

YEAR 11: OF MICE AND MEN REVISION – CONTEXT – CLASSWORK. Hi there, In the comments below, please add at least five useful links with an evaluative description underneath it and three of the key things you found out and how they link to the novella.
Like this… BBC Bitesize – provides a clear summary of the worldwide Depression. Quite a lot of focus on Britain, so not all is directly relevant. I learned that: Alcohol prohibition and drug prohibition. Lessons from alcohol policy for drug policy. Harry G.

Levine and Craig Reinarman (2004), Alcohol prohibition and drug prohibition. Lessons from alcohol policy for drug policy. Amsterdam: CEDRO. . © Copyright 2004 Harry G. Harry G. Since the mid 1980s, growing numbers of Americans have come to recognize the harshness, expense, and ineffectiveness of U.S. drug prohibition, and they have advocated alternative approaches including harm reduction, drug decriminalization and even outright drug legalization.
Vega-AnnualReview-1991.pdf. Calisphere - California Cultures - Hispanic Americans: Migrant Workers and Braceros (1930s-1964) Questions to Consider What was life like for migrant workers in California agriculture?
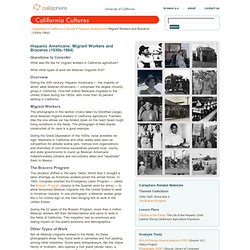
What other types of work did Mexican migrants find? Overview. Blacks and the Great Depression. THE GREAT Depression of the 1930s was catastrophic for all workers.

But as usual, Blacks suffered worse, pushed out of unskilled jobs previously scorned by whites before the depression. Blacks faced unemployment of 50 percent or more, compared with about 30 percent for whites. Black wages were at least 30 percent below those of white workers, who themselves were barely at subsistence level. There was no relief from the liberal Roosevelt administration, whose National Recovery Act (NRA) of 1933 was soon referred to by Blacks as the Negro Removal Act. Although its stated goal was nondiscriminatory hiring and an equal minimum wage for whites and Blacks, NRA public works projects rarely employed Blacks and maintained racist wage differentials when they did. Nor did traditional organized labor offer any alternative. Dust Bowl - Facts & Summary.
Ranchers and farmers in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, driven by the American agricultural ethos of expansion and a sense of autonomy from nature, aggressively exploited the land and set up the region for ecological disaster.
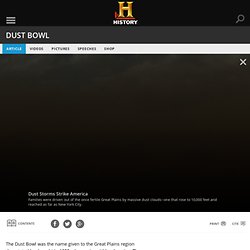
Most early settlers used the land for livestock grazing until agricultural mechanization combined with high grain prices during World War I enticed farmers to plow up millions of acres of natural grass cover to plant wheat. In response, the federal government mobilized several New Deal agencies, principally the Soil Conservation Service formed in 1935, to promote farm rehabilitation. Working on the local level, the government instructed farmers to plant trees and grass to anchor the soil, to plow and terrace in contour patterns to hold rainwater, and to allow portions of farmland to lie fallow each year so the soil could regenerate.
The government also purchased 11.3 million acres of submarginal land to keep it out of production. American RadioWorks - A Better Life. The "American dream" has powered the hopes and aspirations of Americans for generations.
It began as a plain but revolutionary notion: each person has the right to pursue happiness, and the freedom to strive for a better life through hard work and fair ambition. But over time, this dream has come to represent a set of expectations about owning things and making money. So what exactly is the American dream? How did we come to define it? Stereotypical Male and Female in the 1930's. TKAMmilieuWIKI - Women’s Roles of the 1930s. The Forgotten Heroes:Women in the 1930sBy: Tati Gervase & Rachel KiddIntroduction: - Tati & Rachel The women of the 1930s were the cornerstone of the house, the quiet stronghold of the family, and the constant in society.
They often went unnoticed, but they held everyone, and everything, together during one of the hardest decades the United States has ever faced: the Great Depression. Women became more involved in society, supported their families, and fought to have a voice in the nation.State of Women in the 1930s: -Tati During the 1930s, women had already gained rights that they had not previously had, but they still did not have the same rights as men. For example, in 1920, the 19th Amendment of the Constitution was put in place which stated, “The right of citizens of the United States to vote shall not be denied or abridged by the United States or by any State on account of sex” (National Archives). Works Cited "Amelia Earhart. " History of Gambling in the United States.
II.

History of Gambling in the United States Examining the history of gambling in North America suggests important conclusions that are useful today in considering policies related to gambling. The United States has had a long history of allowing some forms of legal gambling and a degree of tolerance of illegal gambling.Societal tolerance and acceptance of legal gambling can change rapidly. Scandals and political control by gaming interests have led to backlashes which result in regulation and/or prohibition. Societal standards and laws related to gambling have tended to change back and forth from prohibition to regulation. The First Wave: 1600's to mid 1800's. Apsummer / Migrant Workers-Farming in California 1930s -2011. The American Dream in the 1930s by Siobhan O'Donnell on Prezi. Prohibition of Alcohol during the Great Depression. Prohibition of Alcohol The 18th Amendment to the U.S.

Constitution – known as the Prohibition Amendment – was adopted in the 1920s and made the making, selling, possessing, and consuming of alcoholic drinks illegal. In the early 1930s, liquor was illegal, but people in Nebraska found ways to buy or make their own alcohol. York County farmer Elroy Hoffman says his father made corn whisky illegally. "It was pretty darn good stuff, too," he says. Because of Prohibition, organized crime increased, especially in major cities. Hollywood. Consider the economic, social, cultural, and technical factors.

By the early 1930s, Hollywood had became well established as a big film factory producing films that were predominantly opportunities for cinema-goers to escape from the humdrum reality of their daily lives into a world of fantasy. The studio system, which was dominated by a few big film companies, such as MGM, Paramount, Twentieth Century Fox, and Universal, controlled the production of films, their distribution, and their exhibition in the cinemas that the studios owned.
Film-making had become a very profitable big business dominated by a small number of Hollywood studios. FACTORS:PoliticalRoss (1998) described how the early American film industry, which comprised a working class cinema and many independent film makers, was destroyed by businessmen in the capitalist system. Racism for blacks in the south during the. Film History of the 1930s. The Golden Age of Hollywood: From 1930 to 1948 The 1930s decade (and most of the 1940s as well) has been nostalgically labeled "The Golden Age of Hollywood" (although most of the output of the decade was black-and-white). The 30s was also the decade of the sound and color revolutions and the advance of the 'talkies', and the further development of film genres (gangster films, musicals, newspaper-reporting films, historical biopics, social-realism films, lighthearted screwball comedies, westerns and horror to name a few). It was the era in which the silent period ended, with many silent film stars not making the transition to sound (e.g., Vilmy Banky, John Gilbert, and Norma Talmadge).
A Civil Rights History: Americans with Disabilities. By Andrea Faville In the name of charity and rehabilitation, Americans with disabilities were effectively segregated from society and denied their constitutional rights for much of U.S. history. Into the late 20th centuries, citizens with disabilities often were treated like charity cases, tragedies or freaks. Unable to support themselves in the United States’ manufacturing and agriculture-based economy, people with disabilities frequently had to panhandle and live on the streets. Others had homes, but not of their choosing. They were forcibly committed to hospitals reserved for the disabled where their lives were governed by doctors and hospital staff. Public perception of people with disabilities shifted after the two World Wars. Ranch Life in the 1930's- California by Kara Link on Prezi. Selling the Lure of the New and Foreign: Hollywood in the 1930s. Selling the Lure of the New and Foreign: Hollywood in the 1930sby Sophie Stanish As unemployment reached an all time high in the early nineteen thirties, the Great Depression firmly settled into place, its grip on the United States almost strangling the nation.
Sandwiched between the Roaring Twenties and World War Two, the nineteen thirties as a decade produced nothing of note, save for the crushing melancholy of the Great Depression. From out of work businessmen to destroyed bankers to farmers whose farm became a part of the Dust Bowl, nearly twenty five percent of the population was out of work and actively searching for a job. (Fig. 1) Pods of roaming job seekers criss-crossed the country, seeking employment, food, and money.1 Thousands more barely eked out a living on limited funds, surviving from day to day, going hungry whenever bills absolutely had to be paid. The economic situation was dire and deteriorating every day. Of Mice and Men Project: - Migrant Farmers in the Depression Era. Treatment of the Mentally Challenged during the Great Depression by Angela Lee on Prezi. Black Americans 1929-1941 - Historic Events for Students: The Great Depression. IntroductionIssue SummaryContributing ForcesPerspectivesImpactNotable PeoplePrimary SourcesSuggested Research TopicsBibliographySee Also Introduction "Let Jesus lead you and Roosevelt feed you" (quoted in Robert S.
McElvaine. The Great Depression: America, 1929–1941, 1993). These words were spoken by a black minister to his congregation shortly before the 1936 presidential election. Hard times were nothing new for black Americans. Racial discrimination was seen in federal housing, social security, and youth programs. With First Lady Eleanor Roosevelt personally taking up the cause of racial equality, initial steps were directed toward racial harmony by the mid-1930s. Issue Summary Tough Times Turn Harder. The United States Prohibition of Alcohol - 1920-1933. U.S. Prohibition Era: January 16, 1920 through December 5, 1933.
Race in the 1930s. The 1930's were a turbulent time for race relations in America. Going to School in Rural America during the 1930s. Going to School Country schools went through hard times in the 1930s. The value of farm land plummeted, and that meant that property taxes that supported schools fell as well. The Farming Problem. Years of plowing and planting left soil depleted and weak. As a result, clouds of dust fell like brown snow over the Great Plains. Film in the 30s: Digital History. Printable Version Hollywood played a valuable psychological role during the Great Depression. It provided reassurance to a demoralized nation. Last Hired, First Fired: Women and Minorities in the Great Depression. 7.2 Last Hired, First Fired: Women and Minorities in the Great Depression Learning Objectives.
Life and death during the Great Depression. Author Affiliations. How the Great Depression inspired Hollywood's golden age. For some months now over-excitable commentators have been comparing the current global economic downturn with the Wall Street Crash of 1929. And while one hopes they're overdoing it a bit, you would think that in the coming recession cinema -- a luxury if ever there was one -- will be among the first industries to be badly hit. Depression Era: 1930s: Education: Locally Decided. Outline of the U.S. Economy. The American labor force has changed profoundly during the nation's evolution from an agrarian society into a modern industrial state. GCSE Bitesize - The Depression of the 1930s. 15 Surprising Facts About Prohibition in the 1930s. Gun Law. Lennie's Aunt Clara and Whore House Boss Clara: Allusions to Asylums. Psychiatric Care in the 1930s - HowStuffWorks.
Gun laws in the United States by state. Prohibition in the United States. International Encyclopedia of Rehabilitation. Hollywood in the ’20s. 1930s, America - Feminist Void? Great Depression: American Social Policy - Social Welfare History Project.