

Audio bit depth. An analogue signal (in red) encoded to 4-bit PCM digital samples (in blue); the bit depth is 4, so each sample's amplitude is one of 16 possible values.
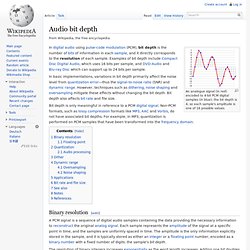
In basic implementations, variations in bit depth primarily affect the noise level from quantization error—thus the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and dynamic range. However, techniques such as dithering, noise shaping and oversampling mitigate these effects without changing the bit depth. Bit depth also affects bit rate and file size. Bit depth is only meaningful in reference to a PCM digital signal. Non-PCM formats, such as lossy compression formats like MP3, AAC and Vorbis, do not have associated bit depths.
Binary resolution[edit] A PCM signal is a sequence of digital audio samples containing the data providing the necessary information to reconstruct the original analog signal. The resolution of binary integers increases exponentially as the word length increases. Floating point[edit] Quantization[edit] Compact Disc Digital Audio. Compact Disc Digital Audio (CDDA or CD-DA) is the standard format for audio compact discs.
The standard is defined in the Red Book, one of a series of "Rainbow Books" (named for their binding colors) that contain the technical specifications for all CD formats. Standard[edit] The first edition of the Red Book was released in 1980 by Philips and Sony;[1][2] it was adopted by the Digital Audio Disc Committee and ratified as IEC 60908 (published in 1987).[3] The second edition of IEC 60908 was published in 1999[4] and it cancels and replaces the first edition, amendment 1 (1992) and the corrigendum to amendment 1.
The IEC 60908 however does not contain all the information for extensions that is available in the Red Book, such as the details for CD-Text, CD+G and CD+EG.[5][6] The standard is not freely available and must be licensed. Basic specifications[edit] The basic specifications state that: Audio format[edit] Sample rate[edit] Pre-emphasis[edit] Storage capacity and playing time[edit] Bit Depth Definition - What is Bit Depth? Definition: In digital audio, there has to be a certain value set for describing the resolution of the sound data (samples) that is to be captured and stored in an audio file -- this attribute is called Bit Depth.
Similarly for video files (images, videos), this measurement range is also used to determine the resolution of a picture -- the higher the bit depth (e.g. 16 bit versus 24 bit) the better the image will be. This attribute is exactly the same for digital audio and thus a higher bit depth will give a much more detailed sound recording. Bit Depth can often be confused with Making sure your digital audio files don't suffer from clipping is important, but having the right bit depth is also a critical aspect to consider in order to reduce the amount of background noise too.
Bit depth also determines how loud a recording will be. Musicovery.