

Deneb. Other names include Arided and Aridif, but these have fallen out of use.
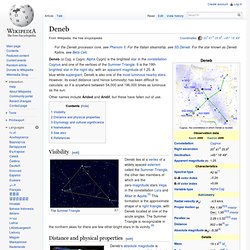
Visibility[edit] Distance and physical properties[edit] Deneb's absolute magnitude is currently estimated as −8.4, placing it among the most luminous stars known, with an estimated luminosity nearly 200,000 times that of our Sun.[4] This is towards the upper end of various published values over the last few decades.[7][8][9] Deneb's exact distance from the Earth is still rather uncertain. The currently accepted distance of around 2,600 light-years (and the associated physical data shown in the starbox) is derived by a variety of methods, including spectral luminosity classes, atmospheric modelling, stellar evolution models, assumed membership of the Cyg OB7 association, and direct measurements of angular diameter.
Deneb is a bluish-white star of spectral type A2Ia, with a surface temperature of 8,500 kelvin. Etymology and cultural significance[edit] Namesakes[edit] See also[edit] Deneb in fiction References[edit] Messier 39. Messier 29. Messier 29 (also known as M 29 or NGC 6913) is an open cluster in the Cygnus constellation.
It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764, and can be seen from Earth by using binoculars. M29 is situated in the highly crowded area of Milky Way near Gamma Cygni, at a distance of 7,200 (most sources including Mallas/Kreimer and Burnham, and agreeing with early estimates or R.J. Trumpler 1930) or 4,000 light years (the latter from Kenneth Glyn Jones and the Sky Catalogue 2000.0). The Night Sky Observer's Guide by Kepple and Sanner gives a deviating value of 6,000 light years – the uncertainty due to inaccurately known absorption of the cluster's light. According to the Sky Catalog 2000, M29 is included in the Cygnus OB1 association, and approaching us at 28 km/s. This cluster can be seen in binoculars. M29 can be found quite easily as it is about 1.7 degrees South and little East of Gamma or 37 Cygni (Sadr). References[edit] External links[edit] Media related to Messier 29 at Wikimedia Commons. Cygnus_IAU. Cygnus (constellation) Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2.
One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, an distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. Cygnus as depicted in Urania's Mirror, a set of constellation cards published in London c.1825. Surrounding it are Lacerta, Vulpecula and Lyra. In Polynesia, Cygnus was often recognized as a separate constellation. Cygnus culminates at midnight on 29 June, and is most visible in the evening from the early summer to mid-autumn in the Northern Hemisphere.[7] Cygnus, Lyra.