

AT-2814FX Fast Ethernet Fiber (SC) ExpressCard. This chapter includes the following topics: » Overview » Starting the Device Manager » Flow Control » Interrupt Moderation » Jumbo Packet » Large Send Offload (IPv4) » Log Status Messages » Max IRQ per Sec » Network Address » Receive Buffers » Speed & Duplex » TCP/UDP Checksum Offload (IPv4) » Transmit Buffers » Wake From Shutdown » Wake-Up Capabilities Overview To modify the advanced properties of the AT-2814FX ExpressCard, you must access the Device Manager on your operating system, then go to each advanced property page.

Guidelines Here are the guidelines to modifying the advanced properties: ■ To change the advanced property settings, you must have Administrator privileges. ■ When you upgrade the driver software, the settings of the advanced properties may change. Starting the Device Manager The procedures for accessing the Device Manager are different among Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows 7. » Device Manager on Windows XP » Device Manager on Windows Vista and Windows 7 Device Manager on Windows XP. 10 Gigabit Programmable NICs. A 10 Gigabit Programmable Network Interface Card - How NICs Work NICs facilitate the transmission and receipt of frames between the network and host operating system.
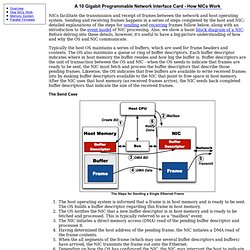
Sending and receiving frames happens in a series of steps completed by the host and NIC; detailed explanations of the steps for sending and receiving frames follow below, along with an introduction to the event model of NIC processing. Also, we show a basic block diagram of a NIC. Before delving into these details, however, it's useful to have a big-picture understanding of how and why the OS and NIC communicate. Typically the host OS maintains a series of buffers, which are used for frame headers and contents. The Send Case The Steps for Sending a Single Ethernet Frame The host operating system is informed that a frame is in host memory and is ready to be sent. The Receive Case The Steps for Receiving a Single Ethernet Frame The NIC receives a frame from the network into its local receive buffer.
The Event Model. 2a_ry053.pdf. Www.cse.ohio-state.edu/~panda/788/papers/2a_ry053.pdf. How Windows XP and 2003 Handle UDP buffer from OS kernel to application - Jack' Weblog. 1.
For each UDP socket which is created by application, OS has an internal structure maps to it. We call this structure as endpoint. Endpoint has an internal buffer which we called receive window to store the UDP data received from NIC card. So for each UDP socket, there is a internal buffer maps to it. 2. default, this receive windows buffer size is 4096 or 8192, the size depends on how much physical memory OS has. For more information, refer to DefaultReceiveWindowunder in below link Above registry will affect all system wide created UDP sockets. If you want to set a specific receive windows buffer size, you can call socket API setsockopt with flag SO_RCVBUF For more information, you can refer to below link NOTE: receive windows buffer size is not necessarily corresponding to the size of the TCP receive window. 3. 4. 5.
WSAIoctl Function. 10 Gigabit Programmable NICs.