

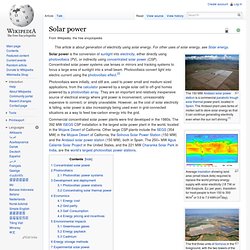
Solar. Solar power. Average insolation showing land area (small black dots) required to replace the world primary energy supply with solar electricity (18 TW or 568 Exajoule, EJ, per year).
Insolation for most people is from 150 to 300 W/m2 or 3.5 to 7.0 kWh/(m2day). The first three units of Solnova in the foreground, with the two towers of the PS10 and PS20 solar power stations in the background. Power electricity. Battery (electricity) An electric battery is a device consisting of one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy.
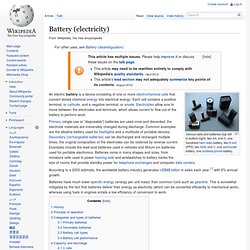
Each cell contains a positive terminal, or cathode, and a negative terminal, or anode. Electrolytes allow ions to move between the electrodes and terminals, which allows current to flow out of the battery to perform work. Primary (single-use or "disposable") batteries are used once and discarded; the electrode materials are irreversibly changed during discharge.
Electricity. Electricity. Battery. Small battery. Car battery. Wind power. Wind power. Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into a useful form of energy, such as using wind turbines to make electrical power, windmills for mechanical power, windpumps for water pumping or drainage, or sails to propel ships.
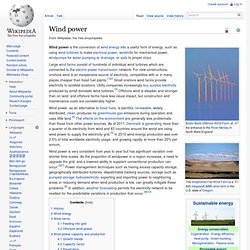
Large wind farms consist of hundreds of individual wind turbines which are connected to the electric power transmission network. For new constructions, onshore wind is an inexpensive source of electricity, competitive with or in many places cheaper than fossil fuel plants.[1][2] Small onshore wind farms provide electricity to isolated locations. Utility companies increasingly buy surplus electricity produced by small domestic wind turbines.[3] Offshore wind is steadier and stronger than on land, and offshore farms have less visual impact, but construction and maintenance costs are considerably higher.