

Free StarWind iSCSI SAN Software Download and Install on VMware. StarWind, the famous premium SAN software is available for free now with very few limitations.
These limitations are very minor and not to be considered for learning, personal usage and even for the small business firms. Free StarWind iSCSI SAN software makes a Windows computer as a professional network storage for VMware, Hyper-V, Xen server virtualization software, and also it can work an iSCSI target storage for any hosts.
It’s a great advantage of having a professional storage without a physical storage hardware. Here, I show how to download the latest free StartWind iSCSI SAN software, get life time free license and install it on desktop virtualization software VMware. I already covered free and open source NAS software FreeNAS which is also a good product for testing purpose, but StarWind is the most professional software with real features of SAN devices. Installing StarWind in VMware or VirtualBox will be very helpful for testing lab at home with one or two physical computers. ZFS Best Practices Guide - Siwiki. From Siwiki [edit] ZFS Administration Considerations [edit] ZFS Storage Pools Recommendations This section describes general recommendations for setting up ZFS storage pools.
[edit] System/Memory/Swap Space Run ZFS on a system that runs a 64-bit kernel One GB or more of memory is recommended. [edit] Storage Pools Set up one storage pool using whole disks per system, if possible. . # zpool create tank mirror c1t0d0 c2t0d0 Set up hot spares to speed up healing in the face of hardware failures. Hardware Recommendations - Freenas. Project - Deduplication - NexentaStor Project. Forums » Help » Added by Andrew Dezha 7 months ago I have some problems with deduplication.
I installed NexentaStor-Enterprise-3.1.2 and configured deduplication. I selected deduplication=on for 100 GB zvol. Block-size on zvol=4K. Dedup uses alot of ram and alot of cpu. Do you mean that 8 GB RAM is not enough for 100 GB volume? There are several formulas floating around for how to calculate the Dedup Table Size. Roughly the way you've got your system as described you will not be able to store a dedup table larger than about 1.75gb in RAM. PCI-X. It has been replaced in modern designs by the similar-sounding PCI Express (officially abbreviated as PCIe),[2] with a completely different connector and a very different logical design, being a single narrow but fast serial connection instead of a number of slower connections in parallel.
History[edit] Background and motivation[edit] In PCI, a transaction that cannot be completed immediately is postponed by either the target or the initiator issuing retry-cycles, during which no other agents can use the PCI bus. Since PCI lacks a split-response mechanism to permit the target to return data at a later time, the bus remains occupied by the target issuing retry-cycles until the read data is ready. In PCI-X, after the master issues the request, it disconnects from the PCI bus, allowing other agents to use the bus. PCI also suffered from the relative scarcity of unique interrupt lines.
The lack of registered I/Os limited PCI to a maximum frequency of 66 MHz. Conventional PCI. PCI Express. PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X, and AGP bus standards.
PCIe has numerous improvements over the aforementioned bus standards, including higher maximum system bus throughput, lower I/O pin count and smaller physical footprint, better performance-scaling for bus devices, a more detailed error detection and reporting mechanism (Advanced Error Reporting (AER)[1]), and native hot-plug functionality. More recent revisions of the PCIe standard support hardware I/O virtualization. The PCIe electrical interface is also used in a variety of other standards, most notably ExpressCard, a laptop expansion card interface. Serial ATA. Serial ATA (SATA) is a computer bus interface that connects host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives and optical drives.
Serial ATA replaces the older AT Attachment standard (later referred to as Parallel ATA or PATA), offering several advantages over the older interface: reduced cable size and cost (seven conductors instead of 40), native hot swapping, faster data transfer through higher signalling rates, and more efficient transfer through an (optional) I/O queuing protocol. SATA host adapters and devices communicate via a high-speed serial cable over two pairs of conductors.
In contrast, parallel ATA (the redesignation for the legacy ATA specifications) used a 16-bit wide data bus with many additional support and control signals, all operating at much lower frequency. To ensure backward compatibility with legacy ATA software and applications, SATA uses the same basic ATA and ATAPI command-set as legacy ATA devices. Performance - Linux Raid Wiki. I have made some testing of performance of different types of RAIDs, with 2 disks involved.
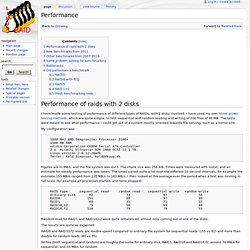
I have used my own home grown testing methods, which are quite simple, to test sequential and random reading and writing of 200 files of 40 MB. The tests were meant to see what performance I could get out of a system mostly oriented towards file serving, such as a mirror site. My configuration was 1800 MHz AMD Sempron(tm) Processor 3100+ 1500 MB RAM nVidia Corporation CK804 Serial ATA Controller 2 x Hitachi Ultrastar A7K 1000 SCSI-II 1 TB. Linux version 2.6.12-26mdk Tester: Keld Simonsen, keld@dkuug.dk Figures are in MB/s, and the file system was ext3. RAID type sequential read random read sequential write random write Ordinary disk 82 34 67 56 RAID0 155 80 97 80 RAID1 80 35 72 55 RAID10,n2 79 56 69 48 RAID10,f2 150 79 70 55 Random read for RAID1 and RAID10,n2 were quite unbalanced, almost only coming out of one of the disks. The results are quite as expected: md details: ext4 details: block details:
View topic - SoftRAID vs. RAID Controller. Raid - SAS Expanders vs Direct Attached (SAS)