

The Summer Palace - Beijing China. Temple of Heaven - Beijing China. Inside Beijing's Forbidden City. Inside the Forbidden City - Documentary Series Trailer. The Great Wall of China- History Channel (3- Eng Subs) Mao Zedong. Mao Zedong, also transcribed as Mao Tse-tung listen , and commonly referred to as Chairman Mao (December 26, 1893 – September 9, 1976), was a Chinese Communist revolutionary and the founding father of the People's Republic of China, which he governed as Chairman of the Communist Party of China from its establishment in 1949 until his death.
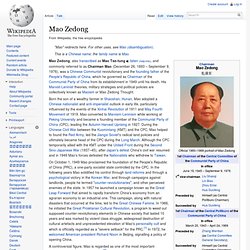
His Marxist-Leninist theories, military strategies and political policies are collectively known as Maoism or Mao Zedong Thought. On October 1, 1949 Mao proclaimed the foundation of the People's Republic of China (PRC), a one-party socialist state controlled by the CPC. In the following years Mao solidified his control through land reforms and through a psychological victory in the Korean War, and through campaigns against landlords, people he termed "counter-revolutionaries", and other perceived enemies of the state. Sun Yat-sen. Names[edit] The original name of Sun Yatsen was Sun Wen (孫文), and his genealogical name was Sun Deming (孫德明).[1][5] As a child, his "milk name" was Dixiang (帝象).[1] The courtesy name of Sun Yat-sen was Zaizhi (載之), and his baptized name was Rixin (日新).[6] While at school in Hong Kong he got the name Yat-sen (逸仙; Hanyu pinyin: Yìxiān).[7] Sūn Zhōngshān (孫中山), the most popular of his Chinese names, came from the "Nakayama" (中山) of Nakayama Shō (中山樵), the Japanese name given to him by Tōten Miyazaki.[1] Early years[edit] Sun Yat-sen (back row, fifth from left) and his family.
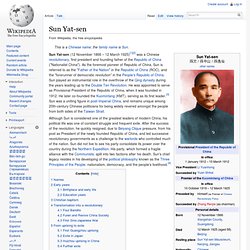
Birthplace and early life[edit] Sun Yat-sen was born on 12 November 1866.[2] His birthplace was the village of Cuiheng, Xiangshan County (now Zhongshan City), Guangdong Province.[2] He had a cultural background of Hakka[8] and Cantonese. Education years[edit] Statue of Sun Yat-sen as a school boy in Honolulu, Hawaii, age 13 In 1886 Sun studied medicine at the Guangzhou Boji Hospital under the Christian missionary John G. Qing Dynasty. The dynasty was founded by the Jurchen Aisin Gioro clan in Northeastern China, historically known as Manchuria.
In the late sixteenth century, Nurhachi, originally a Ming vassal, began organizing Jurchen clans into "Banners," military-social units and forming a Manchu people. By 1636, his son Hong Taiji began driving Ming forces out of southern Manchuria and declared a new dynasty, the Qing. In 1644, peasant rebels led by Li Zicheng conquered the Ming capital Beijing. Rather than serve them, Ming general Wu Sangui made an alliance with the Manchus and opened the Shanhai Pass to the Banner Armies led by Prince Dorgon, who defeated the rebels and seized Beijing.
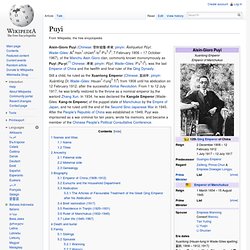
Puyi. Aisin-Gioro Puyi (Chinese: 愛新覺羅·溥儀; pinyin: Àixīnjuéluó Pǔyí; Wade–Giles: Ai4-hsin1-chüeh2-lo2 P'u3-i2; 7 February 1906 – 17 October 1967), of the Manchu Aisin Gioro clan, commonly known mononymously as Puyi (Pu-yi;[1] Chinese: 溥儀; pinyin: Pǔyí; Wade–Giles: P'u3-i2), was the last Emperor of China and the twelfth and final ruler of the Qing Dynasty.
Names and titles[edit] Name[edit] Qin Shi Huang. Qin Shi Huang (260–210 BC[3]) is the modern Chinese name of King Zheng of Qin (r. 246–221 BC[4]), who ended the Warring States period by completing the conquest of China in 221 BC.[4] Rather than maintain the title of king borne by the Shang and Zhou rulers, he ruled as the First Emperor of the Qin dynasty from 220 to 210 BC.
The title would continue to be borne by Chinese rulers for the next two millennia. During his reign, his generals greatly expanded the size of the Chinese state: campaigns south of Chu permanently added the Yue lands of Hunan and Guangdong to the Chinese cultural orbit; campaigns in Central Asia conquered the Ordos loop from the nomad Xiongnu, although eventually causing their confederation under Modu Chanyu. Name[edit] Modern Chinese names have two components, a surname (姓) and a given name (名).