

Dschool.stanford.edu/wp-content/uploads/2011/03/BootcampBootleg2010v2SLIM.pdf. Teaching Creativity Skills - Creative Thinking in Education & Life. Creativity Activities. Creativity is divided into five different categories: fluency, flexibility, redefinition, originality, and elaboration.

On this page you will find an explanation of each along with some creative problems for you to try. At the end of this page you will have the opportunity to participate in the Creativity Challenge. The Creativity Challenge will allow you to come up with your own fluency, flexibility, redefinition, originality, or elaboration problem and then submit it to Ms. Sanchez. Why Being Sleepy and Drunk Are Great for Creativity. Here’s a brain teaser: Your task is to move a single line so that the false arithmetic statement below becomes true.
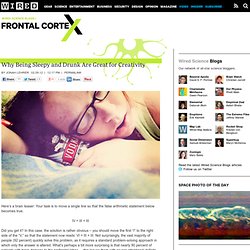
Did you get it? In this case, the solution is rather obvious – you should move the first “I” to the right side of the “V,” so that the statement now reads: VI = III + III. Not surprisingly, the vast majority of people (92 percent) quickly solve this problem, as it requires a standard problem-solving approach in which only the answer is altered. What’s perhaps a bit more surprising is that nearly 90 percent of patients with brain damage to the prefrontal lobes — this leaves them with severe attentional deficits, unable to control their mental spotlight — are also able to find the answer. Here’s a much more challenging equation to fix: In this case, only 43 percent of normal subjects were able to solve the problem. Of course, this doesn’t mean you should take a hammer to your frontal lobes. This helps explain a new study led by Mareike Wieth at Albion College.
Test Your Creativity: 5 Classic Creative Challenges. Fascinated by how brains and creativity work, we frequently share new research on the 99U twitter feed, showing how everything from drinking alcohol, to taking vacations, to moving your eyes from side to side can make you more creative.
What’s particularly interesting, however, is that most of these studies rely on just a small group of core creativity tests – and you don’t need any special lab equipment to take them. Below, we’ve collected five of the most commonly used creativity challenges for your self-testing pleasure. While creativity “testing” is far from an exact science, trying your mettle at these challenges could yield insight into when, where, and how you’re most creative. Or maybe it’ll just be fun. 1. Developed by J.P. Hold papers togetherCufflinksEarringsImitation mini-tromboneThing you use to push that emergency restart button on your routerKeeping headphones from getting tangled upBookmark The test measures divergent thinking across four sub-categories: The Creativity Crisis - Newsweek and The Daily Beast. Back in 1958, Ted Schwarzrock was an 8-year-old third grader when he became one of the “Torrance kids,” a group of nearly 400 Minneapolis children who completed a series of creativity tasks newly designed by professor E.

Paul Torrance. Schwarzrock still vividly remembers the moment when a psychologist handed him a fire truck and asked, “How could you improve this toy to make it better and more fun to play with?” He recalls the psychologist being excited by his answers. In fact, the psychologist’s session notes indicate Schwarzrock rattled off 25 improvements, such as adding a removable ladder and springs to the wheels.
That wasn’t the only time he impressed the scholars, who judged Schwarzrock to have “unusual visual perspective” and “an ability to synthesize diverse elements into meaningful products.” The accepted definition of creativity is production of something original and useful, and that’s what’s reflected in the tests. Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking (TTCT) How Creative Are You? The man nicknamed “the father of creativity” was psychologist E.

Paul Torrance. In the 1940s he began researching creativity in order to improve American education. In order to encourage creativity, we needed to define it — to measure and analyze it. We measured intelligence with an IQ score; why not measure creativity? Torrance drew on contemporary research that related creativity to divergent thinking — the characteristic of coming up with more answers, or more original answers, rather than deriving a single best answer. But there’s a problem. Science and Creativity. The Science of Creativity in 2013: Looking Back to Look Forward. 23Share Synopsis Amid growing interest in creativity in the lab and on the pages of popular books and magazines, these recent studies stand out.

In 1950, the American psychologist Joy P. Guilford delivered a lecture to the American Psychological Association (APA) calling for a scientific focus on creativity. Psychology knew little about creativity at the time. Unfortunately, Guilford’s ideas did not give rise to widespread research in creativity. The 21st century is witnessing a renaissance in creativity in both the lab and the pages of popular books and magazines. The most newsworthy research came from cognitive psychologists researching creativity “boosters”. The neuroscience of creativity is flourishing. Cognitive flexibility, the ability to switch between thinking about two concepts or consider multiple perspectives simultaneously, is also a popular topic in the neuroscience world.