

Magnetic resonance imaging. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (NMRI), or magnetic resonance tomography (MRT) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to investigate the anatomy and function of the body in both health and disease.
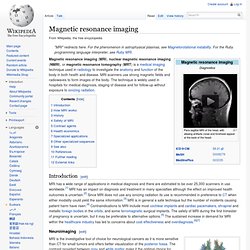
MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields and radiowaves to form images of the body. The technique is widely used in hospitals for medical diagnosis, staging of disease and for follow-up without exposure to ionizing radiation. Introduction[edit] Neuroimaging[edit] MRI image of white matter tracts. MRI is the investigative tool of choice for neurological cancers as it is more sensitive than CT for small tumors and offers better visualization of the posterior fossa. Cardiovascular[edit] Invenio.lib.auth.gr/record/112642/files/GRI-2009-2532.pdf. Deafness in Children. Deafness is a partial or complete loss of hearing, also known as hearing impairment.

The normal threshold range is 0-20 decibels (dB), where 0 dB is the threshold for the perception of sound at a given frequency for people with normal hearing. Hearing Testing and Screening in Young Children. Approximately 840 children are born deaf in both ears each year in the UK.
Some 90% of these babies are born into families with no experience or history of childhood deafness. The Newborn Hearing Screening Programme was introduced in the UK in 2006, replacing the previous infant screening programme (the 'distraction test' at 8 months). Most congenitally deaf children are now identified and managed appropriately before 6 months of age. Διαγνωστικές Εξετάσεις. ΚΑΝΕΛΛΟΣ ΠΑΝΟΣ - Ωτορινολαρυγγολόγος. Ωτοακουστικές Εκπομπές-Ακουστικά Προκλητά Δυναμικά-Ακουόγραμμα-Τυμπανόγραμμα. Ωτοακουστικές εκπομπές «« Ακουστικά Προκλητά Δυναμικά «« Συχνές ερωτήσεις από τους γονείς (για νεογνά και βρέφη !)
Hearing Tests - How they're performed. A hearing test is usually carried out after your ears have been examined and you have been referred to a specialist.

Examination Your GP or practice nurse will first ask about any symptoms you may be experiencing, such as: pain or discharge (fluid) tinnitus – noise in one or both ears vertigo (dizziness) hearing loss previous, relevant medical problems Your ear will be examined using an instrument called an auriscope, also known as an otoscope. An auriscope is a small hand-held torch with a magnifying glass which allows the doctor to see the eardrum and the passageway that leads to it from the outer ear. Hearing Tests. oPatientPlus articles are written by UK doctors and are based on research evidence, UK and European Guidelines.

They are designed for health professionals to use, so you may find the language more technical than the condition leaflets. Hearing impairment may be very variable in severity but can cause severe communication difficulties leading to profound educational, social and psychological problems. Newborn hearing screening - Australian Prescriber. Welcome to Australian Hearing. It’s a common belief that people with a hearing loss just can’t hear sounds loudly enough, but it’s more complicated than that.
The four main problems caused by hearing loss are: Soft sounds can’t be heard.Key parts of particular speech sounds may not be heard.Sounds are difficult to separate, so voices become jumbled with background noise.A reduced range of hearing may make loud sounds intolerable. Hearing test. Audiometer[edit] An audiometer hearing test is usually administered to a person sitting in a soundproof booth wearing a set of headphones which is connected to an audiometer.
Small foam insert earphones placed in the ears may also be used. The audiometer produces tones at specific frequencies and set volume levels to each ear independently. The audiologist or licensed hearing aid specialist plots the loudness, in decibels, on an audiogram. Hearing Tests. Why do I need to register or sign in for WebMD to save?
We will provide you with a dropdown of all your saved articles when you are registered and signed in. How It Is Done continued... A tuning fork is a metal, two-pronged device that produces a tone when it vibrates. The health professional strikes the tuning fork to make it vibrate and produce a tone. These tests assess how well sound moves through your ear. The Audiogram. The audiogram is a graph showing the results of the pure-tone hearing tests.
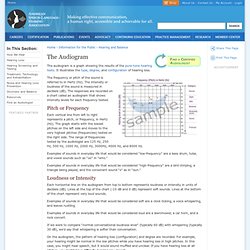
It illustrates the type, degree, and configuration of hearing loss. The frequency or pitch of the sound is referred to in Hertz (Hz). The intensity or loudness of the sound is measured in decibels (dB). The responses are recorded on a chart called an audiogram that shows intensity levels for each frequency tested. Types of Tests Used to Evaluate Hearing in Children and Adults. The CEC’s WIKI / HearingTests. eContact! 9.4 — Perte auditive et sujets connexes / Hearing (Loss) and Related Issues You are invited to contribute to this resource! Once you add or edit any entries, please add your name (and website) to the contributor’s list on the Overview page. Return to... eContact! 9.4 — Perte auditive et sujets connexes / Hearing (Loss) and Related Issues The following list describes the various Audiology/Hearing tests one may undergo, the reasons to get them, side effects and dangers involved, and where/when to get them done.
Acoustic Reflex Test This test is used to measure the contraction of the stapedius and tensor tympani muscles when subjected to high intensity sounds. ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΚΟΧΛΙΟΓΡΑΦΙΑ (ECOCHG)