

Course Materials for Mobile Devices: Key Considerations. In the past term, Duke University piloted a course in introductory chemistry that replaced the standard textbook and course materials with online, multimedia content collected by the instructor from open repositories, as well as materials developed by the instructor under creative commons.
The content included video clips from recorded lectures, ePUB texts and PDF files, and recorded whiteboard animations, all housed online. Students gathered at small tables during the course sessions and collaborated to solve chemistry problems, accessing the course resources as necessary during the class via laptops, tablets, and smaller mobile devices. Rather than lecture at the front of the room, the instructor circulated among the students, checking their progress, offering advice, and asking guiding questions. Projections by technology researchers over the past year confirm the immediacy of this trend: Unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0021/002161/216167e.pdf.
Mobile Learning - E-Learning Faculty Modules. From E-Learning Faculty Modules Module Summary Mobile learning (or “m-learning”) offers many possibilities for both blended and fully online learning—by tapping into the benefits of real-time and real-space (physical space) mixed with digital information and experiences.
Mobile learning is a kind of augmented reality—with the mobile devices enabling connectivity and information access in many urban and other environments—to enhance the learner experience. Wireless fidelity (wifi) technologies and the broad popularization of many mobile devices (smart phones, iPads, tablet PCs, small notebook computers, and others) have meant that access to the Internet and Web really is ubiquitous for many. Eprints.qut.edu.au/5399/1/5399.pdf. Le m-learning en formation professionnelle. Le Mobile Learning Toolkit est un guide sur l'apprentissage mobile initié par l'Organisation internationale du travail (OIT) dans le cadre de son programme de formation My.Coop, abréviation de Managing Your Cooperative.

Comme son nom l'indique donc, ce programme de formation s'adresse à des chefs de coopératives agricoles que l'OIT entend outiller sur les défis qui sont les leurs en matière de management des coopératives, de gestion des intrants et des extrants, et du marketing. Cette formation s'appuie sur le téléphone mobile, technologie de l'information et de la communication la plus accessible pour la cible visée. ce guide vise en effet prioritairement les entrepreneurs d'Afrique. Le Mobile Learning Toolking est une boîte à outils d'une centaine de pages environ qui comprend deux parties : les méthodes d'apprentissage mobile et les outils. Mobile Health Design.
Online University. Stanford's Piazza. By Dan Stober This summer, Stanford will again offer a free online video course on creating apps for the iPhone and iPad – but with a difference.
This time, participants will have their questions answered by course instructors ("course captains") and by their fellow online learners. This peer-to-peer social feature is a first for Stanford online courses. It is also a first for any course hosted on iTunes U, which will once again carry the iPhone/iPad course. The course will run June 25 to Aug. 27. The new social media aspect of the course builds on a technology many students already use: Piazza, a social learning platform. Earlier versions of the 10-week apps course have proved enormously popular, with individual lecture videos downloaded more than 10 million times. The inclusion of Piazza will enhance the learning experience, said Brent Izutsu, Stanford's program manager for iTunes U.
Find out more about the class and register here. Media Contact 1 Stumble 4 Share. Integrating iPads into the Classroom - Download Free Content from Union University. iPads in Education Daily. California Learning Resource Network (CLRN) Bloom's Taxonomy. 4/1/2008 By: Andrew Churches from Educators' eZine Introduction and Background: Bloom's Taxonomy In the 1950's Benjamin Bloom developed his taxonomy of cognitive objectives, Bloom's Taxonomy.
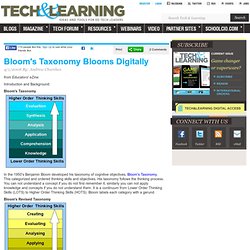
This categorized and ordered thinking skills and objectives. Bloom's Revised Taxonomy In the 1990's, a former student of Bloom, Lorin Anderson, revised Bloom's Taxonomy and published this- Bloom's Revised Taxonomy in 2001.Key to this is the use of verbs rather than nouns for each of the categories and a rearrangement of the sequence within the taxonomy. Bloom's Revised Taxonomy Sub Categories Each of the categories or taxonomic elements has a number of key verbs associated with it Lower Order Thinking Skills (LOTS)
Mbusinesspro.com. The Mobile Tech Classroom. Is multiscreen viewing making consumers more distracted than engaged? By Lauren Johnson June 11, 2012 ITV saw success via Shazam-enabled campaign Second-screen applications, sound recognition and SMS are just some of the ways that marketers are choosing to interact with consumers.
However, with the shift in multiscreen viewing, marketers have to fight for users attention more than ever. In an age where consumers are plugged into their mobile devices while watching television, marketers are scrambling to connect with users on multiple mediums at the same time, which can lead users togettingoverwhelmed. This is a sliding scale as interaction with and focus on the second screen increases, concentration and focus on the first screen TV decreases, said Caroline Park, Buckinghamshire, England-based senior analyst of user experience practice at Strategy Analytics. It is not that they are more of less engaged in activity than they were prior to using the second screen, it is just that their engagement is moving between the two devices, she said. Distracted or engaged?
OpenClassroom. Full courses.

Short Videos. Free for everyone. Learn the fundamentals of human-computer interaction and design thinking, with an emphasis on mobile web applications. A practical introduction to Unix and command line utilities with a focus on Linux.