

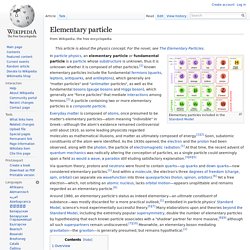
Elementary particle. In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle whose substructure is unknown, thus it is unknown whether it is composed of other particles.[1] Known elementary particles include the fundamental fermions (quarks, leptons, antiquarks, and antileptons), which generally are "matter particles" and "antimatter particles", as well as the fundamental bosons (gauge bosons and Higgs boson), which generally are "force particles" that mediate interactions among fermions.[1] A particle containing two or more elementary particles is a composite particle.
Everyday matter is composed of atoms, once presumed to be matter's elementary particles—atom meaning "indivisible" in Greek—although the atom's existence remained controversial until about 1910, as some leading physicists regarded molecules as mathematical illusions, and matter as ultimately composed of energy.[1][2] Soon, subatomic constituents of the atom were identified. Overview[edit] Main article: Standard Model.
Leptons. Higgs Bason. Gauge Bason.