

Rectifier. A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction.
The process is known as rectification. Physically, rectifiers take a number of forms, including vacuum tube diodes, mercury-arc valves, copper and selenium oxide rectifiers, semiconductor diodes, silicon-controlled rectifiers and other silicon-based semiconductor switches. Historically, even synchronous electromechanical switches and motors have been used. Bipolar junction transistor. Schematic symbols for PNP- and NPN-type BJTs.
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT or bipolar transistor) is a type of transistor that relies on the contact of two types of semiconductor for its operation. BJTs can be used as amplifiers, switches, or in oscillators. BJTs can be found either as individual discrete components, or in large numbers as parts of integrated circuits. Common emitter. Figure 1: Basic NPN common-emitter circuit (neglecting biasing details).
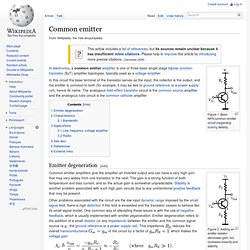
In electronics, a common emitter amplifier is one of three basic single-stage bipolar-junction-transistor (BJT) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage amplifier. Emitter degeneration[edit]