

Research Traces Impacts of Childhood Adversity. Published Online: November 6, 2012 Published in Print: November 7, 2012, as Premium article access courtesy of Edweek.org.

The stress of a spelling bee or a challenging science project can enhance a student's focus and promote learning. But the stress of a dysfunctional or unstable home life can poison a child's cognitive ability for a lifetime, according to new research. While educators and psychologists have said for decades that the effects of poverty interfere with students' academic achievement, new evidence from cognitive and neuroscience is showing exactly how adversity in childhood damages students' long-term learning and health. Those studies show that stress forms the link between childhood adversity and poor academic achievement, but that not all adversity—or all stress—is bad for students.
"Children from their earliest life need to learn how to manage adversity," such as dealing with the first day of school, said Dr. Research from Dr. 'Toxic' Recipe. New Studies Dissect School Turnarounds. Published Online: September 18, 2012 Published in Print: September 19, 2012, as Interplay of Strategies Seen as Key in Turnarounds Focus On: School Turnaround Washington What makes one low-performing school turn around and build momentum over time, while another, seemingly similar school tries the same strategies but continues to struggle?
It's not just particular programs or practices, but the interplay of school implementation with district policies and support, according to the Institute of Education Sciences' Turning Around Low-Performing Schools project—the most comprehensive federal research on such schools to date. "There's not a lot out there on how you know that a school has turned around—and will stay turned around rather than just jumping up for a year," said Rebecca Herman, a managing research analyst and school improvement expert for the American Institutes of Research. Comparing Apples Need to Read In another of the project's studies, Brenda J. No Education Reform Without Tackling Poverty, Experts Say. Narrowing the Achievement Gap for Low-Income Children: A 19-Year Life Cycle Approach.
Stresses of poverty may impair learning ability in young children. (Medical Xpress)—The stresses of poverty—such as crowded conditions, financial worry, and lack of adequate child care—lead to impaired learning ability in children from impoverished backgrounds, according to a theory by a researcher funded by the National Institutes of Health.
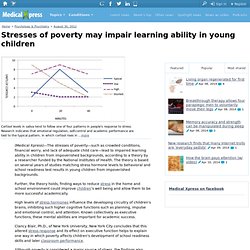
The theory is based on several years of studies matching stress hormone levels to behavioral and school readiness test results in young children from impoverished backgrounds. Further, the theory holds, finding ways to reduce stress in the home and school environment could improve children's well being and allow them to be more successful academically. High levels of stress hormones influence the developing circuitry of children's brains, inhibiting such higher cognitive functions such as planning, impulse and emotional control, and attention. Known collectively as executive functions, these mental abilities are important for academic success. During the course of their research, Dr. However, Dr. In one study, Dr. Cost of living can affect student achievement, study says. By Bernice Young California Watch Poor children living in higher-cost areas like the urban centers of California are more likely to struggle academically than their counterparts in lower-cost areas, according to research published earlier this week.
Students in Carpinteria, Calif. (Photo by Sarah Garland) Based on a sample of more than 17,000 first-graders, the study by researchers from UCLA and the nonprofit Child Trends “provides important empirical evidence … that geographic variations in cost of living indeed matters for children’s well-being,” the article states. Although there is a substantive body of research examining the relationship between family income and child development and educational outcomes, this is among the first studies to look at the effects of cost of living on academic achievement. The hard bigotry of poverty: Why ignoring it will doom school reform - The Answer Sheet. This was written by Brock Cohen, a teacher and student advocate in the Los Angeles Unified School District who contends that we can no longer afford to trivialize the critical role that poverty plays in a child’s learning experiences – and that true school reform begins with social justice.
Brock’s students were recently featured in an NPR piece that charts some of his students’ daily struggles as they pursue their education. By Brock Cohen We have only climbed halfway up the mountain, and halfway isn’t good enough. We want all our children to see the view from the top, to see the world of possibilities that stretch out before them. -New York City Mayor Michael Bloomberg We can’t allow another generation of kids to fall by the wayside while we take our time trying to build consensus in the interest of harmony among adults. -Former D.C. We want to come back year after year and continue to add resources and fund more.
-U.S. -President Barack Obama But our program is no panacea. 4N8b.USAID-FINAL2. Educationweek: Report shows that from 200... Young Child Risk Calculator. The risk factors used in this tool are known to increase the chance of poor health, school, and developmental outcomes for young children.

Economic hardship paired with any of the listed risk factors may indicate a greater chance of poor outcomes. Children with three or more risks are exceptionally vulnerable. Information about the prevalence of young children experiencing these risks can inform policies aimed at improving outcomes for vulnerable children and reducing the number of children experiencing early risks.
Use the form on the left to see the following information for your state: the percentage of young children in a state, within a specified age range, who are experiencing selected risk factorsthe percentage of young children in a state, within a specified age range, who are experiencing both selected risk factors (such as teen parent, residential mobility) and economic hardship at a specified level (extreme poverty, poverty, low-income)