

Pagan Dharma. By Sam Webster ©1997 Hail to the Tathatagharba in all beings!

Our era of profound spiritual crisis is equally an era of spiritual forment rivaled only by that time two thousand years ago that saw the emergence of Gnosticism, Christianity, and the Hermetic Tradition in the West and Mahayana Buddhism and Vedanta in the East. Today, as then, this transformative crisis is being fueled by the confluence of cultures, none of which will remain the same for that contact.
Two such cultures, contemporary Paganism and Tibetan or Vajrayana Buddhism, have the potential to deeply revitalize each other and positively effect our world. Problems with Pagan Practice Paganism has survived awful abuse for thousands of years. Over the years of practicing Pagan magickal ritual I have noticed a variety of consistent problems with our practice. One of these that was very easy to adopt was the dedication of the benefit of the ritual to all beings (this of course includes the ritual practitioners).
Telos. About.com: Five Dhyani Buddhas. Vidyaraja (Jp. = Myo-o, Myoo). Wisdom Kings, Mantra Kings, Prote. OVERVIEW.

The Myō-ō 明王 are warlike and wrathful deities who represent the power of Buddhism to overcome the passions. Five of the Myō-ō are emanations of the Five Buddha of Wisdom (Skt. Dhyāni Buddhas, Jinas), and in this role they guard the four cardinal directions and the center. Introduced to Japan in the 9th century by Japan’s Shingon and Tendai sects of Esoteric Buddhism (Mikkyō 密教), the Myō-ō were originally Hindu deities who were later adopted into the pantheon of Esoteric Buddhism to vanquish blind craving. The teachings of Esoteric Buddhism are mystical and hard to understand, and require a high level of devotion and austerity to master.
Esoteric Buddhism’s main practitioners in Japan were Priest Kūkai 空海 (774 - 835 AD) and Priest Saichō (767 - 822 AD). The Five Great Kings, Nara National Museum (Japanese language only) Fudō (center); Left to Right Gundari, Daitoku, Kongō-Yasha, Gōsanze Fudō 不動明王 (Skt. GROUPING OF EIGHT, Jp. = Hachidai Myō-ō = 八大明王 LEARN MORE - Myō-ō Kings. Buddhist Studies: Mudras: Symbolic Hand Gestures. Buddhist symbolism. Buddhist symbolism is the use of Buddhist art to represent certain aspects of dhamma, which began in the 4th century BCE.
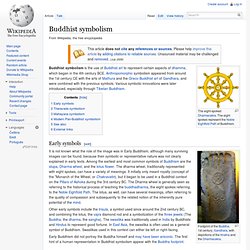
Anthropomorphic symbolism appeared from around the 1st century CE with the arts of Mathura and the Greco-Buddhist art of Gandhara, and were combined with the previous symbols. Various symbolic innovations were later introduced, especially through Tibetan Buddhism. Early symbols[edit] It is not known what the role of the image was in Early Buddhism, although many surviving images can be found, because their symbolic or representative nature was not clearly explained in early texts. Among the earliest and most common symbols of Buddhism are the stupa, Dharma wheel, and the lotus flower.
Other early symbols include the trisula, a symbol used since around the 2nd century BC, and combining the lotus, the vajra diamond rod and a symbolization of the three jewels (The Buddha, the dharma, the sangha). Theravada symbolism[edit] Mahayana symbolism[edit] These symbols are: Desire realm. Tibetan Bhavacakra or "Wheel of Life" in Sera, Lhasa.

Within the desire realm are either five or six domains (S.: gati, also sometimes translated as "realm"). In Indo-Tibetan Mahāyāna Buddhism there are six domains (Standard Tibetan: rigs drug gi skye gnas) and in Theravada Buddhism there are only five, because the domain of the asuras is not regarded as separate from that of the devas. Taoism also features the five realms.[2][3][4][5] The thirty-one realms are also known as the "thirty-one paths of rebirth", the "six paths of suffering", the "six planes", and the "six lower realms".
They stand in contrast to the higher attainments of the Ten spiritual realms. One's previous actions and thoughts determine which of the six domains one is reborn into. The 8th century Buddhist monument Borobudur in Central Java, Indonesia, took the concept of these three realms. Buddhist Symbols and Mudras (Gestures of the Buddha) Define Shivaree at Dictionary.