

Model Simulations Challenge Reductionist Research Approaches to Studying Chronic Low Back Pain. - PubMed - NCBI. Buy and Save on pure Camphor. Menthol Crystals. Methyl Salicylate 1Kg. Buy Pure Medical Lidocaine Powder HCL. GreenHealth - 4oz - Premium Menthol Crystals 100% Natural by Greenals: Beauty. Jet. Save on MSM Powder. Amazon.com : Wintergreen (Large 4 ounce) Best Essential Oil : Beauty. Rose hip seed oil. Rose hip seed oil is a pressed seed oil, extracted from the seeds of the wild rose bush (Rosa moschata or Rosa rubiginosa) in the southern Andes.
Rosehip seed oil can also be extracted from Rosa canina, which grows in many regions of the world including South Africa and Europe. Grape seed oil. Grape seed oil (also called grapeseed oil or grape oil) is pressed from the seeds of grapes, and is thus an abundant by-product of winemaking.[1] Uses[edit] Cooking[edit] Grape seed oil has a moderately high smoke point of approximately 216 °C (421 °F).
Due to its clean, light taste, and high polyunsaturated fat content, it may be used as an ingredient in salad dressings and mayonnaise and as a base for oil infusions of garlic, rosemary, or other herbs or spices. It is widely used in baked goods, pancakes, and waffles. Jojoba oil. Glass vial containing jojoba oil Jojoba oil /həˈhoʊbə/ ( listen) is the liquid produced in the seed of the Simmondsia chinensis (Jojoba) plant, a shrub, which is native to southern Arizona, southern California, and northwestern Mexico.
The oil makes up approximately 50% of the jojoba seed by weight.[1] The terms "jojoba oil" and "jojoba wax" are often used interchangeably because the wax visually appears to be a mobile oil, but as a wax it is composed almost entirely (~97%) of mono-esters of long-chain fatty acids and alcohols, accompanied by only a tiny fraction of triglyceride esters.
This composition accounts for its extreme shelf-life stability and extraordinary resistance to high temperatures, compared with true vegetable oils. Menthol. Menthol is an organic compound made synthetically or obtained from corn mint, peppermint, or other mint oils.
It is a waxy, crystalline substance, clear or white in color, which is solid at room temperature and melts slightly above. The main form of menthol occurring in nature is (−)-menthol, which is assigned the (1R,2S,5R) configuration. Menthol has local anesthetic and counterirritant qualities, and it is widely used to relieve minor throat irritation. Menthol also acts as a weak kappa opioid receptor agonist. Lidocaine. Local anesthetic Lidocaine, also known as xylocaine and lignocaine, is a medication used to numb tissue in a specific area.[4] It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia and to perform nerve blocks.[3][4] Lidocaine mixed with a small amount of adrenaline (epinephrine) is available to allow larger doses for numbing, to decrease bleeding, and to make the numbing effect last longer.[4] When used as an injectable, it typically begins working within four minutes and lasts for half an hour to three hours.[4][5] Lidocaine mixtures may also be applied directly to the skin or mucous membranes to numb the area.[4] Medical uses[edit] Local numbing agent[edit] The efficacy profile of lidocaine as a local anaesthetic is characterized by a rapid onset of action and intermediate duration of efficacy.
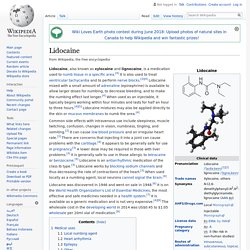
Therefore, lidocaine is suitable for infiltration, block, and surface anaesthesia. For surface anaesthesia, several formulations can be used for endoscopies, before intubations, etc. Capsaicin. Capsaicin (/kæpˈseɪ.ɪsɪn/ (INN); 8-methyl-N-vanillyl-6-nonenamide) is an active component of chili peppers, which are plants belonging to the genus Capsicum.
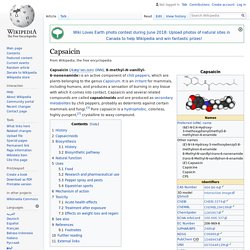
It is an irritant for mammals, including humans, and produces a sensation of burning in any tissue with which it comes into contact. Capsaicin and several related compounds are called capsaicinoids and are produced as secondary metabolites by chili peppers, probably as deterrents against certain mammals and fungi.[3] Pure capsaicin is a hydrophobic, colorless, highly pungent,[2] crystalline to waxy compound.
History[edit] The compound was first extracted in impure form in 1816 by Christian Friedrich Bucholz (1770–1818).[4] He called it "capsicin", after the genus Capsicum from which it was extracted. Camphor. Camphor (/ˈkæmfər/) is a waxy, flammable, white or transparent solid with a strong aroma.[5] It is a terpenoid with the chemical formula C10H16O.
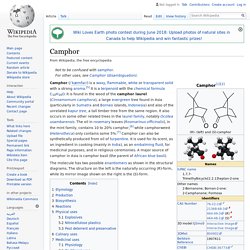
It is found in the wood of the camphor laurel (Cinnamomum camphora), a large evergreen tree found in Asia (particularly in Sumatra and Borneo islands, Indonesia) and also of the unrelated kapur tree, a tall timber tree from the same region. It also occurs in some other related trees in the laurel family, notably Ocotea usambarensis. Methyl salicylate. Thymol. Thymol (also known as 2-isopropyl-5-methylphenol, IPMP) is a natural monoterpene phenol derivative of cymene, C10H14O, isomeric with carvacrol, found in oil of thyme, and extracted from Thymus vulgaris (common thyme) and various other kinds of plants as a white crystalline substance of a pleasant aromatic odor and strong antiseptic properties.
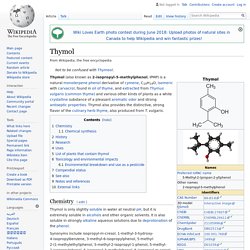
Thymol also provides the distinctive, strong flavor of the culinary herb thyme, also produced from T. vulgaris. Chemistry[edit] Thymol is only slightly soluble in water at neutral pH, but it is extremely soluble in alcohols and other organic solvents. It is also soluble in strongly alkaline aqueous solutions due to deprotonation of the phenol. Thymol has a refractive index of 1.5208[3] and an experimental dissociation exponent (pKa) of 7001105900000000000♠10.59±0.10.[4] Thymol absorbs maximum UV radiation at 274 nm.[5] Thymol is chemically related[clarification needed] to the anesthetic propofol. Boswellic acid. Structure of α-boswellic acid 3D model of α-boswellic acid Structure of β-boswellic acid 3D model of β-boswellic acid Structure of 11-keto-β-boswellic acid 3D model of 11-keto-β-boswellic acid Boswellic acids are a series of pentacyclic triterpene molecules that are produced by plants in the genus Boswellia.
Magnesium. Chemical element with atomic number 12 Magnesium is a chemical element with symbol Mg and atomic number 12.
It is a shiny gray solid which bears a close physical resemblance to the other five elements in the second column (group 2, or alkaline earth metals) of the periodic table: all group 2 elements have the same electron configuration in the outer electron shell and a similar crystal structure. Methylsulfonylmethane. Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM) is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH3)2SO2.
It is also known by several other names including DMSO2, methyl sulfone, and dimethyl sulfone.[2] This colorless solid features the sulfonyl functional group and is considered relatively inert chemically. It occurs naturally in some primitive plants, is present in small amounts in many foods and beverages, and is marketed as a dietary supplement. Vitamin B6. Vitamin B6 refers to a group of chemically similar compounds which can be interconverted in biological systems.
Vitamin B6 is part of the vitamin B group of essential nutrients. Vitamin B3. Vitamin B3, also known as vitamin B3 complex, is vitamin that includes three forms: nicotinamide (niacinamide), niacin (nicotinic acid), and nicotinamide riboside.[1][2][3][4][5] All three forms of vitamin B3 are converted within the body to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD).[3] NAD is required for human life and people are unable to make it within their bodies without one of the vitamin B3 or tryptophan.[3] Nicotinamide riboside was identified as a form of vitamin B3 in 2004.[3] Jump up ^ Krutmann, Jean; Humbert, Philippe (2010). Nutrition for Healthy Skin: Strategies for Clinical and Cosmetic Practice. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 153. ISBN 9783642122644. Archived from the original on 2017-04-10. Nicotinamide. Side effects are minimal.[6][7] At high doses liver problems may occur.[6] Normal amounts are safe for use during pregnancy.[1] Nicotinamide is in the vitamin B family of medications, specifically the vitamin B3 complex.[8][9] It is an amide of nicotinic acid.[6] Foods that contain nicotinamide include yeast, meat, milk, and green vegetables.[10] Nicotinamide was discovered between 1935 and 1937.[11][12] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system.[13] Nicotinamide is available as a generic medication and over the counter.[8] In the United Kingdom a 60 g tube costs the NHS about £7.10.[5] Commercially nicotinamide is made from either nicotinic acid or 3-cyanopyridine.[12][14] In a number of countries grains have nicotinamide added to them.[12] Medical uses[edit]
Niacin. Chamomile: A herbal medicine of the past with bright future. Calendula. Terpene. Many terpenes are derived commercially from conifer resins, such as those made by this pine. The role and mechanism of action of menthol in topical analgesic products - Pergolizzi - 2018 - Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics. Hyaluronic acid. Anionic, nonsulfated glycosaminoglycan. Collagen. Tropocollagen molecule: three left-handed procollagens (red, green, blue) join to form a right-handed triple helical tropocollagen. Collagen /ˈkɒlədʒɪn/ is the main structural protein in the extracellular space in the various connective tissues in animal bodies. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals,[1] making up from 25% to 35% of the whole-body protein content. Ascorbyl palmitate. Vitamin C. Squalene. Retinol. 6 Skincare Ingredients That Really Work. Oil based gel. The most unsaturated fat source.
Which Oils Get Absorbed Fastest By The Skin? - Venusian*Glow. 7 Best Carrier Oils for Radiant Skin - Savory Lotus. The Difference Between Topical and Transdermal Medications - Gensco Pharma. White Paper by Robert L. Wilbur, Pharm.D., CPh | Executive Director, Medical Affairs, Gensco Pharma Abstract Topical medications are widely used as prescription or over the counter (OTC) treatments for a variety of conditions. Though, their use is common, there exists a significant confusion among the general public and some medically trained professionals, as to the difference between topical and transdermal products.
While all topical and transdermal compounds are applied to the skin, only the transdermal formulations are designed to penetrate through the skin layer and exert their effects on deeper or more distant tissues. Introduction Compounds have been applied to the skin for thousands of years to enhance beauty and treat local conditions. More recently, transdermal delivery technology has been developed to treat a range of conditions beyond the local site of application. Discussion. Penetrating oil. A 400 ml can of penetrating fluid Other uses include: removing chewing gum and adhesive stickers, lessening friction on metal-stringed musical instruments, various gardening purposes and household repair tasks. Dermal absorption speed and depth fastest absorbing and deepest absorbing lipids into skin.
Fastest absorbing and deepest absorbing lipids into skin. Absorption (skin) Topical medication. (2.70 Oz) (2-pack) Numb 520 (2.70 oz/76g) 5% Lidocaine, Liposomal Technology for Deeper Penetration, Topical Numbing Cream, Doctor Recommended, Anorectal Discomfort: Health & Personal Care. Best value on Pure Menthol crystals, Mentha arvensis. Lidocaine/prilocaine.