

World Health Organization map of global alcohol consumption shows the which are the world's drunkest countries. Photo by Francois Guillot/AFP/Getty Images This post originally appeared in Business Insider.
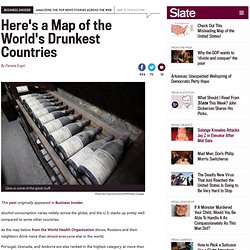
Alcohol consumption varies widely across the globe, and the U.S. stacks up pretty well compared to some other countries. As the map below from the World Health Organization shows, Russians and their neighbors drink more than almost everyone else in the world. Portugal, Grenada, and Andorra are also ranked in the highest category at more than 12.5 liters per person over the age of 15 in 2010. The WHO notes in its report that 48 percent of those included in this data abstain from drinking altogether. Canadians drink more than Americans, keeping pace with most European countries. Alcohol consumption in Russia is a major concern. Other countries near Russia, including Ukraine and Belarus, have similar levels of alcohol consumption. Tratamento Farmacológico Para Dependência Alcoólica. Tratamento Farmacológico Para Dependência Alcoólica A dependência ao álcool é um distúrbio crônico resultante de uma combinação de fatores: genético, psicossocial e ambiental.
Caracteriza-se por aumento da tolerância aos efeitos do álcool, perda do controle da ingestão do álcool, persistência na ingestão de bebidas alcoólicas apesar dos prejuízos que isso vem trazendo. O alcoolismo afeta aproximadamente 10% da população geral. A dependência ao álcool é tratada por médicos, psicólogos e por intervenções sociais com o objetivo de diminuir ou abolir o desejo pelo álcool e seus efeitos lesivos. Benzodiazepinas. Anticonvulsivantes. Reproduzido de: Formulário Terapêutico Nacional 2008: Rename 2006 [Link Livre para o Documento Original]
Sindrome de Abstinencia Alcool - complicações. Complicações psiquiátricas do uso crônico do álcool: síndrome de abstinência e outras doenças psiquiátricas Cláudia MacielI; Florence Kerr-CorrêaII.

Tratamento Alcoolismo. Origem: Wikipédia, a enciclopédia livre.
Unemployment and alcohol abuse: a review. [J Occup Med. 1988. Www.estudosdotrabalho.org/anais-vii-7-seminario-trabalho-ret-2010/francisco_capoulade_e_sandra_bull_e_marcia_bernardo_saude_mental_trabalho_e_desemprego.pdf. Aloe Blacc - I Need A Dollar (lyrics) Institute Drugs And Alcohol - Job Commercial. Efectos crónicos del alcohol en el cerebro. Dementia in hepatic and renal failure - Metabolic Diseases - Other forms of dementia - Dementia - Alzheimer Europe. By Kurt Jellinger General outline.
Hepatic Encephalopathy: Manifestations of Liver Disease. Hepatic encephalopathy (portosystemic encephalopathy, liver encephalopathy, or hepatic coma) is deterioration of brain function that occurs because toxic substances normally removed by the liver build up in the blood and reach the brain.
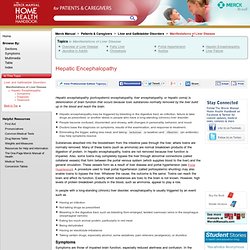
Substances absorbed into the bloodstream from the intestine pass through the liver, where toxins are normally removed. Many of these toxins (such as ammonia) are normal breakdown products of the digestion of protein. In hepatic encephalopathy, toxins are not removed because liver function is impaired. Delirium tremens. Origem: Wikipédia, a enciclopédia livre.
Wernicke Korsakoff syndrome. A Case of Confusion (part) Comorbidity of Alcoholism and Psychiatric Disorders. People with alcohol use disorders often have co–occurring psychiatric disorders, but they frequently do not receive specialized substance abuse treatment that addresses both conditions.

Although pharmacological and psychosocial treatments for alcohol use disorders and psychiatric disorders can be integrated to help these patients, relatively few clinical studies have tested these types of treatments. As mental health and substance abuse facilities expand their services for patients with dual disorders, further research is needed to guide the treatment of this patient population. Key words: AODD (alcohol and other drug dependence); comorbidity; mentally ill; prevalence; health care utilization; drug therapy; antidepressants; serotonin uptake inhibitors; psychosocial treatment method; antipsychotic tranquilizers; 12–step program. Schizophrenia. Schizophrenia (/ˌskɪtsɵˈfrɛniə/ or /ˌskɪtsɵˈfriːniə/) is a mental disorder often characterized by abnormal social behavior and failure to recognize what is real.
Common symptoms include false beliefs, unclear or confused thinking, auditory hallucinations, reduced social engagement and emotional expression, and lack of motivation. Diagnosis is based on observed behavior and the person's reported experiences. Genetics and early environment, as well as psychological and social processes, appear to be important contributory factors.
Some recreational and prescription drugs appear to cause or worsen symptoms. Causes of schizophrenia. The causes of schizophrenia have been the subject of much debate, with various factors proposed and discounted or modified. The language of schizophrenia research under the medical model is scientific. Such studies suggest that genetics, prenatal development, early environment, neurobiology and psychological and social processes are important contributory factors. Currently, there are five different types of schizophrenia listed in the DSM-IV-TR titled: catatonic, residual, disorganized, undifferentiated, and paranoid.[1] Current psychiatric research into the development of the disorder is often based on a neurodevelopmental model (proponents of which see schizophrenia as a syndrome.)[2][3] However, schizophrenia is diagnosed on the basis of symptom profiles. Neural correlates do not provide sufficiently useful criteria.[4] "Current research into schizophrenia has remained highly fragmented, much like the clinical presentation of the disease itself".[5]
Alcohol use and schizophrenia. Generalized Anxiety Disorder - Alcohol. Generalized anxiety disorder. Causes[edit] Genetics[edit] Generalized anxiety disorder may be hereditary with it running in families.[9] Genetics seem to play a role in this; those with genetic predisposition are more likely to develop GAD, usually in response to a life stressor.[10] Comorbidity of Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Alcohol Use Disorders among Individuals Seeking Outpatient Substance Abuse Treatment. Major depressive disorder. Alcohol Use, Abuse, and Depression: Is There a Connection? Why do I need to register or sign in for WebMD to save? We will provide you with a dropdown of all your saved articles when you are registered and signed in. Some people say they drink alcohol to "drown their sorrows" after a bad breakup, job loss, or other major life stress.
Bipolar disorder. Bipolar disorder, also known as bipolar affective disorder (and originally called manic-depressive illness), is a mental disorder characterized by periods of elevated mood and periods of depression.[1][2] The elevated mood is significant and is known as mania or hypomania depending on the severity or whether there is psychosis. During mania an individual feels or acts abnormally happy, energetic, or irritable.[1] They often make poorly thought out decisions with little regard to the consequences. The need for sleep is usually reduced.[2] During periods of depression there may be crying, poor eye contact with others, and a negative outlook on life.[1] The risk of suicide among those with the disorder is high at greater than 6% over 20 years, while self harm occurs in 30–40%.[1] Other mental health issues such as anxiety disorder and drug misuse are commonly associated.[1]
Bipolar Disorder and Alcoholism. Bipolar disorder and alcoholism commonly co–occur. Multiple explanations for the relationship between these conditions have been proposed, but this relationship remains poorly understood. Some evidence suggests a genetic link. Appendix B: DSM-IV-TR Diagnostic Criteria for Alcohol Abuse and Dependence - The Surgeon General's Call to Action To Prevent and Reduce Underage Drinking - NCBI Bookshelf. Alcool doença crónica. National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) Analyses of a national sample of individuals with alcohol dependence (alcoholism) reveal five distinct subtypes of the disease, according to a new study by scientists at the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
“Our findings should help dispel the popular notion of the ‘typical alcoholic,’” notes first author Howard B. Moss, M.D., NIAAA Associate Director for Clinical and Translational Research. How alcohol affects the body long term. Liver. The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion. The liver is necessary for survival; there is currently no way to compensate for the absence of liver function in the long term, although new liver dialysis techniques can be used in the short term. This gland plays a major role in metabolism and has a number of functions in the body, including glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, plasma protein synthesis, hormone production, and detoxification.
Liver Failure - Stem Cell Network. Last update: 07/2013 About liver failure. Cirrhosis: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. Cirrhosis is scarring of the liver and poor liver function. It is the final phase of chronic liver disease. Causes. Alcoholic liver disease: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. Pancreas. Structure[edit] 1. Alcohol and your Brain. Regeneration of Brain Cells. Regeneration of Brain Cells: For almost one hundred years, it has been a mantra of biology - brain cells do not regenerate. In a startling discovery that could have profound implications for treating brain disorders and injuries, researchers at Princeton University have discovered that new neurons are continually being added to the brains of adult monkeys.
Brain Cell Regeneration Studies. Discoveries: Brain Cell Regeneration. News - Scientists Discover Addition of New Brain Cells in Highest Brain Area. Your Brain on Drugs: Alcohol. Hipotálamo. Origem: Wikipédia, a enciclopédia livre. Apesar de relativamente pequeno, é uma região encefálica importante na homeostase corporal, isto é, no ajustamento do organismo às variações externas. Por exemplo, é o hipotálamo que controla a temperatura corporal, o apetite e o balanço de água no corpo, além de ser o principal centro da expressão emocional e do comportamento sexual. O hipotálamo faz também a integração entre os sistemas nervoso e endócrino, atuando na ativação de diversas glândulas produtoras de hormônios. A hipófise e o hipotálamo são estruturas intimamente relacionadas morfológica e funcionalmente que controlam todo o funcionamento do organismo direta ou indiretamente atuando sobre diversas glândulas como a tireóide, adrenais e gônadas.
Funções e Características do hipotálamo[editar | editar código-fonte] Desenvolvimento Embrionário[editar | editar código-fonte] Medula espinhal. Córtex cerebral. Neurónio. Causes of addiction, treatment and healing. Alcoolismo fam lia. Alcoolismo na Familia: Uma analise sobre o impacto social na vida de crianças e adolescentes - Monografias Brasil Escola. Alcoholism - Is Alcoholism Inherited? Alcoolismo sociedade. 2002009. Emotional Habits: The Key to Addiction. Desenvolvimento cerebral: carinho das mães é importante. Alcohol-fuelled violence out of control.
Self-Medicating Your Emotions. Dealing with Fear in Recovery. Common Risk and Protective Factors for Alcohol and Drug Use. Asch conformity experiments. Drinking Alcohol - Top Myths About Drinking Alcohol. Will drinking alcohol help you feel warmer? Alcohol Effects on the Digestive System. Will a Beer Really Quench That Summer Thirst? - Medical Myths - Harvard Commentaries.
Alcohol, Calories, and Weight. The History of Alcohol as an Alternate Medicine. Alcohol, Drugs, And Socializing. Does alcohol make you stronger or give you strength ?