

National Schools' Observatory. Astronomers think that the Universe started with the Big Bang.
As with all science, this is based on evidence; so what is the evidence for the Big Bang theory? The spiral galaxy - M51 1. Redshift of Galaxies The redshift of distant galaxies means that the Universe is probably expanding. Cosmic Microwave Background 2. Very early in its history, the whole Universe was very hot. This is the Cosmic Microwave Background which has been accurately measured by orbiting detectors, and is very good evidence that the Big Bang theory is correct. The Sun is a fairly new star 3. As the Universe expanded and cooled down, some of the elements that we see today were created. You cannot look in new stars, like the Sun, for this evidence, because they contain elements that were created in previous generations of stars. Galaxies of long ago 4. Big Bang Theory. Big Bang The Big Bang model of the universe's birth is the most widely accepted model that has ever been conceived for the scientific origin of everything.

No other model can predict as much as the Big Bang model can. A common question that people ask is "What happened before the Big Bang? " The phrase "in the beginning" is used here to refer to the birth of our universe with the Big Bang. In the creation of the universe, everything was compressed into an infinitesimally small point, in which all physical laws that we know of do not apply. The Big Bang model had its beginnings with Edwin Hubble's discovery in 1929 that, on large scales, everything in the universe is moving away from everything else.
The next step towards the Big Bang model was to take this process in reverse - that is, to go back in time. If the universe is currently growing, then the universe was smaller in the past. This is the basic idea behind the Big Bang. *In calculus, this is an adaptation of "Zeno's Paradox. " Relativistic Doppler effect. Diagram 1.
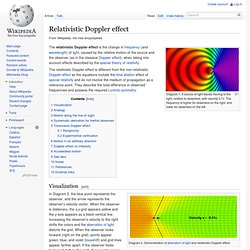
A source of light waves moving to the right, relative to observers, with velocity 0.7c. The frequency is higher for observers on the right, and lower for observers on the left. The relativistic Doppler effect is the change in frequency (and wavelength) of light, caused by the relative motion of the source and the observer (as in the classical Doppler effect), when taking into account effects described by the special theory of relativity. The relativistic Doppler effect is different from the non-relativistic Doppler effect as the equations include the time dilation effect of special relativity and do not involve the medium of propagation as a reference point. They describe the total difference in observed frequencies and possess the required Lorentz symmetry. Visualization[edit] In Diagram 2, the blue point represents the observer, and the arrow represents the observer's velocity vector. Diagram 3. Analogy[edit] Motion along the line of sight[edit] away from him (where where and .
To. File:Dopplereffectsourcemovingrightatmach0.7.gif.