acelera degelo da Antártica. Loja Virtual. Dark Snow Project. Why Are Asia's Glaciers Mysteriously Expanding? L'extension du domaine de la glace. Need to know: How climate change affects the global South. Mar de Gelo da Antártica alcança expansão recorde.